|
X-ray Notation
X-ray notation is a method of labeling atomic orbitals that grew out of X-ray science. Also known as IUPAC notation, it was adopted by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in 1991 as a simplification of the older Siegbahn notation. In X-ray notation, every principal quantum number is given a letter associated with it. In many areas of physics and chemistry, atomic orbitals are described with spectroscopic notation (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, etc.), but the more traditional X-ray notation is still used with most X-ray spectroscopy techniques including AES and XPS. Conversion Uses *X-ray sources are classified by the type of material and orbital used to generate them. For example, CuKα X-rays are emitted from the K orbital of copper. *X-ray absorption is reported as which orbital absorbed the x-ray photon. In EXAFS and XMCD the L-edge or the L absorption edge is the point where the L orbital begins to absorb x-rays. *Auger peaks are identified with three orbital def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Orbitals
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term ''atomic orbital'' may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component ( magnetic quantum number). Alternative to the magnetic quantum number, the orbitals are often labeled by the associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ). Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simple names s orbital, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegbahn Notation
The Siegbahn notation is used in X-ray spectroscopy to name the spectral lines that are characteristic to elements. It was introduced by Manne Siegbahn. The characteristic lines in X-ray emission spectra correspond to atomic electronic transitions where an electron jumps down to a vacancy in one of the inner shells of an atom. Such a hole in an inner shell may have been produced by bombardment with electrons in an X-ray tube, by other particles as in PIXE, by other X-rays in X-ray fluorescence or by radioactive decay of the atom's nucleus. Although still widely used in spectroscopy, this notation is unsystematic and often confusing. For these reasons, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends another nomenclature. History The use of the letters K and L to denote X-rays originates in a 1911 paper by Charles Glover Barkla, titled ''The Spectra of the Fluorescent Röntgen Radiations'' ("Röntgen radiation" is an archaic name for "X-rays"). By 1913, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopic Notation
Spectroscopic notation provides a way to specify atomic ionization states, atomic orbitals, and molecular orbitals. Ionization states Spectroscopists customarily refer to the spectrum arising from a given ionization state of a given element by the element's symbol followed by a Roman numeral. The numeral I is used for spectral lines associated with the neutral element, II for those from the first ionization state, III for those from the second ionization state, and so on. For example, "He I" denotes lines of neutral helium, and "C IV" denotes lines arising from the third ionization state, C3+, of carbon. This notation is used for example to retrieve data from thNIST Atomic Spectrum Database Atomic and molecular orbitals Before atomic orbitals were understood, spectroscopists discovered various distinctive series of spectral lines in atomic spectra, which they identified by letters. These letters were later associated with the azimuthal quantum number, ''ℓ''. The let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auger Electron Spectroscopy
A Hanford scientist uses an Auger electron spectrometer to determine the elemental composition of surfaces. Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. It is a form of electron spectroscopy that relies on the Auger effect, based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal ''Zeitschrift für Physik'' in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in X-ray spectroscopy data. Sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
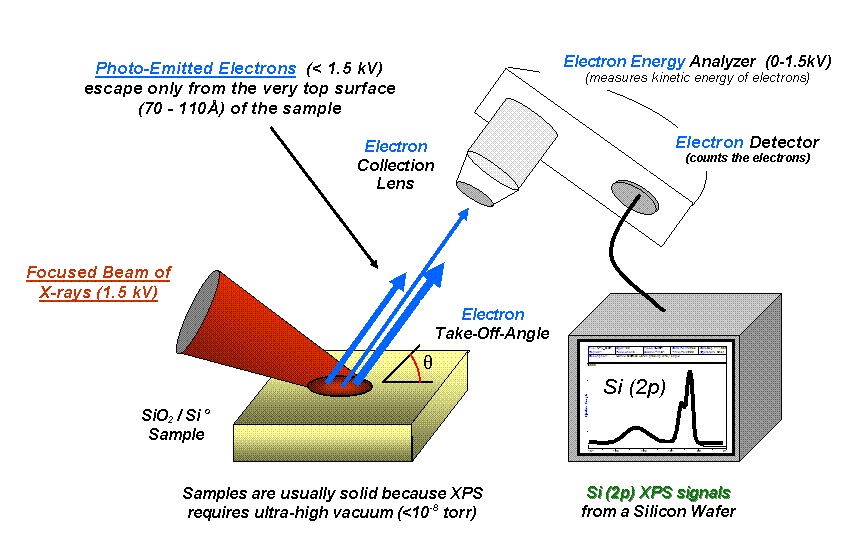
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique based on the photoelectric effect that can identify the elements that exist within a material (elemental composition) or are covering its surface, as well as their chemical state, and the overall electronic structure and density of the electronic states in the material. XPS is a powerful measurement technique because it not only shows what elements are present, but also what other elements they are bonded to. The technique can be used in line profiling of the elemental composition across the surface, or in depth profiling when paired with ion-beam etching. It is often applied to study chemical processes in the materials in their as-received state or after cleavage, scraping, exposure to heat, reactive gasses or solutions, ultraviolet light, or during ion implantation. XPS belongs to the family of photoemission spectroscopies in which electron population spectra are obtained by irr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Numbers
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of a quantum system. Quantum numbers correspond to eigenvalues of operators that commute with the Hamiltonian—quantities that can be known with precision at the same time as the system's energyspecifically, observables \widehat that commute with the Hamiltonian are simultaneously diagonalizable with it and so the eigenvalues a and the energy (eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian) are not limited by an uncertainty relation arising from non-commutativity.—and their corresponding eigenspaces. Together, a specification of all of the quantum numbers of a quantum system fully characterize a basis state of the system, and can in principle be measured together. An important aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of many observable quantities of interest.Many observables have discrete spectra (sets of eigenvalues) in quantum mechanics, so the quantities can only be measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Term Symbol
In quantum mechanics, the term symbol is an abbreviated description of the (total) angular momentum quantum numbers in a multi-electron atom (however, even a single electron can be described by a term symbol). Each energy level of an atom with a given electron configuration is described by not only the electron configuration but also its own term symbol, as the energy level also depends on the total angular momentum including spin. The usual atomic term symbols assume LS coupling (also known as Russell– Saunders coupling or spin-orbit coupling). The ground state term symbol is predicted by Hund's rules. The use of the word ''term'' for an energy level is based on the Rydberg–Ritz combination principle, an empirical observation that the wavenumbers of spectral lines can be expressed as the difference of two ''terms''. This was later summarized by the Bohr model, which identified the terms (multiplied by ''hc'', where ''h'' is the Planck constant and ''c'' the speed of light) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect is attenuation, or the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning synonymous with "absorption coefficient") * The Molar attenuation coefficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), along with X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), is a subset of X-ray absorption spectroscopy ( XAS). Like other absorption spectroscopies, XAS techniques follow Beer's law. The X-ray absorption coefficient of a material as a function of energy is obtained using X-rays of a narrow energy resolution are directed at a sample and the incident and transmitted x-ray intensity is recorded as the incident x-ray energy is incremented. When the incident x-ray energy matches the binding energy of an electron of an atom within the sample, the number of x-rays absorbed by the sample increases dramatically, causing a drop in the transmitted x-ray intensity. This results in an absorption edge. Every element has a set of unique absorption edges corresponding to different binding energies of its electrons, giving XAS element selectivity. XAS spectra are most often collected at synchrotrons because of the high intensity of synchrotron X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism
X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) is a difference spectrum of two X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) taken in a magnetic field, one taken with left circularly polarized light, and one with right circularly polarized light. By closely analyzing the difference in the XMCD spectrum, information can be obtained on the magnetic properties of the atom, such as its spin and orbital magnetic moment. Using XMCD magnetic moments below 10−5 µB can be observed. In the case of transition metals such as iron, cobalt, and nickel, the absorption spectra for XMCD are usually measured at the L-edge. This corresponds to the process in the iron case: with iron, a 2p electron is excited to a 3d state by an X-ray of about 700 eV. Because the 3d electron states are the origin of the magnetic properties of the elements, the spectra contain information on the magnetic properties. In rare-earth elements usually, the M4,5-edges are measured, corresponding to electron excitations from a 3d sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |