|
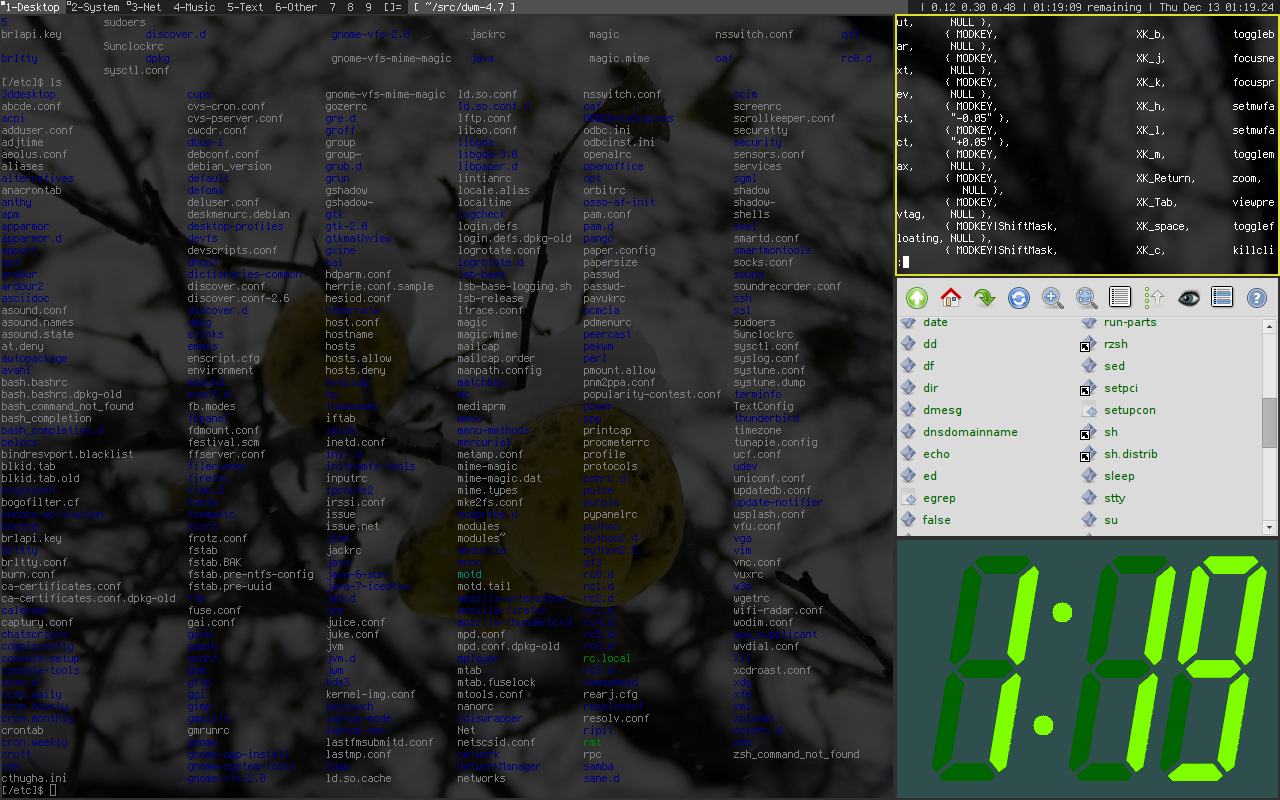
Xmonad
xmonad is a dynamic window manager ( tiling) for the X Window System, noted for being written in the functional programming language Haskell. Window manager Begun in March 2007, version 0.1 was announced in April 2007 as 500 lines of Haskell (which have since grown to 2000 lines). xmonad is a tiling window manager—akin to dwm, larswm, and StumpWM. It arranges windows in a non-overlapping pattern, and enables managing windows without using the mouse. xmonad is packaged and distributed on a wide range of Unix-like operating systems, such as a large number of Linux distributions, and Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) systems. While originally a clone of dwm (derivative in areas such as default keybindings), xmonad now supports features not available to dwm users such as per-workspace layout, tiling reflection, state preservation, layout mirroring, GNOME support and per-screen status bars; it can be customised by modifying an external configuration file and 'reload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinerama
Xinerama is an extension to the X Window System that enables X applications and window managers to use two or more physical displays as one large virtual display. Developed under the name ''PanoramiX'' by Madeline T. Asmus of the Digital Equipment Corporation's Unix X Server Engineering Group, the software was contributed to The Open Group for X11 Release 6.4 (X11R6.4) and renamed Xinerama. It was then incorporated into the XFree86 4.0 release in 1998 and the Solaris 7 11/99 release. According to X Server project lead Rob Lembree, the name was inspired by the Cinerama widescreen theatre process. "We were frustrated by having big Alpha machines with multiple displays, and being unable to move applications from one to another. It was developed as much out of frustration as out of competitive advantage." Xinerama advantages include the ability to only maximize windows to the dimensions of the active physical display, and to allow new pop-up windows on the active physical display. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haskell
Haskell () is a general-purpose, statically typed, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language features such as type classes, which enable type-safe operator overloading, and monadic input/output (IO). It is named after logician Haskell Curry. Haskell's main implementation is the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC). Haskell's semantics are historically based on those of the Miranda programming language, which served to focus the efforts of the initial Haskell working group. The last formal specification of the language was made in July 2010, while the development of GHC continues to expand Haskell via language extensions. Haskell is used in academia and industry. , Haskell was the 28th most popular programming language by Google searches for tutorials, and made up less than 1% of active users on the GitHub source code repository ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
StumpWM
In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with the organization of the screen often dependant on mathematical formulas to organise the windows into a non-overlapping frame. This is opposed to the more common approach used by stacking window managers, which allow the user to drag windows around, instead of windows snapping into a position. This allows for a different style of organization, although it departs from the traditional desktop metaphor. History Xerox PARC The first Xerox Star system (released in 1981) tiled application windows, but allowed dialog boxes and property windows to overlap. Later, Xerox PARC also developed CEDAR (released in 1982), the first windowing system using a tiled window manager. Various vendors Next in 1983 came Andrew WM, a complete tiled windowing system later replaced by X11. Microsoft's Windows 1.0 (released in 1985) also used tiling (see sections below). In 1986 came Digital Research's GEM 2.0, a windowing system for the CP/M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Type
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usually the terms are various language constructs of a computer program, such as variables, expressions, functions, or modules. A type system dictates the operations that can be performed on a term. For variables, the type system determines the allowed values of that term. Type systems formalize and enforce the otherwise implicit categories the programmer uses for algebraic data types, data structures, or other data types, such as "string", "array of float", "function returning boolean". Type systems are often specified as part of programming languages and built into interpreters and compilers, although the type system of a language can be extended by optional tools that perform added checks using the language's original type syntax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man Page
A man page (short for manual page) is a form of software documentation found on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. Topics covered include programs, system libraries, system calls, and sometimes local system details. The local host administrators can create and install manual pages associated with the specific host. A manual end user may invoke a documentation page by issuing the man command followed by the name of the item for which they want the documentation. These manual pages are typically requested by end users, programmers and administrators doing real time work but can also be formatted for printing. By default, man typically uses a formatting program such as nroff with a macro package or mandoc, and also a terminal pager program such as more or less to display its output on the user's screen. Man pages are often referred to as an ''online'' form of software documentation, even though the man command does not require internet access. The environment variable M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Versioning
Software versioning is the process of assigning either unique ''version names'' or unique ''version numbers'' to unique states of computer software. Within a given version number category (e.g., major or minor), these numbers are generally assigned in increasing order and correspond to new developments in the software. At a fine-grained level, revision control is used for keeping track of incrementally-different versions of information, whether or not this information is computer software, in order to be able to roll any changes back. Modern computer software is often tracked using two different software versioning schemes: an ''internal version number'' that may be incremented many times in a single day, such as a revision control number, and a ''release version'' that typically changes far less often, such as semantic versioning or a project code name. History File numbers were used especially in public administration, as well as companies, to uniquely identify files or cases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-monitor
Multi-monitor, also called multi-display and multi-head, is the use of multiple physical display devices, such as Computer monitor, monitors, Television set, televisions, and Video projector, projectors, in order to increase the area available for computer programs running on a single computer system. Research studies show that, depending on the type of work, multi-head may increase the productivity by between 50 and 70 percent. Implementation Multiple computers can be connected to provide a single display, e.g. over Gigabit Ethernet/Ethernet to drive a large video wall. Studies and safety Measurements of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the German Social Accident Insurance showed that the quality and quantity of worker performance varies according to the screen setup and type of task. Overall, the results of physiological studies and the preferences of the test persons favour a dual-monitor rather than single-monitor setup. Physiologically limiting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exec (operating System)
In computing, exec is a functionality of an operating system that runs an executable file in the context of an already existing process (computing), process, replacing the previous executable. This act is also referred to as an overlay. It is especially important in Unix-like systems, although it also exists elsewhere. As no new process is created, the process identifier (PID) does not change, but the machine code, data (computing), data, heap (programming), heap, and run-time stack, stack of the process are replaced by those of the new program. The ''exec'' call or some variant is available for many programming languages including compiler, compiled languages and some scripting languages. In Command-line interface, command interpreters, the shell builtin, built-in command replaces the shell process with the specified program. Nomenclature Interfaces to ''exec'' and its implementations vary. Depending on programming language it may be accessible via one or more function (progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME
A gnome () is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and widely adopted by authors, including those of modern fantasy literature. They are typically depicted as small humanoids who live underground. Gnome characteristics are reinterpreted to suit various storytellers and artists. Paracelsus's gnome is recognized to have derived from the German miners' legend about or , the "metallurgical or mineralogical demon", according to Georg Agricola (1530), also called (literal Latinization of ''Bergmännlein'', "mountain manikin") by Agriocola in a later work (1549), and described by other names such as (sing. ; Latinization of German ). Agricola recorded that, according to the legends of that profession, these mining spirits acted as miming and laughing pranksters who sometimes threw pebbles at miners, but could also reward them by depositing a rich vein of silver ore. Paracelsus also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clone (computing)
In computing, a clone is hardware or software that is designed to function in exactly the same way as another system. A specific subset of clones are remakes (or remades), which are revivals of old, obsolete, or discontinued products. Motivation Clones and remakes are created for reasons including competition, standardization, availability across platforms, and as homage. Compatibility with the original system is usually the explicit purpose of cloning hardware or low-level software such as operating systems (e.g. AROS and MorphOS are intended to be compatible with AmigaOS). Application software is cloned by providing the same functionality. Commercially-motivated clones are made often during a competitor product's initial successful commercial run, intentionally competing with the original and trying to participate in their success. Hardware Hardware clones When IBM announced the IBM PC in 1981, other companies such as Compaq decided to offer clones of the PC as a leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley Software Distribution
The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), also known as Berkeley Unix or BSD Unix, is a discontinued Unix operating system developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley, beginning in 1978. It began as an improved derivative of AT&T's original Unix that was developed at Bell Labs, based on the source code but over time diverging into its own code. BSD would become a pioneer in the advancement of Unix and computing. BSD's development was begun initially by Bill Joy, who added virtual memory capability to Unix running on a VAX-11 computer. In the 1980s, BSD was widely adopted by workstation vendors in the form of proprietary Unix distributions such as DEC Ultrix and Sun Microsystems SunOS due to its permissive licensing and familiarity to many technology company founders and engineers. It also became the most popular Unix at universities, where it was used for the study of operating systems. BSD was sponsored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distributions
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel (operating system), kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply distribution (marketing), product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to Server (computing), servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an Init, init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and Library (computing), libraries, documentation, Internet Protocol, IP network configuration utilities, the Getty (Unix), getty TTY setup program, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |