|
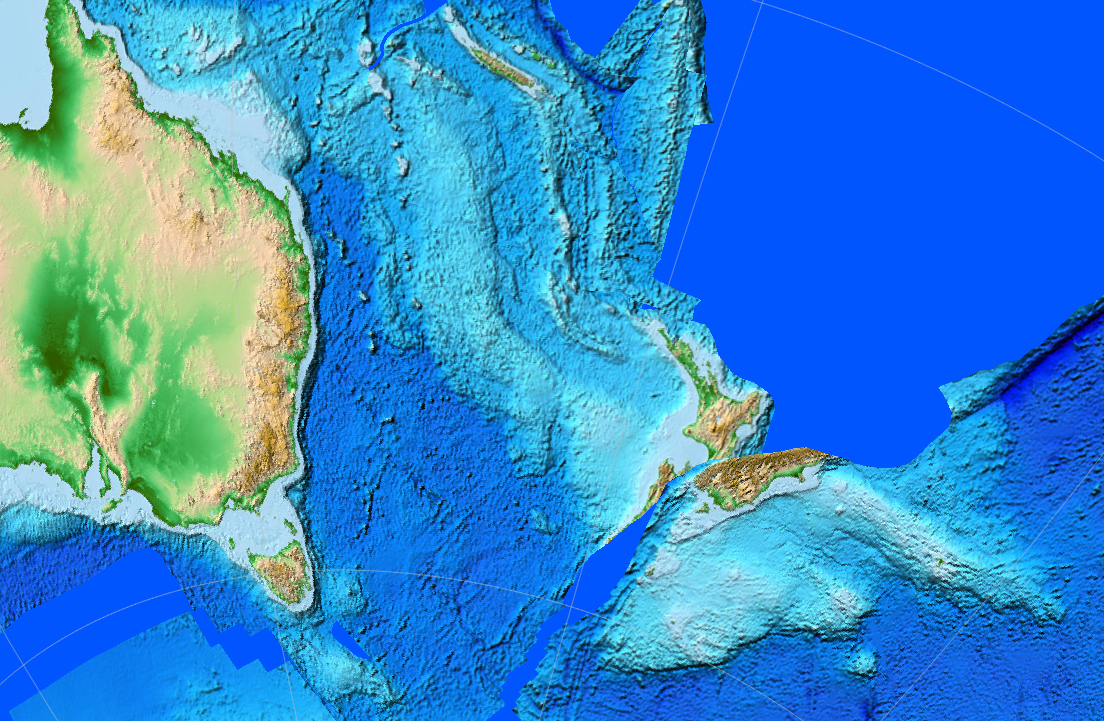
Wairau Fault
The Wairau Fault is an active dextral (right lateral) strike-slip fault in the northeastern part of South Island, New Zealand. It forms part of the Marlborough Fault System, which accommodates the transfer of displacement along the oblique convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian Plate and Pacific Plate, from the transform Alpine Fault to the Hikurangi Trench subduction zone. Extent Depending on the precise definition used, the Wairau Fault runs either from southern or northern end of 'The Bends' region. In the former case it is regarded as the Wairau segment of the Alpine Fault. In the latter case it is regarded as a separate fault and runs about 100 km from near Lake Rotoiti to Cloudy Bay in the east. To the west, the fault is a single strand but near Wairau Valley township, the fault splits into two strands. These two strands continue to within about 15 km of the coast near Renwick. Further to the east only the southernmost strand can be detected. It ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hikurangi Trench
The Hikurangi Trench, also called the Hikurangi Trough, is an oceanic trench in the bed of the Pacific Ocean off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, lying between the southern end of the Cook Strait and the Chatham Rise. It is the southward continuation of the much deeper Kermadec Trench. It lies in the Hikurangi Margin subduction zone, which is the southern extension of the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone. The Hikurangi Margin is the subduction zone where the thick oceanic Hikurangi Plateau is subducting beneath continental crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. By contrast, the Kermadec and Tonga trenches represent the parts of the subduction zone where oceanic crust of the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath oceanic crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. Although shallower than the trenches north of it, the Hikurangi Trench reaches depths of 3,000 metres as close as 80 kilometres from shore. Its maximum depth is about .Keith B. Lewis, Jean-Yves Collott and Serge E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairau River
The Wairau River is one of the longest rivers in New Zealand's South Island. It flows for from the Spenser Mountains (a northern range of the Southern Alps), firstly in a northwards direction and then northeast down a long, straight valley in inland Marlborough. The river's lower reaches and surrounding fertile plain provide the basis for the Marlborough wine region. The river has its outflow into Cook Strait at Cloudy Bay, just north of Blenheim in the island's northeast. The Wairau River meets the sea at the Wairau Bar, an important archaeological site. In pre-European and early colonial New Zealand, one of the South Island's largest Māori Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ... settlements was close to the mouth of the Wairau. The Wairau Valley was the sce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renwick, New Zealand
Renwick is a small town in Marlborough, New Zealand, close to the south bank of the Wairau River. It is located on , west of Blenheim. Havelock is north. State Highway 63 runs southwest from Renwick through the Wairau River valley. The town was initially known as "Upper Wairau", and then as "Renwicktown" after an early landowner, Dr. Thomas Renwick. Renwick is located in the centre of Marlborough's grape growing region. Sauvignon blanc is the variety usually associated with the area, and famous wineries such as Isabel Estate and Forrest Estate are in close proximity. Pinot Gris (Grey Pinot) is also exported. Demographics Renwick is defined by Statistics New Zealand as a small urban area and covers . It had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Renwick had a population of 2,418 at the 2018 New Zealand census Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairau Valley
Wairau Valley is the valley of the Wairau River in Marlborough, New Zealand and also the name of the main settlement in the upper valley. State Highway 63 runs through the valley. The valley opens onto the Wairau Plain, where Renwick and Blenheim are sited. The Alpine–Wairau Fault runs along the length of the valley. Wairauite is an iron-cobalt alloy which is named after the valley. History and culture European settlement J. S. Cotterell surveyed the Wairau Valley in November 1842, and reported it contained rich land. Settlers from Nelson, led by Arthur Wakefield, tried to take possession of the land but the Ngāti Toa, led by Te Rauparaha and Te Rangihaeata objected. The dispute escalated into the Wairau Affray at Tuamarina on 23 June 1843, in which 22 settlers and four Māori were killed. An enquiry held in 1844 by Governor Robert FitzRoy decided that the settlers were in the wrong. In November 1846, Nelson farmers Nathaniel Morse and John Cooper drove sheep into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloudy Bay
Te Koko-o-Kupe / Cloudy Bay is located at the northeast of New Zealand's South Island, to the south of the Marlborough Sounds and north of Clifford Bay. In August 2014, the name Cloudy Bay, given by Captain Cook in 1770, was officially altered to Te Koko-o-Kupe / Cloudy Bay, with the Māori name recalling the early explorer Kupe scooping up oysters from the bay. The area lends its name to one of the best known New World white wines ( Cloudy Bay Vineyards Sauvignon Blanc) although the grapes used in production of that wine are grown in the Marlborough wine region further inland. Features The bay faces Cook Strait, stretching north-south over a distance of from the southern extremity of the Marlborough Sounds ( Port Underwood) to White Bluffs. Along its length is the delta of the Wairau River, which reaches the sea at two points. The southern of these forms an entrance to the Big Lagoon, just to the north of White Bluffs. The central point is known as the Wairau Diversion. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotoiti, Tasman
Lake Rotoiti, previously also known as Lake Arthur, is a lake in the Tasman Region of New Zealand. It is a substantial mountain lake within the borders of Nelson Lakes National Park. The lake is fed by the Travers River, water from the lake flows into the Buller River. The lake is surrounded by beech forest and is deep. Saint Arnaud is a small community at the northern end of the lake. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "little lake" for . The first European to see the lake was John Sylvanus Cotterell on 18 January 1843. Thomas Brunner and Charles Heaphy reached the lake in November 1843, and Heaphy named it Lake Arthur after Captain Arthur Wakefield, but the Māori name remained. For many years the lake formed part of Nelson politician and landowner John Kerr's beloved Lake Station - including Mt Robert. Kerr (who introduced Trout to the lake),drowned there with many believing his son Robert to be responsible. The lake and Mt Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fault over the last 12 million years in a series of earthquakes. However, most of the motion on the fault is strike-slip (side to side), with the Tasman district and West Coast moving North and Canterbury and Otago moving South. The average slip rates in the fault's central region are about 38 mm a year, very fast by global standards. The last major earthquake on the Alpine Fault was in c. 1717 AD, and the probability of another one occurring within the next 50 years is estimated at about 75 percent. Geographic extent and plate motion ThPacific Plate and Indo-Australian Plate boundaryforms the Macquarie Fault Zone in the Puysegur Trench off the southwestern corner of the South Island and comes onshore as the Alpine Fault just n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Fault
An active fault is a fault that is likely to become the source of another earthquake sometime in the future. Geologists commonly consider faults to be active if there has been movement observed or evidence of seismic activity during the last 10,000 years. * Active faulting is considered to be a geologic hazard - one related to earthquakes as a cause. Effects of movement on an active fault include strong ground motion, surface faulting, tectonic deformation, landslides and rockfalls, liquefaction, tsunamis, and seiches. Quaternary faults are those active faults that have been recognized at the surface and which have evidence of movement during the Quaternary Period. Related geological disciplines for ''active-fault'' studies include geomorphology, seismology, reflection seismology, plate tectonics, geodetics and remote sensing, risk analysis, and others. Location Active faults tend to occur in the vicinity of tectonic plate boundaries, and active fault research has foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a '' strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate. The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Izanagi Plates. The Pacific Plate subsequently grew to where it underlies most of the Pacific Ocean basin. This reduced the Farallon Plate to a few remnants along the west coast of North America and the Phoenix Plate to a small remnant near the Drake Passage, and destroyed the Izanagi Plate by subduction under Asia. The Pacific Plate contains an interior hot spot forming the Hawaiian Islands. Boundaries The north-eastern side is a divergent boundary with the Explorer Plate, the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Gorda Plate forming respectively the Explorer Ridge, the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. In the middle of the eastern side is a transform boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault, and a boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |