|
Whippet Mk A
The Medium Mark A Whippet was a British tank of the First World War. It was intended to complement the slower British heavy tanks by using its relative mobility and speed in exploiting any break in the enemy lines. Development and production history On 3 October 1916 William Tritton, about to be knighted for developing the Mark I, proposed to the Tank Supply Committee that a faster and cheaper tank, equipped with two engines like the Flying Elephant, should be built to exploit gaps that the heavier but slow tanks made, an idea that up till then had been largely neglected. This was accepted on 10 November and approved by the War Office on 25 November. At that time the name for the project was the ''Tritton Chaser''. Traditionally, the name ''Whippet'' (after the fast-running dog breed) is attributed to Sir William himself. Actual construction started on 21 December. The first prototype, with a revolving turret taken from an Austin armoured car — the first for a British tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Tank
A medium tank is a classification of tanks, particularly prevalent during World War II which represented a compromise between the mobility oriented light tanks and the armour and armament oriented heavy tanks. A medium tank's classification is not actually based on weight, but off of tactical usage and intended purpose; for instance the German Panzerkampfwagen V Panther medium tank has a mass similar to contemporary Allied heavy tanks. The most widely produced, cost effective and successful tanks of World War II (the German Panzer IV, the Soviet T-34, and the American M4 Sherman) were all medium tank designs. Many of the medium tank lines became what are called main battle tanks in most countries. History The first tanks to carry the name "Medium" appeared in the First World War with the British Medium Mark A Whippet. It was smaller, lighter and faster than the British heavy tanks of the time and only carried machine guns. The medium tank doctrine came into use in the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin Armoured Car
The Austin Armoured Car was a British armoured car produced during the First World War. The vehicle is best known for its employment by the Imperial Russian Army in the First World War and by different forces in the Russian Civil War. In addition to the British-built Austins, a few dozens of vehicles were manufactured in Russia in 1918–20. These are usually referred to as Austin-Putilov or – if fitted with a Kégresse halftrack chassis – Austin-Kégresse. Production history British Austins In August 1914, just after the beginning of the First World War, the army of the Russian Empire started to form armoured car units. Due to limited production capabilities of the country's automotive industry it was decided to order a number of vehicles abroad. A committee was sent to the United Kingdom, but failed to find an armoured car that met their requirements for overhead protection and two machine gun turrets. To meet these requirements, the Austin Motor Company designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
303 British
The .303 British (designated as the 303 British by the C.I.P. and SAAMI) or 7.7×56mmR, is a calibre rimmed rifle cartridge. The .303 inch bore diameter is measured between rifling lands as is the common practice in Europe which follows the traditional black powder convention. It was first manufactured in Britain as a stop-gap black powder round put into service in December 1888 for the Lee–Metford rifle. From 1891 the cartridge used smokeless powder which had been the intention from the outset, but the decision on which smokeless powder to adopt had been delayed. It was the standard British and Commonwealth military cartridge for rifles and machine guns from 1889 until the 1950s when it was replaced by the 7.62×51mm NATO. Cartridge specifications The .303 British has 3.64 ml (56 grains H2O) cartridge case capacity. The pronounced tapering exterior shape of the case was designed to promote reliable case feeding and extraction in bolt-action rifles and machine guns a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-decker Bus
A double-decker bus or double-deck bus is a bus that has two storeys or decks. They are used for mass transport in the United Kingdom, the United States, New Zealand, Europe, Asia and also in cities such as Sydney; the best-known example is the red London bus, namely the AEC Routemaster. Early double-deckers put the driver in a separate cab. Passenger access was via an open platform at the rear and a bus conductor collected fares. Modern double-deckers have a main entrance door at the front and the driver takes fares, thus halving the number of workers aboard, but slowing the boarding process. The rear open platform, popular with passengers, was abandoned for safety reasons, as there was a risk of passengers falling when running and jumping onto the bus. Double-deckers are primarily for commuter transport, but open-top models are used as sight-seeing buses for tourists. William Gladstone, speaking of London's double-deck horse-drawn omnibuses, once observed that "...the best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt Tractor
The Holt tractors were a range of continuous track haulers built by the Holt Manufacturing Company from California (U.S.), which was named after Benjamin Holt. Between 1908 and 1913, twenty-seven of the first 100 Holt caterpillar track-type tractors were used on the Los Angeles Aqueduct project, which provided a good proving ground for these machines. Military use They were widely used by the British, French and American armies in the First World War for hauling heavy artillery including the BL 9.2-inch howitzer and the BL 8-inch howitzer. Around 2,000 Holt 75s along with 698 Holt 120s and 63 Holt 60s saw military use during the war. The French Schneider CA1 and Saint-Chamond and German A7V tanks were based on Holt tractors. Specification There were at least three models used for military purposes: the Holt 75, the Holt 120 and to a lesser extent the Holt 60. The Holt 75 was first produced in 1913. It used two tracks for steering. It had a maximum speed of and had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark I (tank)
British heavy tanks were a series of related armoured fighting vehicles developed by the UK during the First World War. The Mark I was the world's first tank, a tracked, armed, and armoured vehicle, to enter combat. The name "tank" was initially a code name to maintain secrecy and disguise its true purpose by making it appear to be a water transport vehicle for bringing water to the troops at the front line. The tank was developed in 1915 to break the stalemate of trench warfare. It could survive the machine gun and small-arms fire in " no man's land", travel over difficult terrain, crush barbed wire, and cross trenches to assault fortified enemy positions with powerful armament. Tanks also carried supplies and troops. British heavy tanks are distinguished by an unusual rhomboidal shape with a high climbing face of the track, designed to cross the wide and deep trenches prevalent on the battlefields of the Western Front. Due to the height necessary for this shape, an armed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Fighting Vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured cars, assault guns, self-propelled guns, infantry fighting vehicles, and armoured personnel carriers. Armoured fighting vehicles are classified according to their characteristics and intended role on the battlefield. The classifications are not absolute; two countries may classify the same vehicle differently, and the criteria change over time. For example, relatively lightly armed armoured personnel carriers were largely superseded by infantry fighting vehicles with much heavier armament in a similar role. Successful designs are often adapted to a wide variety of applications. For example, the MOWAG Piranha, originally designed as an APC, has been adapted to fill numerous roles such as a mortar carrier, infantry fighting vehicle, and ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Mark D
Medium Mark D was a British tank developed at the end of the First World War. It was envisaged as a vehicle to be used in "Plan 1919" an offensive on the Western Front which would use large numbers of heavy and medium tanks to break through the German defences, destroy lines of communication crippling the German army and thus end the war. The Armistice ended the war in 1918 and it would never be tested in combat but development continued for the post-war needs of the British Army. The unusual suspension proved problematic and the earlier tanks were replaced by a Vickers design - the Medium Mark I - in the 1920s It should not be confused with export Vickers Medium Mark D tank, built in one unit for Ireland in 1929. Development J F C Fuller's plan 1919 (circulated in mid-1918) was for the heavy tanks to engage and pin the German troops allowing faster tanks to penetrate the flanks and encircle the enemy isolating them from the chain of command precipitating a breakdown of moral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
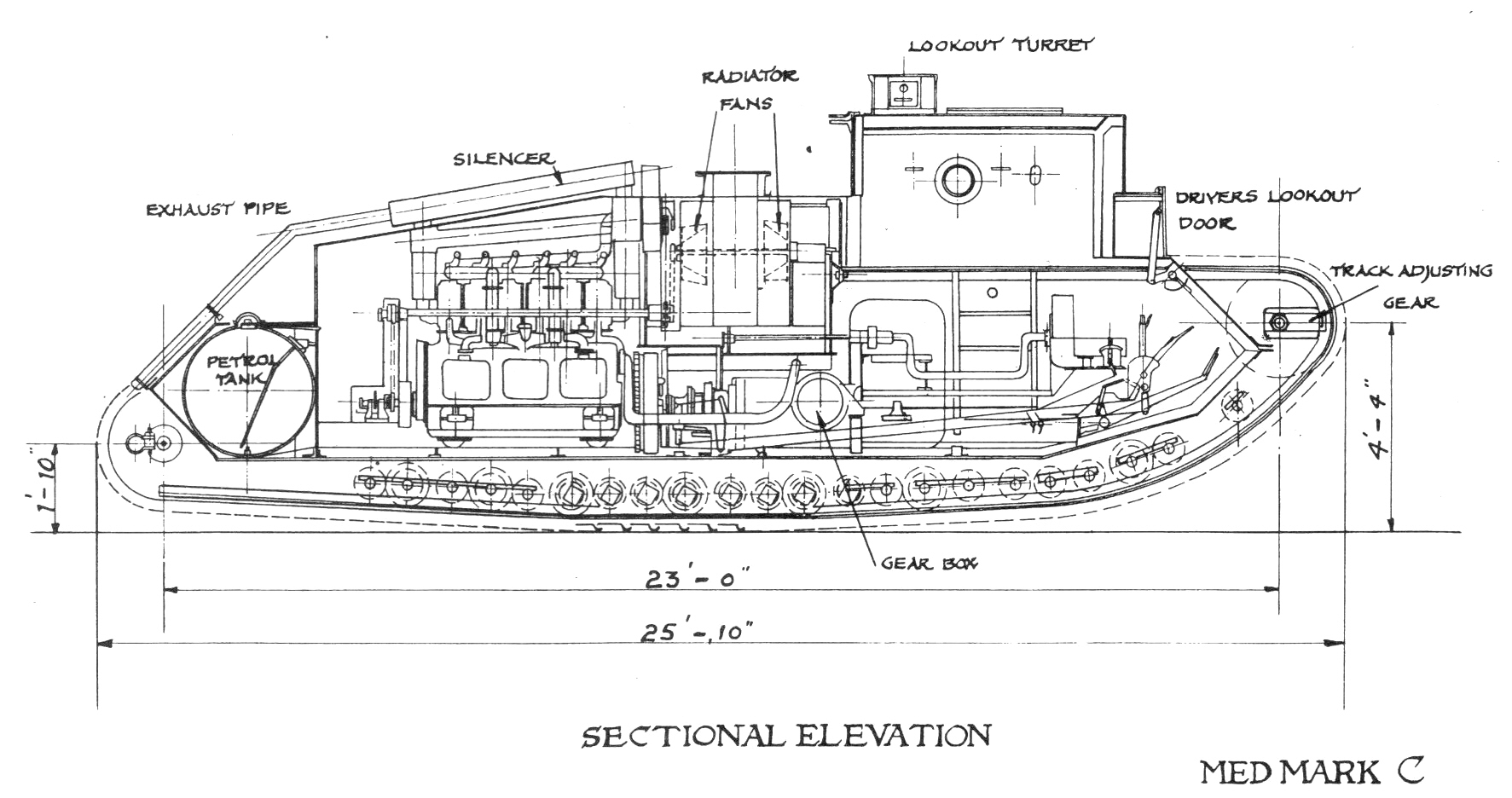
Medium Mark C
The Medium Mark C Hornet was a British tank developed during the First World War, but produced too late to see any fighting. Development In 1917 Sir William Tritton had developed the Medium Mark A Whippet without involving his former co-worker Walter Gordon Wilson. In response Major Wilson began to design an improved type on his own, the Medium Mark B, in July 1917. As soon as he became aware of Wilson's intentions, Tritton ordered his chief designer, William Rigby, to design a rival type: the Medium Mark C. The drawings were approved by the British Army on 19 April 1918. The prototype was finished in August, a few weeks before the Medium B prototype also in construction at Tritton's own factory. At first 200 tanks were ordered; later this was increased to 600, all to be produced by William Foster & Co Ltd at Lincoln with Armlet & Wortley as subcontractor. The colloquial name of the tank was to be "Hornet", but it seems nobody ever used it. Description Superficially, the Medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Mark B
The Medium Mark B was a British tank of the First World War developed as a successor to the Whippet, but ultimately unsatisfactory and production was cancelled at the end of the war. History The engineer Lieutenant Walter Wilson and the industrialist Sir William Tritton had cooperated in 1915 to develop the Mark I, the world's first operational tank. However, when Tritton decided to build the Medium Mark A "Whippet", Wilson was left out. The Medium A was designed by Tritton's chief engineer, William Rigby. The Whippet was a successful design and proved effective but suffered from a lack of power, complex steering and unsprung suspension. Wilson, now a Major, decided he could by himself develop a better tank as replacement: the 'Medium Tank Mark B'. He probably started drawing in July 1917. Major Philip Johnson of Central Tank Workshops was impressed when he was shown a wooden mock-up during a visit to Britain late 1917. The prototype was built by Tritton's firm, the Metropol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Royal Tank Regiment
The 6th Royal Tank Regiment (6 RTR) was a regiment of the Royal Tank Regiment, of the British Army, until 1959. It originally saw action as 6th Battalion Tank Corps in 1917. First World War When tanks were first used in action in 1916, they were operated by the Heavy Branch of the Machine Gun Corps. This constituted six companies, A through F. With the rapid growth of the tank forces, these companies were used as the cadre of new battalions, which were quickly transferred to the newly formed Tank Corps, and then changed from letters to numbers. F Company thus became F Battalion of the Heavy Branch in November 1916, then F Battalion of the Tank Corps, then redesignated as 6th Battalion of the Tank Corps in January 1918. During this time, the unit saw heavy action; it fought at the Battle of Messines, Passchendaele, Cambrai, Amiens (using Whippet Mk A light tanks), Bapaume, 2nd Arras and Cambrai-St Quentin. During this time, a Victoria Cross was awarded to Captain Richard A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Haig
Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, (; 19 June 1861 – 29 January 1928) was a senior officer of the British Army. During the First World War, he commanded the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the Western Front from late 1915 until the end of the war. He was commander during the Battle of the Somme, the Battle of Arras, the Third Battle of Ypres, the German Spring Offensive, and the Hundred Days Offensive.Sheffield 2002, p. 21.Sheffield 2002, p. 263.Hart 2008, p. 2. His military career included service in the War Office, where he was instrumental in the creation of the Territorial Force in 1908. In January 1917 he was raised up to the rank of Field Marshal, subsequently leading the BEF during the final Hundred Days Offensive, when it crossed the Canal du Nord and broke through the Hindenburg line, capturing 195,000 German prisoners. This campaign, in combination with the Kiel mutiny, the Wilhelmshaven mutiny, the proclamation of a republic on 9 November 1918, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






.jpg)