|
Web Services Invocation Framework
The Web Services Invocation Framework (WSIF) supports a simple and flexible Java API (Application Programming Interface) for invoking any Web Services Description Language (WSDL)-described service. Using WSIF, WSDL can become the centerpiece of an integration framework for accessing software running on diverse platforms which use different protocols. The software needs to be described using WSDL and have a binding included in its description ,that the client's WSIF framework has a provider for. WSIF defines and comes packaged with providers for local Java, Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB), Java Message Service (JMS), and Java EE Connector Architecture (JCA) protocols, which means that a client can define an EJB or a Java Message Service-accessible service directly as a WSDL binding and access it transparently using WSIF, using the same API one would use for a SOAP service or a local Java class. Structure In WSDL, a binding defines how to map between the abstract ''PortType'' and a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache Software Foundation
The Apache Software Foundation ( ; ASF) is an American nonprofit corporation (classified as a 501(c)(3) organization in the United States) to support a number of open-source software projects. The ASF was formed from a group of developers of the Apache HTTP Server, and incorporated on March 25, 1999. it includes approximately 1000 members. The Apache Software Foundation is a decentralized open source community of developers. The software they produce is distributed under the terms of the Apache License, a permissive open-source license for free and open-source software (FOSS). The Apache projects are characterized by a collaborative, consensus-based development process and an open and pragmatic software license, which is to say that it allows developers, who receive the software freely, to redistribute it under non-free terms. Each project is managed by a self-selected team of technical experts who are active contributors to the project. The ASF is a meritocracy, implying tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOAP
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, emulsifiers, and catalysts. Soaps are often produced by mixing fats and oils with a Base (chemistry), base. Humans have used soap for millennia; evidence exists for the production of soap-like materials in ancient Babylon around 2800 BC. Types Toilet soaps In a domestic setting, "soap" usually refers to what is technically called a toilet soap, used for household and personal cleaning. Toilet soaps are salts of fatty acids with the general formula (Carboxylate ion, RCO2−)M+, where M is Sodium, Na (sodium) or Potassium, K (potassium). When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache XML
Apache XML is a category of projects at the Apache Software Foundation that focus on XML-related projects. Active projects * Xerces: An XML parser for Java, C++ and Perl *Xalan: An XSLT stylesheet processor for Java and C++ which implements the XPath query language. *Forrest: A standards-based documentation framework *XML-Security: A project providing security functionality for XML data *Xindice: A native XML database *XML Commons: A project focusing on common code and guidelines for XML projects *XMLBeans: An XML-Java binding tool Projects related to webservices *SOAP: Is an old implementation of the SOAP. This project based on IBM's SOAP4J implementation. It should no longer be used for new projects. Instead you should favour the Axis implementation. *XML-RPC: Apache XML-RPC is a Java implementation of XML-RPC, a protocol that uses XML over HTTP to implement remote procedure calls. *Axis: Apache Axis is the current implementation of the SOAP for Java and C++. It is the suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WSIF
WSIF (90.9 FM) is a radio station with an Album Adult Alternative/ Americana format, rebroadcasting the programming of station WNCW. It is owned and operated by Isothermal Community College in Spindale, North Carolina, which took over the station on January 5, 2010.Monte Mitchell, "Station gains Wilkes listeners," ''Winston-Salem Journal'', January 6, 2010. Previously, the station was owned and operated by Wilkes Community College, Wilkesboro, North Carolina. According to FCC filings in May 2008, the school decided to end its broadcasting program, and requested permission to remain silent while the license was transferred to another educational institution. At the expiration of the six month "Stay Silent" authorization in November 2008, the College asked for an extension of the order to finalize the details of the transfer to an unspecified community college. In 2009, Isothermal Community College acquired the license of WSIF, Wilkesboro, North Carolina, formerly operated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Message Queue
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter- thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content. Group communication systems provide similar kinds of functionality. The message queue paradigm is a sibling of the publisher/subscriber pattern, and is typically one part of a larger message-oriented middleware system. Most messaging systems support both the publisher/subscriber and message queue models in their API, e.g. Java Message Service (JMS). Competing Consumers pattern enables multiple concurrent consumers to process messages on the same message queue. Remit and ownership Message queues implement an asynchronous communication pattern between two or more processes/threads whereby the sending and receiving party do not need to interact with the message queue at the same time. Messages placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise JavaBean
Jakarta Enterprise Beans (EJB; formerly Enterprise JavaBeans) is one of several List of Java APIs, Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software. EJB is a server-side component (software), software component that Encapsulation (object-oriented programming), encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java Servlet#Life cycle of a servlet, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services. The EJB specification is a subset of the Jakarta EE specification. Specification The EJB specification was originally developed in 1997 by International Business Machines, IBM and later adopted by Sun Microsystems (EJB 1.0 and 1.1) in 1999 and enhanced under the Java Community Process aJSR 19(EJB 2.0)JSR 153(EJB 2.1)JSR 220(EJB 3.0)JSR 318(EJB 3.1) anJSR 345(EJB 3.2). The EJB specification provides a standard way to implement the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
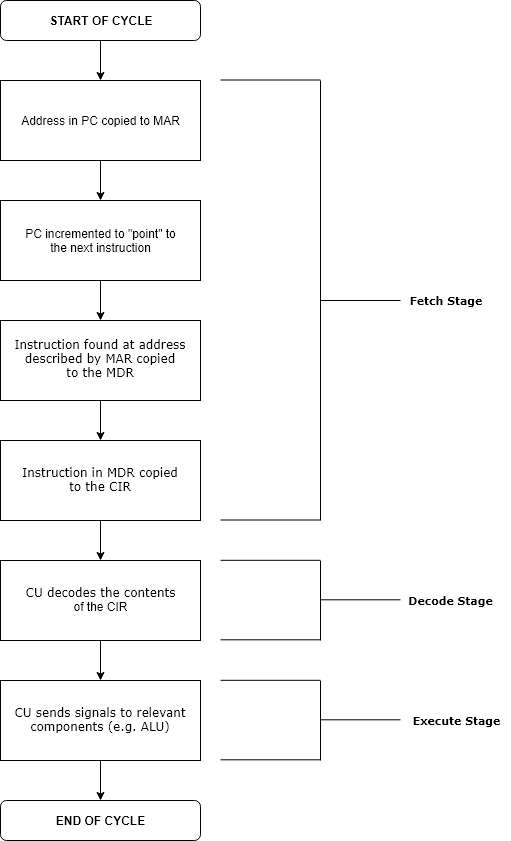
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Inter-ORB Protocol
In distributed computing, General Inter-ORB Protocol (GIOP) is the message protocol by which object request brokers (ORBs) communicate in CORBA. Standards associated with the protocol are maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG). The current version of GIOP is 2.0.2. The GIOP architecture provides several concrete protocols, including: # Internet InterORB Protocol (IIOP) — The Internet Inter-Orb Protocol is an implementation of the GIOP for use over the Internet, and provides a mapping between GIOP messages and the TCP/IP layer. # SSL InterORB Protocol (SSLIOP) — SSLIOP is IIOP over SSL, providing encryption and authentication. # HyperText InterORB Protocol (HTIOP) — HTIOP is IIOP over HTTP HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, wher ..., providing tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Message Service
The Jakarta Messaging API (formerly Java Message Service or JMS API) is a Java application programming interface (API) for message-oriented middleware. It provides generic messaging models, able to handle the producer–consumer problem, that can be used to facilitate the sending and receiving of messages between software systems. Jakarta Messaging is a part of Jakarta EE and was originally defined by a specification developed at Sun Microsystems before being guided by the Java Community Process. General idea of messaging Messaging is a form of '' loosely coupled'' distributed communication, where in this context the term 'communication' can be understood as an exchange of messages between software components. Message-oriented technologies attempt to relax ''tightly coupled'' communication (such as TCP network sockets, CORBA or RMI) by the introduction of an intermediary component. This approach allows software components to communicate with each other indirectly. Benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java EE Connector Architecture
Jakarta Connectors (JCA; formerly known as Java EE Connector Architecture and J2EE Connector Architecture) are a set of Java programming language tools designed for connecting application servers and enterprise information systems (EIS) as a part of enterprise application integration (EAI). While JDBC is specifically used to establish connections between Java applications and databases, JCA provides a more versatile architecture for connecting to legacy systems. JCA and Java EE JCA was developed through the Java Community Process, with versions including JSR 16 (JCA 1.0), JSR 112 (JCA 1.5), and JSR 322 (JCA 1.6). J2EE Version 1.3 requires application servers to support JCA Version 1.0. J2EE Version 1.4 requires application servers to support JCA Version 1.5. Java EE Version 6 requires application servers to support JCA version 1.6. Contracts The Jakarta Connector Architecture defines a standard for connecting a compliant application server to an EIS. It defines a standard set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise JavaBeans
Jakarta Enterprise Beans (EJB; formerly Enterprise JavaBeans) is one of several Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software. EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services. The EJB specification is a subset of the Jakarta EE specification. Specification The EJB specification was originally developed in 1997 by IBM and later adopted by Sun Microsystems (EJB 1.0 and 1.1) in 1999 and enhanced under the Java Community Process aJSR 19(EJB 2.0)JSR 153(EJB 2.1)JSR 220(EJB 3.0)JSR 318(EJB 3.1) anJSR 345(EJB 3.2). The EJB specification provides a standard way to implement the server-side (also called " back-end") 'business' software typically found in enterprise applications (as opposed to 'front-end' user interface software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |