|
Write Now
WriteNow was one of the two original word processor applications developed for the launch of the Apple Macintosh in 1984, and was the primary word processor for computers manufactured by NeXT. WriteNow was purchased from T/Maker by WordStar in 1993, but shortly after that, WordStar merged with SoftKey, which ultimately led to its discontinuation. It had a combination of powerful features, excellent performance, and small system requirements. History WriteNow was written for Apple Computer, Inc., by John Anderson and Bill Tschumy in Seattle, separate from the Macintosh computer and MacWrite word processor development teams. Steve Jobs was concerned that those programming MacWrite were not going to be ready for the 1984 release date of the Macintosh; Apple Computer therefore commissioned a team of programmers, friends of Apple engineer Bud Tribble, to work independently on a similar project, which eventually became WriteNow. Members of the WriteNow team knew about MacWrite, but me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macworld
''Macworld'' is a website dedicated to products and software of Apple Inc., published by Foundry, a subsidiary of IDG Inc. It started life as a print magazine in 1984 and had the largest audited circulation (both total and newsstand) of Macintosh-focused magazines in North America, more than double its nearest competitor, '' MacLife'' (formerly ''MacAddict''). ''Macworld'' was founded by David Bunnell and Cheryl Woodard (publishers) and Andrew Fluegelman (editor). It was the oldest Macintosh magazine still in publication, until September 10, 2014, when IDG, its parent company, announced it was discontinuing the print edition and laid off most of the staff, while continuing an online version. History of Macworld In 1997, the publication was renamed ''Macworld, incorporating MacUser'' (a name reflected subtly on the magazine's Table of Contents page) to reflect the consolidation of the Ziff-Davis-owned '' MacUser'' magazine into the International Data Group-owned ''Macworld' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bud Tribble
Guy L. "Bud" Tribble is Vice President of Software Technology at Apple Inc. Work Tribble was a member of the original Apple Macintosh design team. He served as manager of the software development team, and helped to design the classic Mac OS and its user interface. He was among the founders of NeXT, Inc., serving as NeXT's vice president of software development. Tribble is one of the industry's top experts in software design and object-oriented programming. Tribble's career includes time at Sun Microsystems and Eazel. At Eazel, he was vice president of Engineering leading development of next generation user interface software and Internet services for Linux computers. Tribble was also chief technology officer for the Sun-Netscape Alliance, responsible for guiding Internet and e-commerce software R&D. Tribble earned a BA degree in physics at the University of California, San Diego, and an MD and PhD in biophysics and physiology at the University of Washington in Seattle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology. Generally, the goal of user interface design is to produce a user interface that makes it easy, efficient, and enjoyable (user-friendly) to operate a machine in the way which produces the desired result (i.e. maximum usability). This generally means that the operator needs to provide minimal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 680x0
The Motorola 68000 series (also known as 680x0, m68000, m68k, or 68k) is a family of 32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and were the primary competitors of Intel's x86 microprocessors. They were best known as the processors used in the early Apple Macintosh, the Sharp X68000, the Commodore Amiga, the Sinclair QL, the Atari ST, the Sega Genesis (Mega Drive), the Capcom System I (Arcade), the AT&T UNIX PC, the Tandy Model 16/16B/6000, the Sun Microsystems Sun-1, Sun-2 and Sun-3, the NeXT Computer, NeXTcube, NeXTstation, and NeXTcube Turbo, the Texas Instruments TI-89/TI-92 calculators, the Palm Pilot (all models running Palm OS 4.x or earlier) and the Space Shuttle. Although no modern desktop computers are based on processors in the 680x0 series, derivative processors are still widely used in embedded systems. Motorola ceased development of the 680x0 series a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of ChromeOS. macOS succeeded the classic Mac OS, a Mac operating system with nine releases from 1984 to 1999. During this time, Apple cofounder Steve Jobs had left Apple and started another company, NeXT, developing the NeXTSTEP platform that would later be acquired by Apple to form the basis of macOS. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released in March 2001, with its first update, 10.1, arriving later that year. All releases from Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and after are UNIX 03 certified, with an exception for OS X 10.7 Lion. Apple's other operating systems (iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, tvOS, audioOS) are derivatives of macOS. A prominent pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Environment
This is a list of macOS built-in apps and system components. Applications App Store The Mac App Store is macOS's digital distribution platform for macOS apps, created and maintained by Apple Inc. based on the iOS version, the platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's "Back to the Mac" event. First launched on January 6, 2011, as part of the free Mac OS X 10.6.6 update for all current Snow Leopard users, Apple began accepting app submissions from registered developers on November 3, 2010, in preparation for its launch. After 24 hours of release, Apple announced that there were over one million downloads. Automator Automator is an app used to create workflows for automating repetitive tasks into batches for quicker alteration via point-and-click (or drag and drop). This saves time and effort over human intervention to manually change each file separately. Automator enables the repetition of tasks across a wide variety of programs, including Finder, Safari, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple– IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors. PowerPC was the cornerstone of AIM's PReP and Common Hardware Reference Platform (CHRP) initiatives in the 1990s. Originally intended for personal computers, the architecture is well known for being used by Apple's Power Macintosh, PowerBook, iMac, iBook, eMac, Mac Mini, and Xserve lines from 1994 until 2005, when Apple migrated to Intel's x86. It has since become a niche in personal computers, but remains popular for embedded and high-performance processors. Its use in 7th generation of video game consol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac 68k Emulator
The Mac 68k emulator is a software emulator built into all versions of the classic Mac OS for PowerPC. This emulator enabled running applications and system code that were originally written for the 680x0-based Macintosh models. With a few exceptions, notably Connectix's RAM Doubler, the emulator ran all software with no noticeable impact other than lower performance relative to the same program when compiled for PowerPC. Origins The first version was written by Gary Davidian, who had originally created it for use on the Motorola 88000 CPU, used in Apple's abortive first attempt at a RISC target platform. A later version, using dynamic recompilation, was developed by Eric Traut, who later worked on successful emulation projects at Connectix such as Virtual Game Station and Virtual PC. Prior to Traut's arrival there, Connectix had released Speed Doubler, which included an even faster PowerPC 68k emulator. Implementation All versions of this emulator emulated the "user" subset of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copy Protection
Copy protection, also known as content protection, copy prevention and copy restriction, describes measures to enforce copyright by preventing the reproduction of software, films, music, and other media. Copy protection is most commonly found on videotapes, DVDs, Blu-ray discs, HD-DVDs, computer software discs, video game discs and cartridges, audio CDs and some VCDs. Some methods of copy protection have also led to criticism because it caused inconvenience for paying consumers or secretly installed additional or unwanted software to detect copying activities on the consumer's computer. Making copy protection effective while protecting consumer rights remains a problem with media publication. Terminology Media corporations have always used the term copy protection, but critics argue that the term tends to sway the public into identifying with the publishers, who favor restriction technologies, rather than with the users. Copy prevention and copy control may be more neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
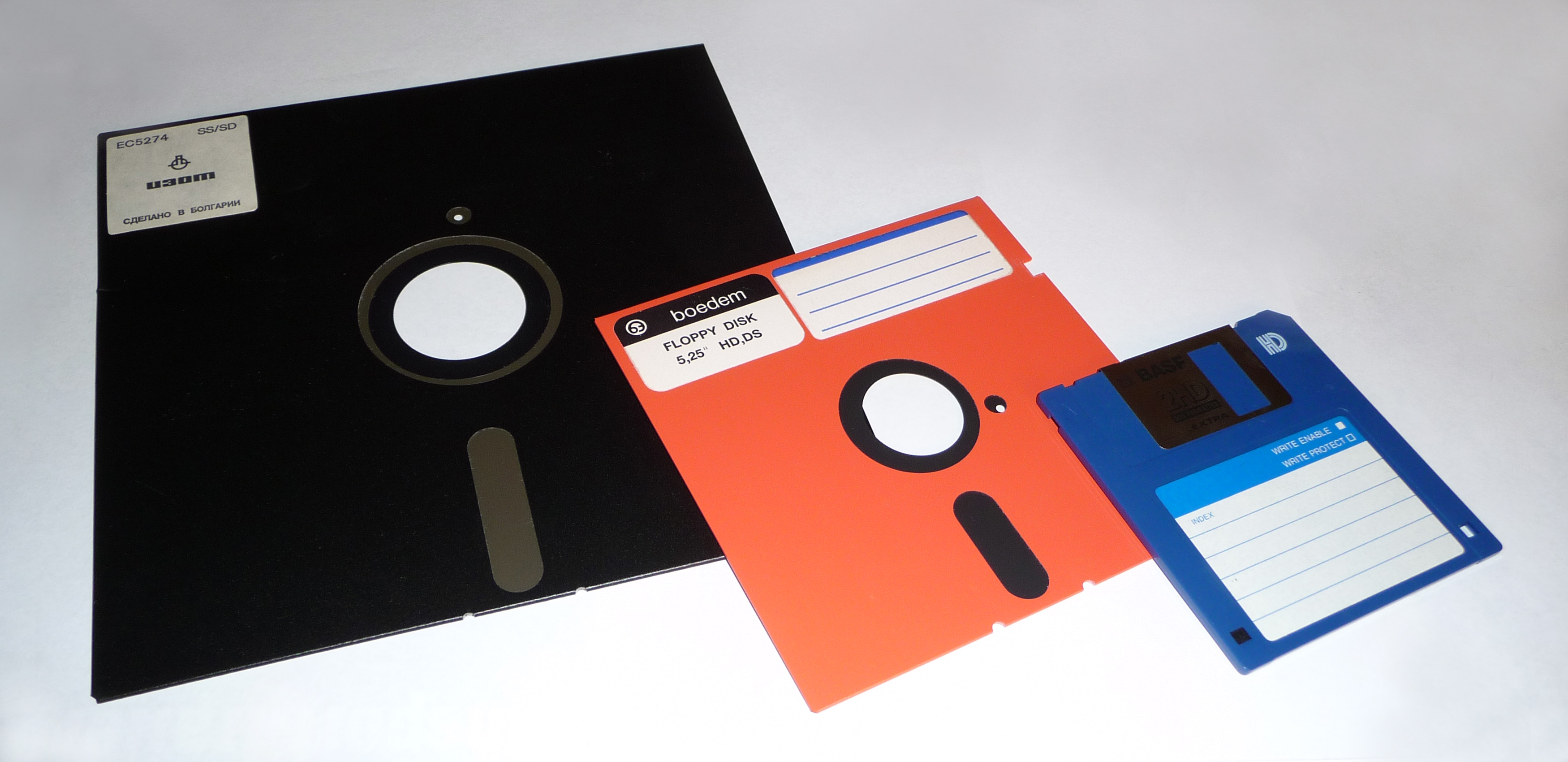
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix '' kilo'' as 1000 (103); per this definition, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to solid-state memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead typically refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the accident that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. A kibibyte is defined by Clause 4 of IEC 80000-13 as 1024 bytes. Definitions and usage Base 10 (1000 bytes) In the International System of Units (SI) the prefix '' kilo'' means 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book '' The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |