|
WiFi 6E
IEEE 802.11ax, officially marketed by the Wi-Fi Alliance as (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) and (6 GHz), is an IEEE standard for wireless local-area networks (WLANs) and the successor of 802.11ac. It is also known as ''High Efficiency'' , for the overall improvements to clients under dense environments. It is designed to operate in license-exempt bands between 1 and 7.125 GHz, including the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands already in common use as well as the much wider 6 GHz band (5.925–7.125 GHz in the US). The main goal of this standard is enhancing throughput-per-area in high-density scenarios, such as corporate offices, shopping malls and dense residential apartments. While the nominal data rate improvement against 802.11ac is only 37%, the overall throughput increase (over an entire network) is 300% (hence ''High Efficiency''). This also translates to 75% lower latency. The quadrupling of overall throughput is made possible by a higher spectral efficiency. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a non-profit organization that owns the Wi-Fi trademark. Manufacturers may use the trademark to brand products certified for Wi-Fi interoperability. History Early 802.11 products suffered from interoperability problems because the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) had no provision for testing equipment for compliance with its standards. In 1999, pioneers of a new, higher-speed variant endorsed the IEEE 802.11b specification to form the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA) and branded the new technology Wi-Fi. The group of companies included 3Com, Aironet (acquired by Cisco), Harris Semiconductor (now Intersil), Lucent (was Alcatel-Lucent, then acquired by Nokia), Nokia and Symbol Technologies (now Zebra Technologies). The alliance lists Apple, Comcast, Samsung, Sony, LG, Intel, Dell, Broadcom, Cisco, Qualcomm, Motorola, Microsoft, Texas Instruments, and T-Mobile as key sponsors. The charter for this independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-user MIMO
Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for multipath wireless communication, in which multiple users or terminals, each radioing over one or more antennas, communicate with one another. In contrast, single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO) involves a single multi-antenna-equipped user or terminal communicating with precisely one other similarly equipped node. Analogous to how OFDMA adds multiple-access capability to OFDM in the cellular-communications realm, MU-MIMO adds multiple-user capability to MIMO in the wireless realm. SDMA,N. JindalMIMO Broadcast Channels with Finite Rate Feedback IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 5045–5059, 2006.D. Gesbert, M. Kountouris, R.W. Heath Jr., C.-B. Chae, and T. SälzerShifting the MIMO Paradigm IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 36-46, 2007.R. Tweg, R. Alpert, H. Leizerovich, A. Steiner, E. Levitan, E. Offir-Arad, A.B. Guy, B. Zickel, A. Aviram, A. Frieman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Interval
In telecommunications, guard intervals are used to ensure that distinct transmissions do not interfere with one another, or otherwise cause overlapping transmissions. These transmissions may belong to different users (as in TDMA) or to the same user (as in OFDM). The purpose of the guard interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes and reflections, to which digital data is normally very sensitive. Use in digital communications systems In OFDM, the beginning of each symbol is preceded by a guard interval. As long as the echoes fall within this interval, they will not affect the receiver's ability to safely decode the actual data, as data is only interpreted outside the guard interval. In TDMA, each user's timeslot ''ends'' with a guard interval. Thus, the guard interval protects against data loss within the same timeslot, and protects the following user's timeslot from interference caused by propagation delay. It is a common misconception that TDMA times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Allocation Vector
The network allocation vector (NAV) is a virtual carrier-sensing mechanism used with wireless network protocols such as IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) and IEEE 802.16 (WiMax). The virtual carrier-sensing is a logical abstraction which limits the need for physical carrier-sensing at the air interface in order to save power. The MAC layer frame headers contain a ''duration'' field that specifies the transmission time required for the frame, in which time the medium will be busy. The stations listening on the wireless medium read the ''Duration'' field and set their NAV, which is an indicator for a station on how long it must defer from accessing the medium. The NAV may be thought of as a counter, which counts down to zero at a uniform rate. When the counter is zero, the virtual carrier-sensing indication is that the medium is idle; when nonzero, the indication is busy. The medium shall be determined to be busy when the station (STA) is transmitting. In IEEE 802.11, the NAV represents the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Interframe Space
Short Interframe Space (SIFS), is the amount of time in microseconds required for a wireless interface to process a received frame and to respond with a response frame. It is the difference in time between the first symbol of the response frame in the air and the last symbol of the received frame in the air. A SIFS time consists of the delay in receiver RF, PLCP delay and the MAC processing delay, which depends on the physical layer used. In IEEE 802.11 networks, SIFS is the interframe spacing prior to transmission of an acknowledgment, a Clear To Send (CTS) frame, a block ack frame that is an immediate response to either a block ack request frame or an A-MPDU, the second or subsequent MPDU of a fragment burst, a station responding to any polling a by point coordination function and during contention free periods of point coordination function. Implications for Software Radio Because most Software-Defined Radios use a host computer for processing, the SIFS impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Link
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links. A telecommunications link is generally based on one of several types of information transmission paths such as those provided by communication satellites, terrestrial radio communications infrastructure and computer networks to connect two or more points. The term ''link'' is widely used in computer networking to refer to the communications facilities that connect nodes of a network. Sometimes the communications facilities that provide the communication channel that constitutes a link are also included in the definition of ''link''. Types Point-to-point A point-to-point link is a dedicated link that connects exactly two communication facilities (e.g., two nodes of a network, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-user MIMO
Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for multipath wireless communication, in which multiple users or terminals, each radioing over one or more antennas, communicate with one another. In contrast, single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO) involves a single multi-antenna-equipped user or terminal communicating with precisely one other similarly equipped node. Analogous to how OFDMA adds multiple-access capability to OFDM in the cellular-communications realm, MU-MIMO adds multiple-user capability to MIMO in the wireless realm. SDMA,N. JindalMIMO Broadcast Channels with Finite Rate Feedback IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 5045–5059, 2006.D. Gesbert, M. Kountouris, R.W. Heath Jr., C.-B. Chae, and T. SälzerShifting the MIMO Paradigm IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 36-46, 2007.R. Tweg, R. Alpert, H. Leizerovich, A. Steiner, E. Levitan, E. Offir-Arad, A.B. Guy, B. Zickel, A. Aviram, A. Frieman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
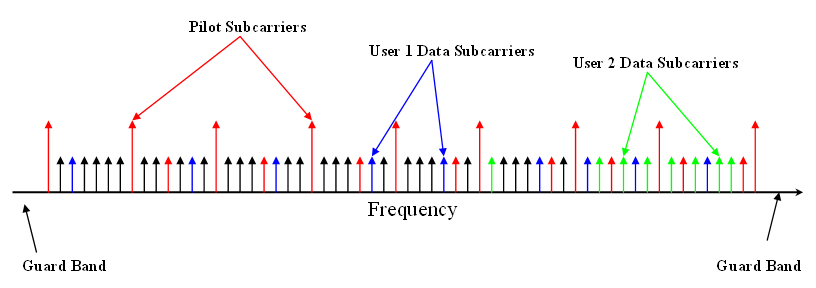
Orthogonal Frequency-division Multiple Access
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users. This allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users. Comparisons OFDMA is often compared to the combination of OFDM with statistical time-division multiplexing. The advantages and disadvantages summarized below are further discussed in the Characteristics and principles of operation section. See also the list of OFDM key features. Advantages * Allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users. * Pulsed carrier can be avoided. * Lower maximal transmission power for low-data-rate users. * Shorter delay and constant delay. * Contention-based multiple access (collision avoidance) is simplified. * Further improves OFDM robustness to fading and interference. * Combat narrow-band inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Interval
In telecommunications, guard intervals are used to ensure that distinct transmissions do not interfere with one another, or otherwise cause overlapping transmissions. These transmissions may belong to different users (as in TDMA) or to the same user (as in OFDM). The purpose of the guard interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes and reflections, to which digital data is normally very sensitive. Use in digital communications systems In OFDM, the beginning of each symbol is preceded by a guard interval. As long as the echoes fall within this interval, they will not affect the receiver's ability to safely decode the actual data, as data is only interpreted outside the guard interval. In TDMA, each user's timeslot ''ends'' with a guard interval. Thus, the guard interval protects against data loss within the same timeslot, and protects the following user's timeslot from interference caused by propagation delay. It is a common misconception that TDMA times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Unit
Resource Unit (RU) is a unit in OFDMA terminology used in 802.11ax WLAN to denote a group of 78.125 kHz bandwidth subcarriers (tones) used in both DownLink (DL) and UpLink (UL) transmissions. With OFDMA, different transmit powers may be applied to different RUs. There are maximum of 9 RUs for 20 MHz bandwidth, 18 in case of 40 MHz and more in case of 80 or 160 MHz bandwidth. The RUs enables an Access Point station to allow WLAN stations to access it simultaneously and efficiently. Description In the older WLAN standard (802.11ac) only single-user station is allowed to transmit ( uplink transmission) at one point in time, although multi-user downlink (DL-MU-MIMO) from AP to Non-AP stations has been supported through MIMO beamforming. The more stations active in the network, the longer the stations need to wait before allowed to transmit, hence the overall wireless traffic gets slower. 802.11ax WLAN is the first WLAN standard to use OFDMA to enable transmiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
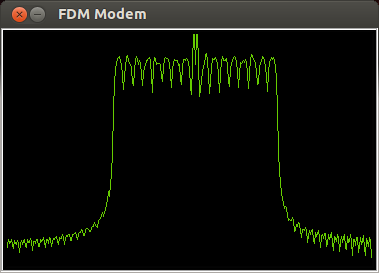
Frequency-division Multiplexing
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel. The most common example of frequency-division multiplexing is radio and television broadcasting, in which multiple radio signals at different frequencies pass through the air at the same time. Another example is cable television, in which many television channels are carried simultaneously on a single cable. FDM is also used by telephone systems to transmit multiple telephone calls through high capacity trunklines, communications satellites to transmit multiple channels of data on uplink and down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Station (networking)
In IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) terminology, a station (abbreviated as STA) is a device that has the capability to use the 802.11 protocol. For example, a station may be a laptop, a desktop PC, PDA, access point or Wi-Fi phone. An STA may be fixed, mobile or portable. Generally, in wireless networking terminology, a station, a wireless client and a node In general, a node is a localized swelling (a " knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex). Node may refer to: In mathematics * Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph * Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, line ... are often used interchangeably, with no strict distinction existing between these terms. A station may also be referred to as a transmitter or receiver based on its transmission characteristics. IEEE 802.11-2007 formally defines station as: ''Any device that contains an IEEE 802.11-conformant media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) interface to the wireless medium (WM).'' See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |