|
Xiangliu (moon)
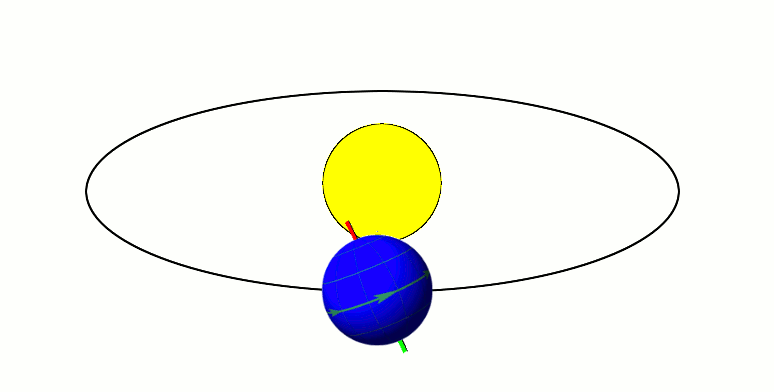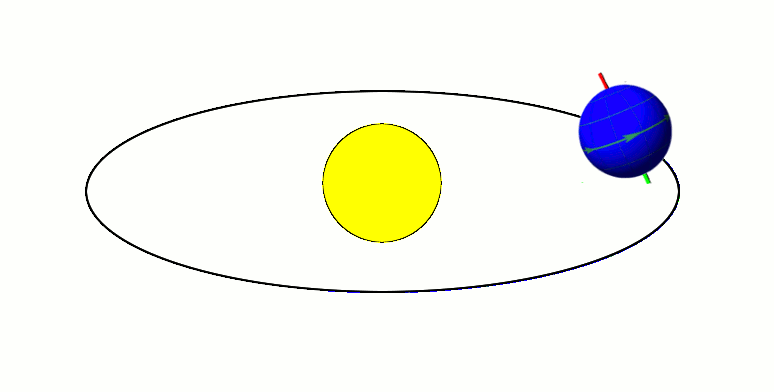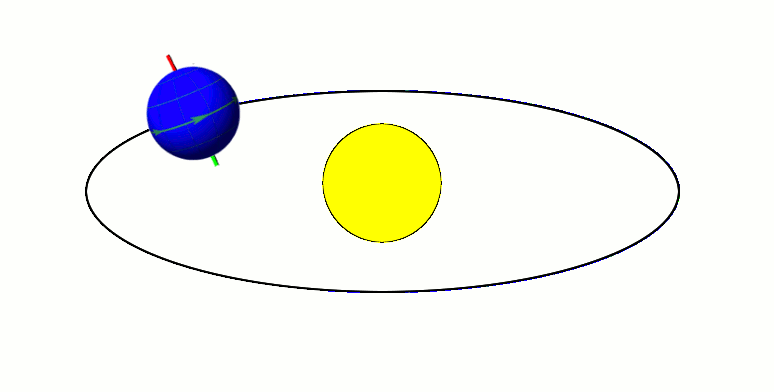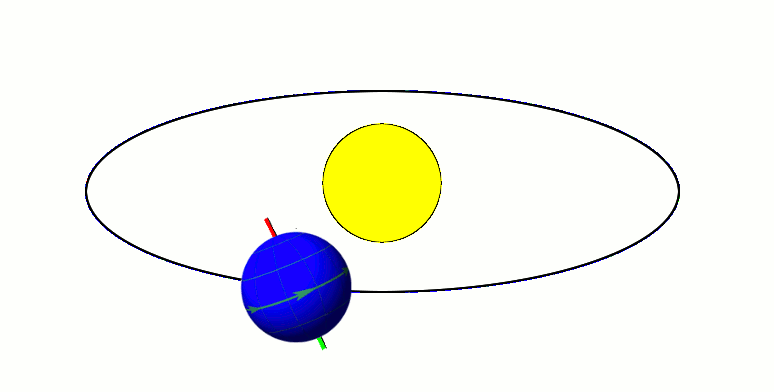
Xiangliu, formal designation 225088 Gonggong I, is the only known Minor-planet moon, moon of the scattered disc, scattered-disc dwarf planet Gonggong (dwarf planet), Gonggong. It was discovered by a team of astronomers led by Csaba Kiss during an analysis of archival Hubble Space Telescope images of Gonggong. The discovery team had suspected that the Slow rotator (minor planet), slow rotation of Gonggong was caused by tidal forces exerted by an orbiting satellite. Xiangliu was first identified in archival Hubble images taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on 18 September 2010. Its discovery was reported and announced by Gábor Marton (astronomer), Gábor Marton, Csaba Kiss, and Thomas Müller at the 48th Meeting of the Division for Planetary Sciences on 17 October 2016. The satellite is named after Xiangliu, a nine-headed venomous snake monster in Chinese mythology that attended the water god Gonggong as his chief minister. Observations Following the March 2016 discovery tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
225088 Gonggong
Gonggong (minor-planet designation: 225088 Gonggong) is a dwarf planet and a member of the scattered disc beyond Neptune. It has a highly orbital eccentricity, eccentric and orbital inclination, inclined orbit during which it ranges from from the Sun. , its distance from the Sun is , and it is the sixth-farthest known Solar System object. According to the Deep Ecliptic Survey, Gonggong is in a 3:10 orbital resonance with Neptune, in which it completes three orbits around the Sun for every ten orbits completed by Neptune. Gonggong was discovered in July 2007 by American astronomers Megan Schwamb, Michael E. Brown, Michael Brown, and David Rabinowitz at the Palomar Observatory, and the discovery was announced in January 2009. At approximately in diameter, Gonggong is similar in size to Pluto, Pluto's moon Charon (moon), Charon, making it the List of Solar System objects by size, fifth-largest known trans-Neptunian object (apart possibly from Charon). It may be sufficiently massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiangliu Orbiting 225088 Gonggong (2009-2010)
Xiangliu (), known in the ''Classic of Mountains and Seas'' as Xiangyao (), is a venomous nine-headed snake monster that brings floods and destruction in Chinese mythology. Xiangliu may be depicted with his body coiled on itself. The nine heads are arranged differently in different representations. Modern depictions resemble the hydra, with each head on a separate neck.For example, ithis © illustration/ref> Older wood-cuts show the heads clustered on a single neck, either side-by-side or in a stack three high, facing three directions. Legend According to the ''Classic of Mountains and Seas'' (''Shanhaijing''), Xiangliu (Xiangyao) was a minister of the snake-like water deity Gonggong. Xiangliu devastated the ecology everywhere he went. He was so gluttonous that all nine heads would feed at the same meal. Everywhere he rested or breathed upon (or that his tongue touched, depending on the telling) became boggy with poisonously bitter water, devoid of human and animal life. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee On Small Body Nomenclature
In ancient times, only the Sun and Moon, a few stars, and the most easily visible planets had names. Over the last few hundred years, the number of identified astronomical objects has risen from hundreds to over a billion, and more are discovered every year. Astronomers need to be able to assign systematic designations to unambiguously identify all of these objects, and at the same time give names to the most interesting objects, and where relevant, features of those objects. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the recognized authority in astronomy for assigning designations to celestial bodies such as stars, planets, and minor planets, including any surface features on them. In response to the need for unambiguous names for astronomical objects, it has created a number of systematic naming systems for objects of various sorts. Stars There are no more than a few thousand stars that appear sufficiently bright in Earth's sky to be visible to the naked eye. This represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded on 28 July 1919 in Brussels, Belgium and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. the Union had 85 national members and 12,734 individual members, spanning 90 countries and territories. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weywot (moon)
Weywot (formal designation (50000) Quaoar I; provisional designation S/2006 (50000) 1) is a natural satellite or moon of the trans-Neptunian dwarf planet Quaoar. It was discovered by Michael Brown and Terry-Ann Suer using images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope on 14 February 2006. It is named after the Tongva sky god and son of Quaoar. Weywot is about in diameter and orbits Quaoar every 12.4 days at an average distance of . Weywot is thought to play a role in maintaining Quaoar's outer ring by gravitationally influencing it in an orbital resonance. Discovery Weywot was first imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope on 14 February 2006, during Michael Brown's survey for satellites around large trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) using ''Hubble''s high-resolution Advanced Camera for Surveys. Consecutive images from that date showed that Weywot appeared stationary relative to Quaoar and was visibly separated at an angular distance of 0.35 arcseconds. After Brown's Hubble surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaoar
Quaoar (minor-planet designation: 50000 Quaoar) is a ringed dwarf planet in the Kuiper Belt, a ring of many icy planetesimals beyond Neptune. It has an elongated ellipsoidal shape with an average diameter of , about half the size of the dwarf planet Pluto, and is a possible dwarf planet. The object was discovered by American astronomers Chad Trujillo and Michael Brown at the Palomar Observatory on 4 June 2002. Quaoar's surface contains crystalline water ice and ammonia hydrate, which suggests that it might have experienced cryovolcanism. A small amount of methane is present on its surface, which is only retained by the largest Kuiper belt objects. Quaoar has one known moon, Weywot, which was discovered by Brown in February 2007. Both objects were named after mythological figures from the Native American Tongva people in Southern California. Quaoar is the Tongva creator deity and