|
XMD
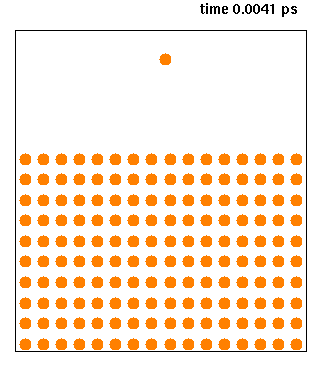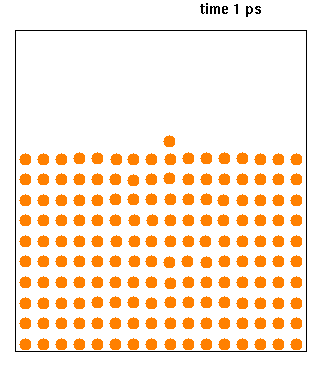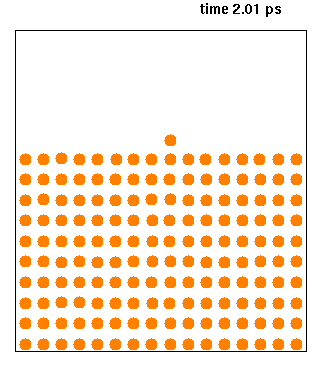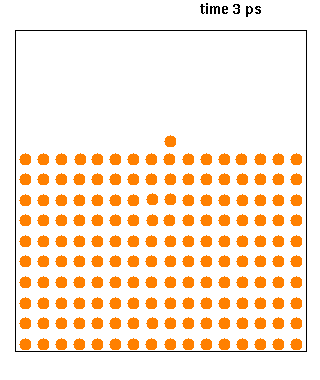
XMD is a classical molecular dynamics software designed to simulate problems related to materials science. The code was developed by Jon Rifkin of University of Connecticut and is being distributed under GNU General Public License. Source code is available in C and can be compiled using POSIX thread functions to take advantage of multi-CPU computers. See also *Molecular design software Molecular design software is notable software for molecular modeling, that provides special support for developing molecular models ''de novo''. In contrast to the usual molecular modeling programs, such as for molecular dynamics and quantum chemi ... External links XMD Homepage Molecular dynamics software Free science software Free software programmed in C {{molecular-modelling-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Design Software
Molecular design software is notable software for molecular modeling, that provides special support for developing molecular models ''de novo''. In contrast to the usual molecular modeling programs, such as for molecular dynamics and quantum chemistry, such software ''directly'' supports the aspects related to constructing molecular models, including: * Molecular graphics * interactive molecular drawing and conformational editing * building polymeric molecules, crystals, and solvated systems * partial charges development * geometry optimization * support for the different aspects of force field development Comparison of software covering the major aspects of molecular design Notes and references See also {{columns-list, colwidth=30em, * Molecule editor *Molecular modelling * Molecular modeling on GPUs * Protein design *Drug design * Force field (chemistry) * Comparison of force field implementations * Comparison of nucleic acid simulation software *Comparison of softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
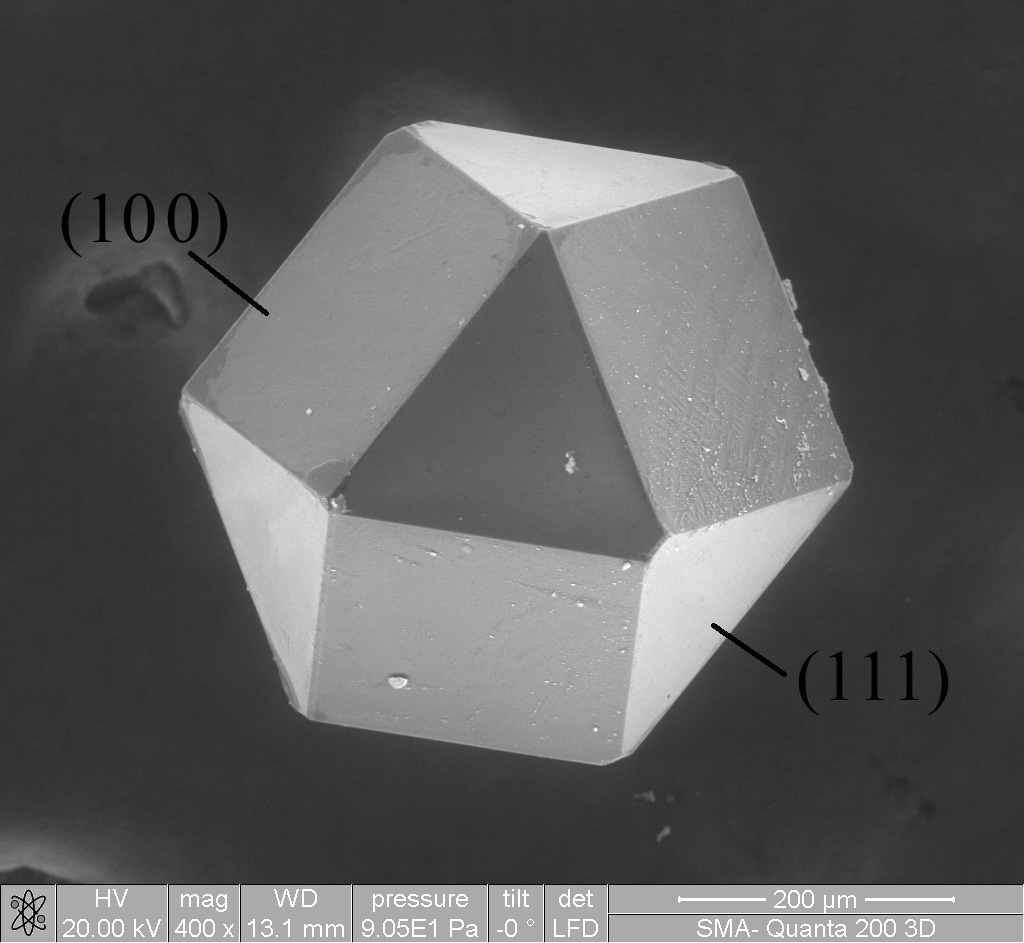
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first copyleft license available for general use. It was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. The GPL is more restrictive than the GNU Lesser General Public License, and even more distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses such as BSD, MIT, and Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open-source software (FOSS) domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX; ) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers. As of POSIX 2024, the standard is aligned with the C17 language standard. Name Originally, the name "POSIX" referred to IEEE Std 1003.1-1988, released in 1988. The family of POSIX standards is formally designated as IEEE 1003 and the ISO/IEC standard number is ISO/ IEC 9945. The standards emerged from a project that began in 1984 building on work from related activity in the ''/usr/group'' association. Richard Stallman suggested the name ''POSIX'' to the IEEE instead of the former ''IEEE-IX''. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Dynamics Software
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Science Software
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * ''Free'' (film), a 2001 American dramed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |