|
Wide Local Excision
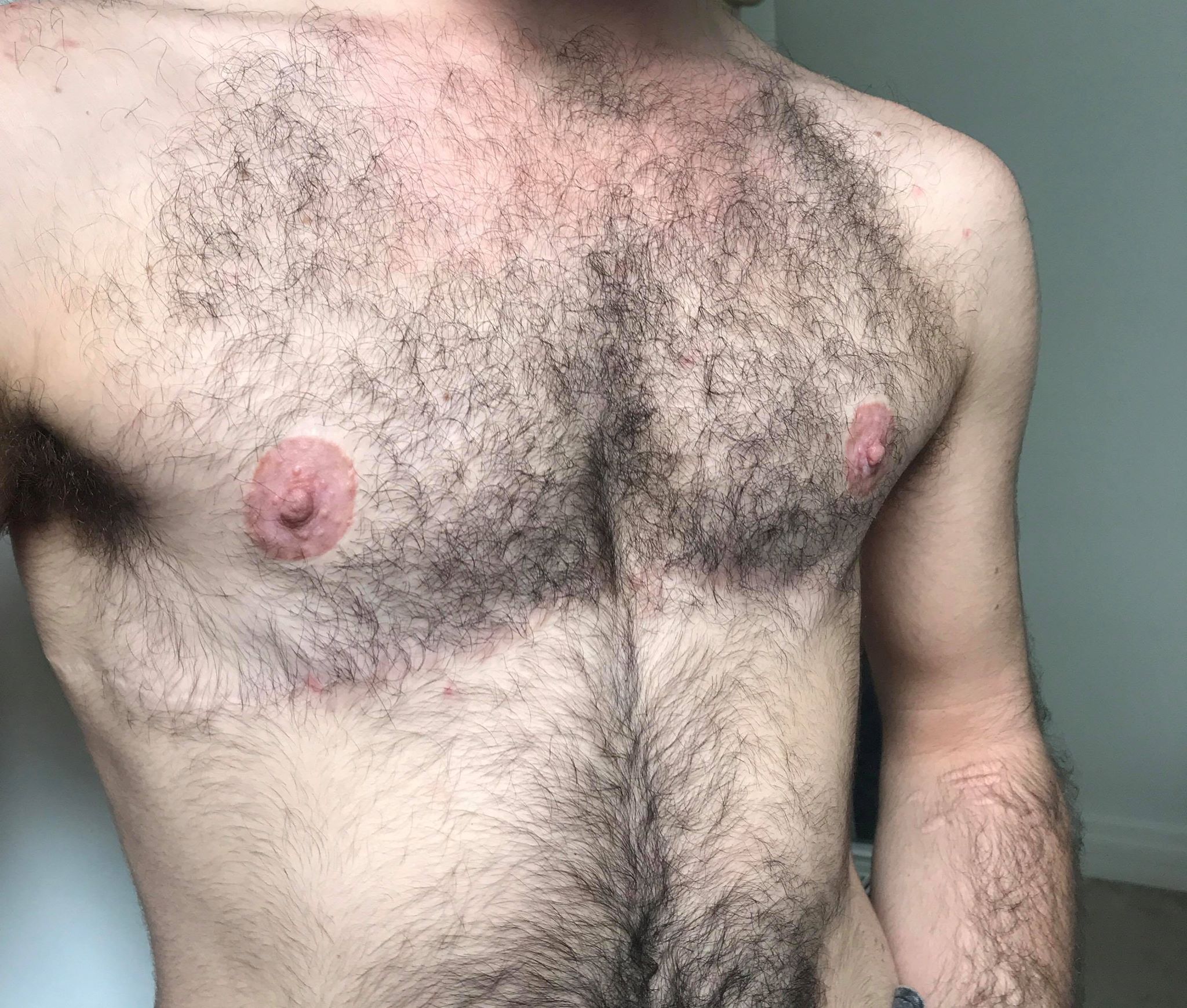
A wide local excision (WLE) is a surgical procedure to remove a small area of diseased or problematic tissue with a margin of normal tissue. This procedure is commonly performed on the breast and to skin lesions, but can be used on any area of the body. The tissue removed is examined under a microscope to confirm the type of lesion and to grade malignant tumours. This examination also determines if all of the lesion has been removed without leaving any behind. The results of a WLE will determine any future treatments if needed. Wide local excision of the breast A wide local excision of the breast aims to remove benign and malignant lesions while conserving the normal shape of the breast as much as possible. It is a form of breast-conserving surgery. A WLE can only be used for lesions up to 4 cm in diameter, as removal of any larger lesions could leave a visibly dented area in the breast. The extent of excision is variable, ranging from lumpectomy to quadrantectomy A quadrantecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumour
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast-conserving Surgery
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) refers to an operation that aims to remove breast cancer while avoiding a mastectomy. Different forms of this operation include: lumpectomy (tylectomy), wide local excision, segmental resection, and quadrantectomy. BCS has been increasingly accepted as an alternative to mastectomy in specific patients, as it provides tumor removal while maintaining an acceptable cosmetic outcome. This page reviews the history of this operation, important considerations in decision making and patient selection, and the emerging field of oncoplastic breast conservation surgery. Medical uses For clinical stages I and II breast cancer, breast-conserving surgery, with radiotherapy and possibly chemotherapy may be indicated if one or two sentinel lymph nodes are found to have cancer which is not extensive. In this case, the sentinel lymph nodes would be examined, and lymphadenectomy as further evaluation is not indicated as this result from the sentinel lymph nodes is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy (sometimes known as a tylectomy, partial mastectomy, breast segmental resection or breast wide local excision) is a surgical removal of a discrete portion or "lump" of breast tissue, usually in the treatment of a malignant tumor or breast cancer. It is considered a viable breast conservation therapy, as the amount of tissue removed is limited compared to a full-breast mastectomy, and thus may have physical and emotional advantages over more disfiguring treatment. Sometimes a lumpectomy may be used to either confirm or rule out that cancer has actually been detected. A lumpectomy is usually recommended to patients whose cancer has been detected early and who do not have enlarged tumors. Although a lumpectomy is used to allow for most of the breast to remain intact, the procedure may result in adverse affects that can include sensitivity and result in scar tissue, pain, and possible disfiguration of the breast if the lump taken out is significant. According to National C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrantectomy
A quadrantectomy, also referred to as a segmental or partial mastectomy, is a breast-conserving surgery for breast cancer in which one quarter of breast tissue is removed along with muscles of the chest wall within a 2 to 3 centimeter radius of a tumor. This procedure is an alternative to a radical or simple mastectomy, in which an entire breast is removed. In a study that followed patients who underwent this procedure, it was found that only 9% of people who had a quadrantectomy experienced a relapse of the cancer. See also * Mastectomy * Lumpectomy Lumpectomy (sometimes known as a tylectomy, partial mastectomy, breast segmental resection or breast wide local excision) is a surgical removal of a discrete portion or "lump" of breast tissue, usually in the treatment of a malignant tumor or brea ... References {{Operations and other procedures of the integumentary system Surgical removal procedures Breast cancer Breast surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastectomy
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operation as a preventive measure. Alternatively, some women can choose to have a wide local excision, also known as a lumpectomy, an operation in which a small volume of breast tissue containing the tumor and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue is removed to conserve the breast. Both mastectomy and lumpectomy are referred to as "local therapies" for breast cancer, targeting the area of the tumor, as opposed to systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, or immunotherapy. The decision to perform a mastectomy is based on various factors, including breast size, the number of lesions, biologic aggressiveness of a breast cancer, the availability of adjuvant radiation, and the willingness of the patient to accept higher rates of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Removal Procedures
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)