Weywot is his son. In 2023, astronomers announced the discovery of two thin rings orbiting Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Mechanics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to rockets, satellites, and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation. Astrodynamics is a core discipline within space-mission design and control. Celestial mechanics treats more broadly the orbital dynamics of systems under the influence of gravity, including both spacecraft and natural astronomical bodies such as star systems, planets, moons, and comets. Orbital mechanics focuses on spacecraft trajectories, including orbital maneuvers, orbital plane changes, and interplanetary transfers, and is used by mission planners to predict the results of propulsive maneuvers. General relativity is a more exact theory than Newton's laws for calculating orbits, and it is sometimes necessary to use it for greater accuracy or in high-gravity situations (e.g. orbits near the Sun). History Until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Potential
In classical mechanics, the gravitational potential is a scalar potential associating with each point in space the work (energy transferred) per unit mass that would be needed to move an object to that point from a fixed reference point in the conservative gravitational field. It is analogous to the electric potential with mass playing the role of charge. The reference point, where the potential is zero, is by convention infinitely far away from any mass, resulting in a negative potential at any finite distance. Their similarity is correlated with both associated fields having conservative forces. Mathematically, the gravitational potential is also known as the Newtonian potential and is fundamental in the study of potential theory. It may also be used for solving the electrostatic and magnetostatic fields generated by uniformly charged or polarized ellipsoidal bodies. Potential energy The gravitational potential (''V'') at a location is the gravitational potential ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The table of spherical harmonics contains a list of common spherical harmonics. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, every function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozai Mechanism
In celestial mechanics, the Kozai mechanism is a dynamical phenomenon affecting the orbit of a binary system perturbed by a distant third body under certain conditions. The mechanism is also named von Zeipel-Kozai-Lidov, Lidov–Kozai, Kozai–Lidov, etc., and may be termed an ''effect'', ''oscillation'', ''cycle'', or ''resonance''. This effect causes the orbit's argument of pericenter to oscillate about a constant value, which in turn leads to a periodic exchange between its eccentricity and inclination. The process occurs on timescales much longer than the orbital periods. It can drive an initially near-circular orbit to arbitrarily high eccentricity, and ''flip'' an initially moderately inclined orbit between a prograde and a retrograde motion. The effect has been found to be an important factor shaping the orbits of irregular satellites of the planets, trans-Neptunian objects, extrasolar planets, and multiple star systems. It hypothetically promotes black hole mergers. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |