|
William Lukin
Vice-Admiral William Lukin, later William Lukin Windham (20 September 1768 – 12 January 1833), was a Royal Navy officer who rose to the rank of Vice Admiral and served with great distinction through the Napoleonic Wars. Eventually he inherited the house and estates of William Windham. Early life William Lukin was born in the village of Felbrigg, Norfolk on 20 September 1768. He was the son of the Rev. George Lukin and Susan Katherine Doughty. His father was the rector of Felbrigg and Aylmerton. The Rev. George Lukin was the half brother of William Windham. who was the local squire of Felbrigg Hall and one time member of parliament for Norwich and Secretary at War in the Cabinet. Windham had a special affection for all the children of the Rev. Lukin and in particular William Lukin who would eventually become his heir. The young William Lukin went to sea probably around 1781 at the age of 13. He appears to have been a keen seaman and a fast learner and survived the harsh life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Clint
George Clint (12 April 1770 – 10 May 1854) was an English portrait painter and engraver, especially notable for his many theatrical subjects. Life Clint was born in Brownlow Street, Drury Lane, Covent Garden, London, the son of Michael Clint, a hairdresser in Lombard Street. He went to school in Yorkshire and was then apprenticed to a fishmonger, but left after a violent dispute with his employer. He found alternative employment in an attorney's office, but took exception to the work and became a house-painter instead - one of his jobs was painting the stones of the arches in the nave of Westminster Abbey. He also decorated the exterior of a house built by Sir Christopher Wren in Cheapside, and was later employed by the bookseller Thomas Tegg. He married the daughter of a small farmer in Berkshire; they had five sons and four daughters. His wife died a fortnight after giving birth to their son Alfred, who also became an artist. Clint took up miniature painting. He had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwich (UK Parliament Constituency)
Norwich was a borough constituency in Norfolk which was represented in the House of Commons of England from 1298 to 1707, in the House of Commons of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800, and in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom from 1801 until it was abolished for the 1950 general election. Consisting of the city of Norwich in Norfolk, it returned two members of parliament (MPs), elected by the bloc vote system. It was replaced in 1950 by two new single-member constituencies, Norwich North and Norwich South. Members of Parliament 1298–1660 1640–1950 Election results Elections in the 1940s Elections in the 1930s Elections in the 1920s Elections in the 1910s Elections in the 1900s Elections in the 1890s Elections in the 1880s * Caused by Bullard being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Norfolk
North Norfolk is a local government district in Norfolk, England. Its council is based in Cromer. The population at the 2011 Census was 101,149. History The district was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972. It was a merger of Cromer Urban District, North Walsham Urban District, Sheringham Urban District, Wells-next-the-Sea Urban District, Erpingham Rural District, Smallburgh Rural District, and Walsingham Rural District. The district was originally to be called Pastonacres, but changed its name by resolution of the council and permission of the Secretary of State for Environment before it formally came into existence on 1 April 1974. Politics Elections to the district council are held every four years, with all of the seats on the council up for election every fourth year. The council was run by a Conservative administration, the Conservative party having gained a majority of 8 seats at the 2011 elections, which they increased to 18 at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of The United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign ( King-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament. However, the Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto'' vested in the House of Commons. The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, all govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill (proposed Law)
A bill is proposed legislation under consideration by a legislature. A bill does not become law until it is passed by the legislature as well as, in most cases, approved by the executive. Once a bill has been enacted into law, it is called an '' act of the legislature'', or a ''statute''. Bills are introduced in the legislature and are discussed, debated and voted upon. Usage The word ''bill'' is primarily used in Anglophone United Kingdom and United States, the parts of a bill are known as ''clauses'', until it has become an act of parliament, from which time the parts of the law are known as ''sections''. In Napoleonic law nations (including France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Spain and Portugal), a proposed law may be known as a "law project" (Fr. ''projet de loi''), which is a government-introduced bill, or a "law proposition" (Fr. ''proposition de loi''), a private member's bill. For example the Dutch parliamentary system does not make this terminological distinction (''wetsontw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Philip Yorke
Charles Philip Yorke (12 March 1764 – 13 March 1834) was a British politician. He notably served as Home Secretary from 1803 to 1804. Political career He sat as a Member of Parliament (MP) for Cambridgeshire from 1790 to 1810. He was commissioned as an officer in the Cambridgeshire Militia in 1793. He was promoted to major in 1795, a fellow officer was Captain George Manby By 1806 he was their colonel. He was MP for Liskeard from 1812 to 1818. In 1801 he was appointed Secretary at War in Henry Addington's ministry, transferring to the Home Office in 1803, where he was a strong opponent of concession to the Roman Catholics. He made himself exceedingly unpopular in 1810 by bringing about the exclusion of strangers, including reporters for the press, from the House of Commons under the standing order, which led to the imprisonment of Sir Francis Burdett, 5th Baronet in the Tower and to riots in London. In the same year, Yorke joined Spencer Perceval's government as First Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Pardon
In the English and British tradition, the royal prerogative of mercy is one of the historic royal prerogatives of the British monarch, by which they can grant pardons (informally known as a royal pardon) to convicted persons. The royal prerogative of mercy was originally used to permit the monarch to withdraw, or provide alternatives to death sentences; the alternative of penal transportation to "partes abroade" was used since at least 1617. It is now used to change any sentence or penalty. A royal pardon does not overturn a conviction. Officially, this is a power of the monarch. Formally, in Commonwealth realms, this has been delegated to the governor-general of the realm, which in practice means to government ministers who advise the monarch or viceroy, usually those responsible for justice. Specifically, it has been delegated to the Lord Chancellor in England and Wales, the Scottish Ministers in Scotland, and the federal and provincial cabinets in Canada, in respect of fede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
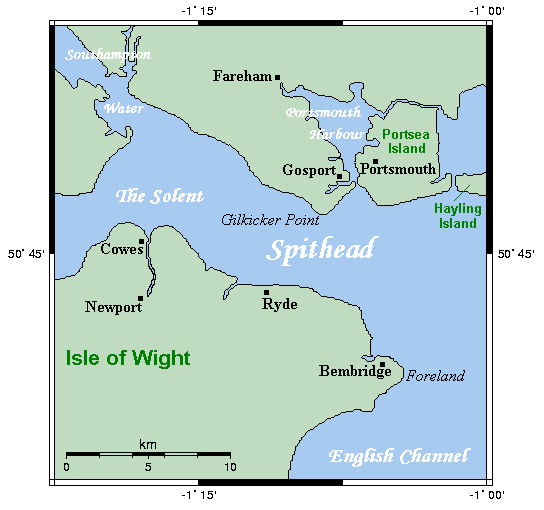
Spithead Mutiny
The Spithead and Nore mutinies were two major mutinies by sailors of the Royal Navy in 1797. They were the first in an increasing series of outbreaks of maritime radicalism in the Atlantic World. Despite their temporal proximity, the mutinies differed in character. The Spithead mutiny was a simple, peaceful, successful strike action to address economic grievances, while the Nore mutiny was a more radical action, articulating political ideals as well, which failed. The mutinies were extremely problematic for Britain, because at the time the country was at war with Revolutionary France, and the Navy was the main component of the war effort. There were also concerns among the government that the mutinies might be part of wider attempts at revolutionary sedition instigated by societies such as the London Corresponding Society and the United Irishmen. Spithead The mutiny at Spithead (an anchorage near Portsmouth) lasted from 16 April to 15 May 1797. Sailors on 16 ships in the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of The First Lords Of The Admiralty
The First Lord of the Admiralty, or formally the Office of the First Lord of the Admiralty, was the political head of the English and later British Royal Navy. He was the government's senior adviser on all naval affairs, responsible for the direction and control of the Admiralty, and also of general administration of the Naval Service of the Kingdom of England, Great Britain in the 18th century, and then the United Kingdom, including the Royal Navy, the Royal Marines, and other services. It was one of the earliest known permanent government posts. Apart from being the political head of the Naval Service the post holder was simultaneously the pre-eminent member of the Board of Admiralty. The office of First Lord of the Admiralty existed from 1628 until it was abolished when the Admiralty, Air Ministry, Ministry of Defence, and War Office were all merged to form the new Ministry of Defence in 1964. Its modern-day equivalent is the Secretary of State for Defence. History In 1628, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)