|
Xenon Oxytetrafluoride
Xenon oxytetrafluoride () is an inorganic chemical compound. It is an unstable colorless liquid with a melting point of that can be synthesized by partial hydrolysis of , or the reaction of with silica or : : + → + + A high-yield synthesis proceeds by the reaction of with at . Like most xenon oxides, it is extremely reactive, and it hydrolyses in water to give hazardous and corrosive products, including hydrogen fluoride: :2 + 4 → 2 + 8 + 3 In addition, some ozone and fluorine is formed. Reactions reacts with in the following steps: : + → + 2 : + → + 2 The formed is a dangerous explosive, decomposing explosively to Xe and : :2 → 2 + 3 In its liquid form, exhibits amphoteric behaviour, forming complexes with both strong Lewis bases like and strong Lewis acids like . It forms a 1:1 adduct with , isostructural with ·, as well as various heavy alkali metal The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Pyramidal
Square pyramidal geometry describes the shape of certain chemical compounds with the formula where L is a ligand. If the ligand atoms were connected, the resulting shape would be that of a pyramid with a square base. The point group symmetry involved is of type C4v. The geometry is common for certain main group compounds that have a stereochemically-active lone pair, as described by VSEPR theory. Certain compounds crystallize in both the trigonal bipyramidal and the square pyramidal structures, notably . As a transition state in Berry pseudorotation As a trigonal bipyramidal molecule undergoes Berry pseudorotation, it proceeds via an intermediary stage with the square pyramidal geometry. Thus even though the geometry is rarely seen as the ground state, it is accessed by a low energy distortion from a trigonal bipyramid. Pseudorotation also occurs in square pyramidal molecules. Molecules with this geometry, as opposed to trigonal bipyramidal, exhibit heavier vibration. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Compounds
Xenon compounds are compounds containing the element xenon (Xe). After Neil Bartlett's discovery in 1962 that xenon can form chemical compounds, a large number of xenon compounds have been discovered and described. Almost all known xenon compounds contain the electronegative atoms fluorine or oxygen. The chemistry of xenon in each oxidation state is analogous to that of the neighboring element iodine in the immediately lower oxidation state. Halides Three fluorides are known: , , and . XeF is theorized to be unstable. These are the starting points for the synthesis of almost all xenon compounds. The solid, crystalline difluoride is formed when a mixture of fluorine and xenon gases is exposed to ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet component of ordinary daylight is sufficient. Long-term heating of at high temperatures under an catalyst yields . Pyrolysis of in the presence of NaF yields high-purity . The xenon fluorides behave as both fluoride acceptors and fluoride dono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Physical Chemistry A
''The Journal of Physical Chemistry A'' is a scientific journal which reports research on the chemistry of molecules - including their dynamics, spectroscopy, kinetics, structure, chemical bond, bonding, and quantum chemistry. It is published weekly by the American Chemical Society. Before 1997 the title was simply ''Journal of Physical Chemistry''. Owing to the ever-growing amount of research in the area, in 1997 the journal was split into ''Journal of Physical Chemistry A'' (molecular theoretical and experimental physical chemistry) and ''The Journal of Physical Chemistry B'' (solid state, soft matter, liquids, etc.). Beginning in 2007, the latter underwent a further split, with ''The Journal of Physical Chemistry C'' now being dedicated to nanotechnology, molecular electronics, and related subjects. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal have an impact factor of 2.7 for 2023. Editors-in-chief *1896–1932 Wilder Dwight Bancroft, Joseph E. Trevor *1933– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names for the elements in some languages, such as German and Russian. rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute Group (periodic table)#Group names, group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of periodic trends, group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised Homologous series, homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element. The alkali metals are all shiny, hardness, sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the atmosphere, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odor is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 chemical structure, structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetism, diamagnetic. At standard temperature and pressure, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
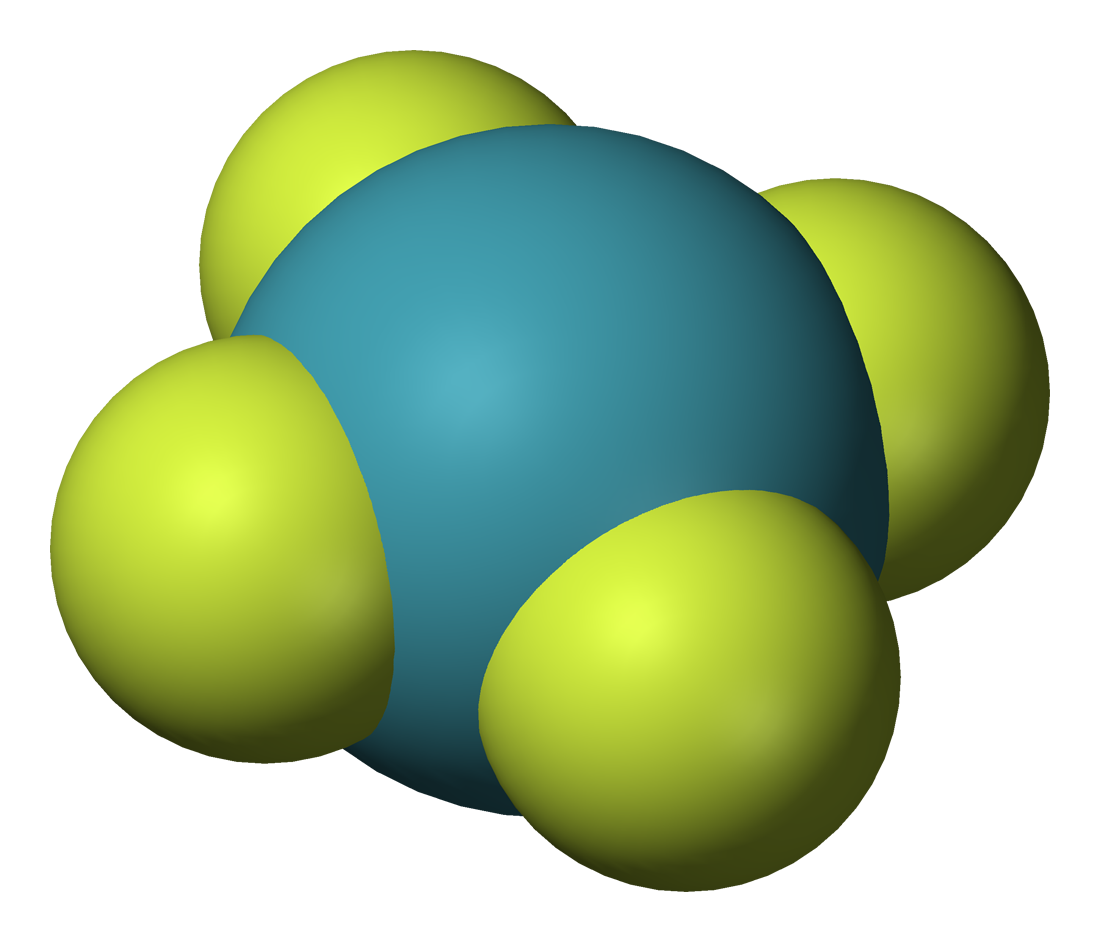
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Hexafluoride
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon that have been studied experimentally, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All of them are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors. Preparation Xenon hexafluoride can be prepared by heating of XeF2 at about 300 °C under 6 MPa (60 atmospheres) of fluorine. With as catalyst, however, this reaction can proceed at 120 °C even in xenon-fluorine molar ratios as low as 1:5. Structure The structure of XeF6 required several years to establish in contrast to the cases of and . In the gas phase the compound is monomeric. VSEPR theory predicts that due to the presence of six fluoride ligands and one lone pair of electrons the structure lacks perfect octahedral symmetry, and indeed electron diffraction combined with high-level cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry (journal)
''Inorganic Chemistry'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society since 1962. It covers research in all areas of inorganic chemistry. The current editor-in-chief is Stefanie Dehnen ( Karlsruhe Institute of Technology). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 4.6. See also * '' Organometallics'' References External links * American Chemical Society academic journals Biweekly journals Academic journals established in 1962 English-language journals Inorganic chemistry journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Chemical Physics
''The Journal of Chemical Physics'' is a scientific journal published by the American Institute of Physics that carries research papers on chemical physics."About the Journal" from the ''Journal of Chemical Physics'' website. Two volumes, each of 24 issues, are published annually. It was established in 1933 when '''' editors refused to publish theoretical works. The editors have been: *2019–present: Tim Lian *2008–2018: Marsha I. Lester *2007–2008: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Physical Chemistry
''Annual Review of Physical Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Annual Reviews. It covers all topics pertaining to physical chemistry. The editors are Todd J. Martínez (Stanford University) and Anne McCoy (University of Washington). As of 2023, ''Annual Review of Physical Chemistry'' is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. The journal is indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded and Chemical Abstracts Service. As of 2024, ''Journal Citation Reports'' gives it a 2023 impact factor of 11.7. History The ''Annual Review of Physical Chemistry'' published its first volume in 1950. Its founding editor was University of California chemist Gerhard Krohn Rollefson. Some branches of physical chemistry were designated to be reviewed with each volume, while other branches would be reviewed less frequently. Upon Rollefson's death in 1955, he was succeeded by Henry Eyring. The editorial committee considered changing the name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |