|
West Highland Railway
The West Highland Railway was a railway company that constructed a railway line from Craigendoran (on the River Clyde west of Glasgow, Scotland) to Fort William, Highland, Fort William and Mallaig. The line was built through remote and difficult terrain in two stages: the section from Craigendoran to Fort William opened in 1894, with a short extension to Banavie on the Caledonian Canal opening in 1895. It had originally been intended to extend to Roshven, to give good access to sea-going fishery vessels, but the end point was altered to Mallaig, and this section opened in 1901. The Mallaig Extension Railway, Mallaig Extension was notable for the extensive use of mass concrete in making structures for the line; at the time this was a considerable novelty. The line never made a profit, and relied on government financial support, which was given (amid much controversy) to improve the depressed economic conditions of the region. It was worked by the North British Railway, which lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William, Highland
Fort William is a town in the Lochaber region of the Scottish Highlands, located on the eastern shore of Loch Linnhe in the Highland Council of Scotland. At the 2011 census, Fort William had a population of 15,757, making it the second-largest settlement both in the Highland council area and in the whole of the Scottish Highlands; only the city of Inverness has a larger population. Fort William is a major tourist centre with Glen Coe just to the south, to the east, and Glenfinnan to the west. It is the start and end of the Road to the Isles. It is a huge centre for hillwalking and climbing due to its proximity to Ben Nevis, the largest mountain in Scotland and the United Kingdom, and many other Munros. It is also known for its nearby downhill mountain bike track. It is the start/end of both the West Highland Way (a walk/cycleway, Milngavie – Fort William) and the Great Glen Way (a walk/cycleway, Fort William – Inverness). Around 726 people (7.33% of the popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrour Summit - Geograph
Corrour railway station ( ) is on the West Highland Line, near Loch Ossian on the Corrour Lodge#Corrour Estate, Corrour Estate, in the Highland (council area), Highland council area (formerly Inverness-shire) of Scotland. It is the highest mainline (railway), mainline train station, railway station in the United Kingdom at an elevation of above sea level. It is located between Rannoch railway station, Rannoch and Tulloch railway station, Tulloch, and is sited from Craigendoran railway station, Craigendoran Junction, near Helensburgh Upper railway station, Helensburgh. ScotRail manage the station and provide most services, along with Caledonian Sleeper. History Corrour station was built by the West Highland Railway between 1893 and 1894 on its line linking Glasgow with Fort William, and was operated from its opening on 7 August 1894 by the North British Railway. It has a passing loop around an island platform with a siding (rail), siding on the east side. In common with the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
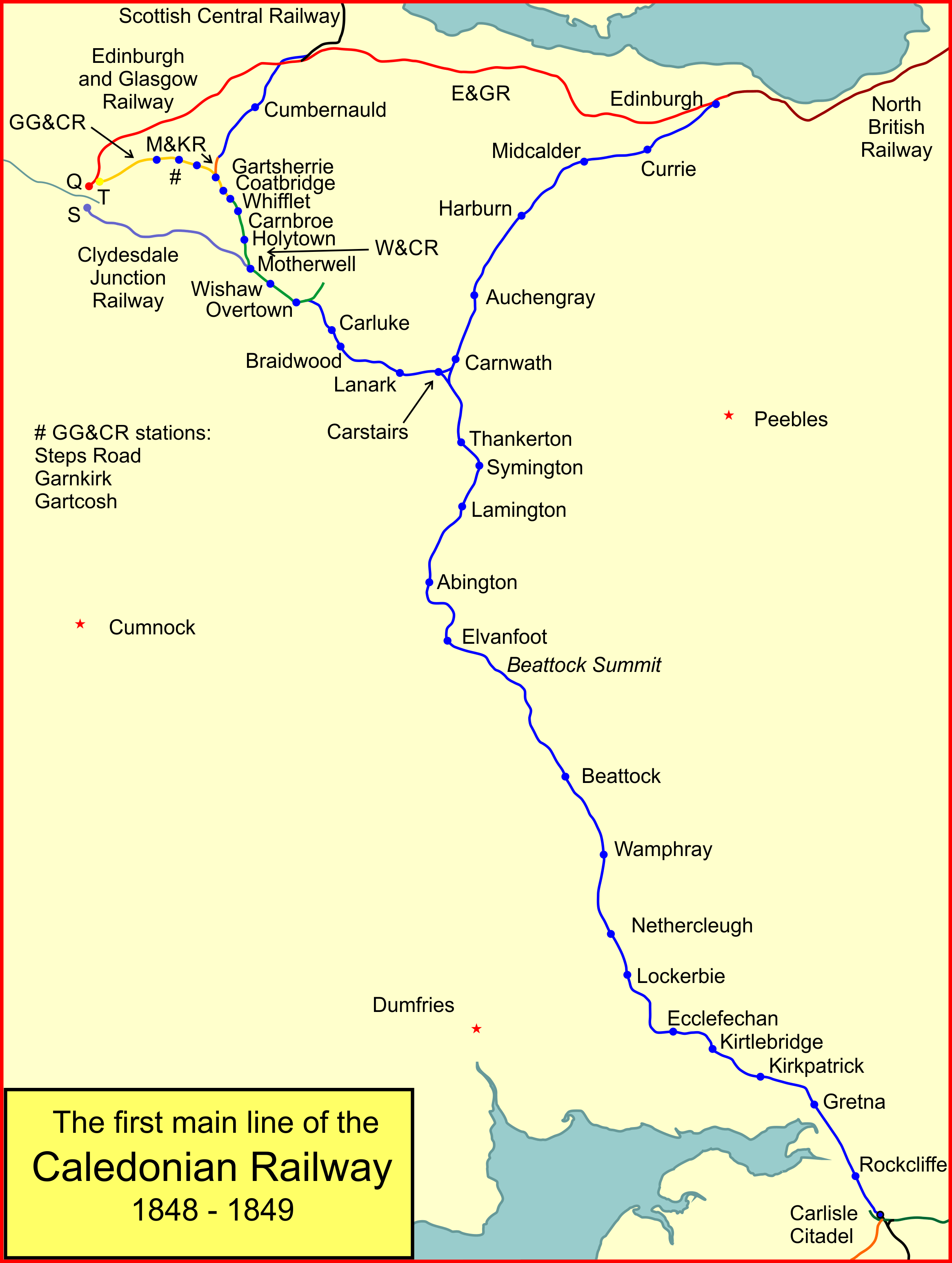
Caledonian Railway Act 1845
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway (with a modified entry into Glasgow itself). Introduction In the mid-1830s, railways in England evolved from local concerns to longer routes that connected cities, and then became networks. In Scotland it was clear that this was the way forward, and there was a desire to connect the Central Belt to the incipient English network. There was controversy over the route that such a line might take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David MacBrayne
David MacBrayne is a limited company owned by the Scottish Government. Formed in 1851 as the private shipping company David Hutcheson & Co. with three partners, David Hutcheson, Alexander Hutcheson and David MacBrayne, it passed in 1878 to David MacBrayne. It became the main carrier for freight and passengers in the Hebrides, with a co-ordinated network of shipping, road haulage and bus operations. In 1973, it was merged with Caledonian Steam Packet Company as state-owned Caledonian MacBrayne. Since 2006 it has been the holding company for ferry operators CalMac Ferries Ltd (operating as Caledonian MacBrayne) and Argyll Ferries, and is classified as an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government. Formation In 1851, Sir George Burns, 1st Baronet, Burns Brothers, G. and J. Burns of Glasgow, passed their fleet of Hebridean vessels to their chief clerk, David Hutcheson. David Hutcheson was married to Margaret Dawson, who was born at her parents home 'Bonnytoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Railway
The Highland Railway (HR) was one of the two smallest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping, operating north of Perth railway station, Scotland, Perth railway station in Scotland and serving the farthest north of Britain. Based in Inverness, the company was formed by merger in 1865, absorbing over 249 miles (401 km) of line. It continued to expand, reaching Wick, Highland, Wick and Thurso in the north and Kyle of Lochalsh in the west, eventually serving the counties of Caithness, Sutherland, Ross & Cromarty, Inverness, Perth, Nairn, Moray and Banff. Southward it connected with the Caledonian Railway at Stanley Junction, north of Perth, and eastward with the Great North of Scotland Railway at Boat of Garten, Elgin, Keith and Portessie.Conolly 2004. During the First World War the British Navy's base at Scapa Flow, in the Orkney Islands, was serviced from Scrabster Harbour near Thurso. The Highland Railway provided transport, including a daily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
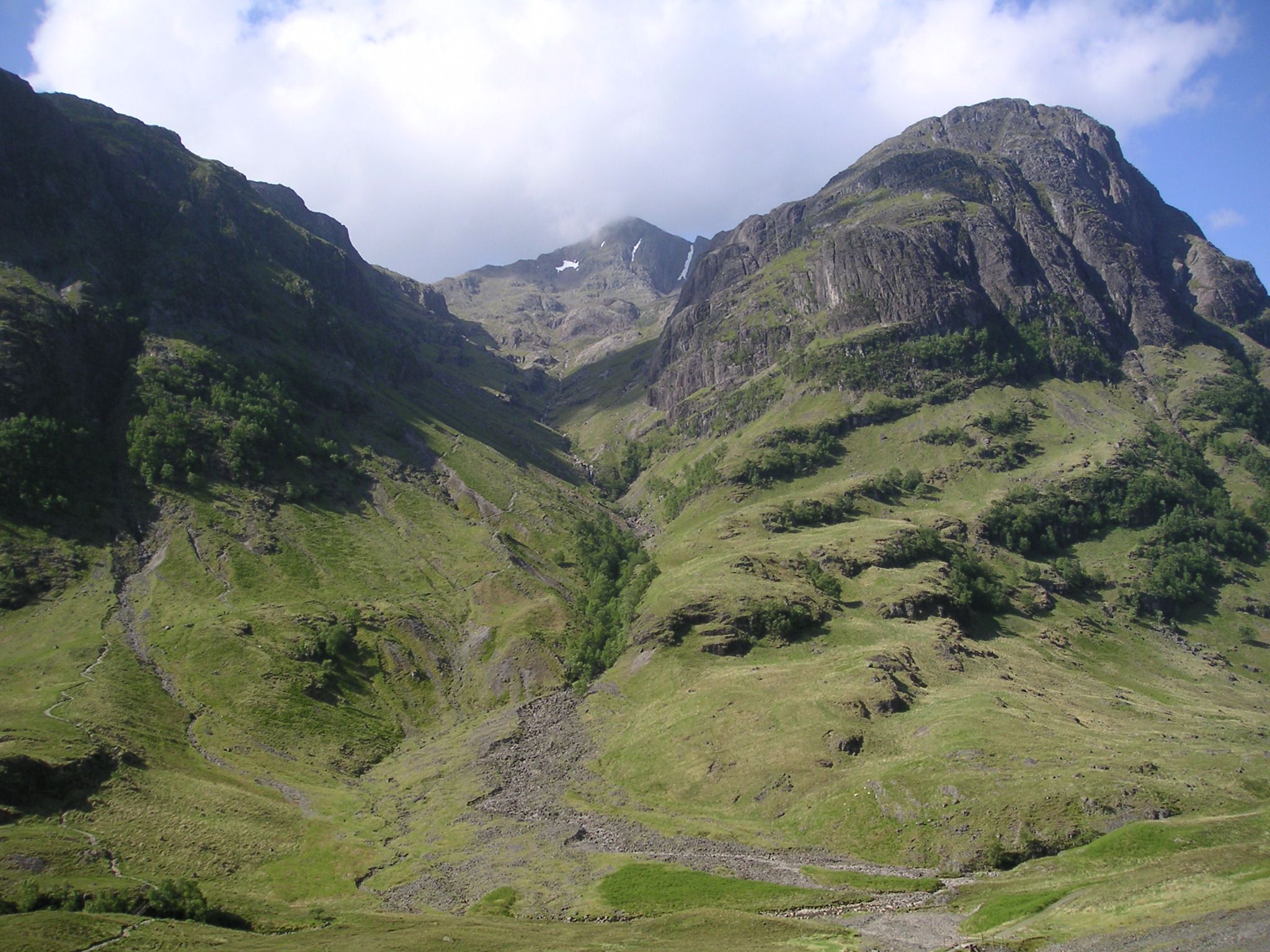
Glen Coe
Glen Coe ( ) is a glen of glacial origins, that cuts though volcanic rocks in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. It lies in the north of the shires of Scotland, county of Argyll, close to the border with the history of local government in Scotland#Provinces, historic province of Lochaber, within the modern subdivisions of Scotland, council area of Highland (council area), Highland. Glen Coe is regarded as the home of Scottish mountaineering and is popular with hillwalkers and climbers. A 2010 review by NatureScot, Scottish Natural Heritage into the special qualities of Scotland's National scenic area (Scotland), National scenic areas listed the "soaring, dramatic splendour of Glen Coe", and "the suddenness of the transition between high mountain pass and the lightly wooded strath" as being of note. The review also described the journey through the glen on the main A82 road as "one of the classic Highland journeys". The main settlement is the village of Glencoe, Highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rannoch Moor
Rannoch Moor (; ) is an expanse of around of boggy moorland to the west of Loch Rannoch in Scotland, from where it extends into westerly Perth and Kinross, northerly Lochaber (in Scottish Highlands, Highland), and the area of Highland Scotland toward its south-west, northern Argyll and Bute. Rannoch Moor is designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and a Special Area of Conservation. Much of the western part of the moor lies within the Ben Nevis and Glen Coe National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland. It is notable for its wildlife, and is particularly famous as being the sole British location for the Scheuchzeria, Rannoch-rush, named after the moor. It was frequently visited by Horace Donisthorpe, who collected many unusual species of ants on the moor and surrounding hilly ground. Today it is still one of the few remaining habitats for ''Formica exsecta'', the "narrow-headed ant", although recent surveys have failed to produce any sign of ''Formica pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond (; ) is a freshwater Scottish loch which crosses the Highland Boundary Fault (HBF), often considered the boundary between the lowlands of Central Scotland and the Highlands.Tom Weir. ''The Scottish Lochs''. pp. 33-43. Published by Constable and Company, 1980. Traditionally forming part of the boundary between the shires of Scotland, counties of Stirlingshire and Dunbartonshire, Loch Lomond is split between the Subdivisions of Scotland, council areas of Stirling (council area), Stirling, Argyll and Bute and West Dunbartonshire. Its southern shores are about northwest of the centre of Glasgow, Scotland's largest city. The Loch forms part of the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park which was established in 2002. From a limnological perspective, Loch Lomond is classified as a dimictic lake, meaning it typically undergoes two mixing periods each year. This occurs in the spring and autumn when the water column becomes uniformly mixed due to temperature-driven dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverness
Inverness (; ; from the , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness") is a city in the Scottish Highlands, having been granted city status in 2000. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Historically it served as the county town of the Counties of Scotland, county of Inverness-shire. Inverness lies near two important battle sites: the 11th century, 11th-century battle of Blar Nam Feinne, Blàr nam Fèinne against Norway which took place on the Aird, and the 18th century Battle of Culloden which took place on Culloden, Highland#Battlefield of Culloden, Culloden Moor. It is the northernmost city in the United Kingdom and lies within the Great Glen (Gleann Mòr) at its northeastern extremity where the River Ness enters the Beauly Firth. With human settlement dating back to at least 5,800 BC, Inverness was an established self-governing settlement by the 6th century with the first Royal Charter being granted by Dabíd mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crofters Commission
The Crofting Commission () took the place of the Crofters Commission () on 1 April 2012 as the statutory regulator for crofting in Scotland. Based in Inverness, it is an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government. The Commission comprises six Crofting Commissioners elected from geographic areas in the crofting counties, and three Commissioners appointed by the Scottish Government. The Convener is appointed from among Commission members. The Commission is supported by around 60 staff led by a Chief Executive. The vision of the Commission is to be guiding regulatorthat uses its powers to support thcrofting system Its purpose is to regulate the crofting system fairly and reasonably to protect it for future generations Future generations are Cohort (statistics), cohorts of hypothetical people not yet born. Future generations are contrasted with current and past generations and evoked in order to encourage thinking about intergenerational equity. The Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49 & 50 Vict
49 may refer to: * 49 (number) * "Forty Nine", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''V (Karma to Burn album), V'', 2011 * one of the years 49 BC, AD 49, 1949, 2049 * 49 Pales, a main-belt asteroid * Tatra 49, a three-wheeled motor vehicle {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crofters Holdings (Scotland) Act 1886
The Crofters Holdings (Scotland) Act 1886 ( 49 & 50 Vict. c. 29) () is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that created legal definitions of ''crofting parish'' and ''crofter'', granted security of land tenure to crofters and produced the first Crofters Commission, a land court which ruled on disputes between landlords and crofters. The same court ruled on whether parishes were or were not crofting parishes. In many respects the Act was modelled on the Irish Land Acts of 1870 and 1881. By granting the crofters security of tenure, the Act put an end to the Highland Clearances. The Act was largely a result of crofters' agitation which had become well organised and very persistent in Skye and of growing support, throughout the Highlands, for the Crofters Party, which had gained five members of parliament in the general election of 1885. Agitation took the form of rent strikes (withholding rent payments) and land raids (occupying land which the landlord had reserved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |