|
Walvis Ridge
The Walvis Ridge (''walvis'' means whale in Dutch and Afrikaans) is an aseismic ocean ridge in the southern Atlantic Ocean. More than in length, it extends from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, near Tristan da Cunha and the Gough Islands, to the African coast (at 18°S in northern Namibia). The Walvis Ridge is one of few examples of a hotspot seamount chain that links a flood basalt province to an active hotspot. It is also considered one of the most important hotspot tracks because the Tristan Hotspot is one of few primary or deep mantle hotspots. Geology Apart from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the Walvis Ridge and the Rio Grande Rise are the most distinctive feature of the South Atlantic sea floor. They originated from hotspot volcanism and together they form a mirrored symmetry across the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, with the Tristan Hotspot at its centre. Two of the distinct sections in the Walvis Ridge have similar mirrored regions in the Rio Grande Rise; for example, the eastern section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
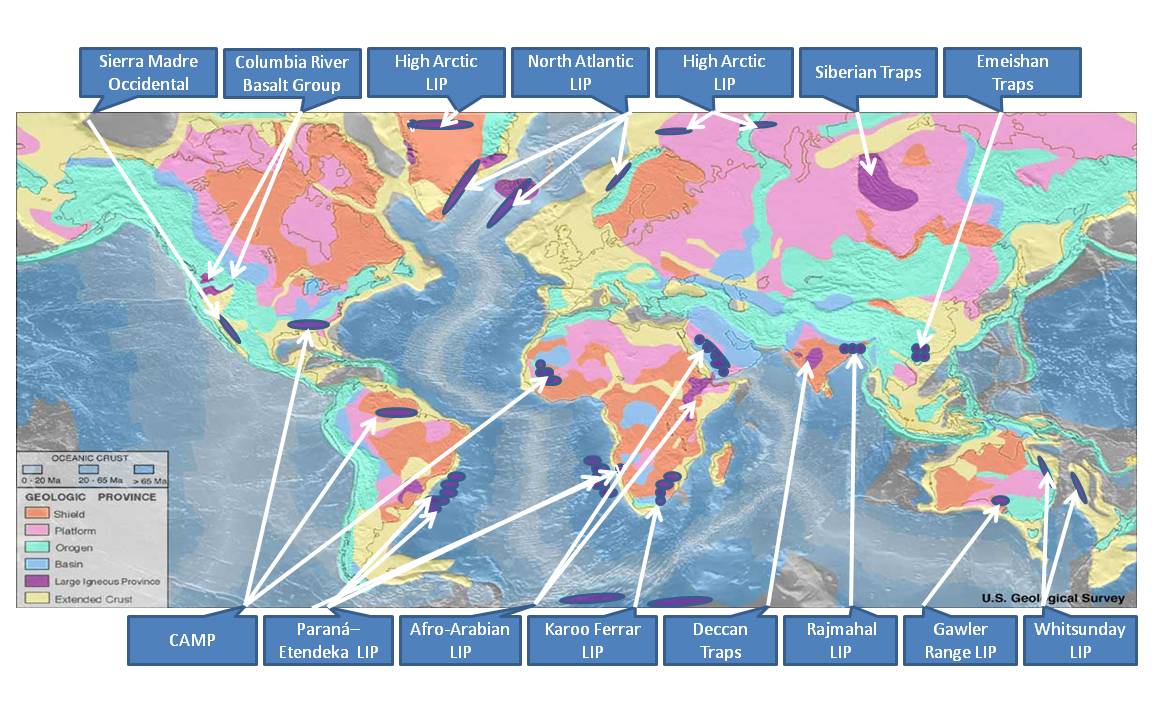
Continental Flood Basalt
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive rock, intrusive (sill (geology), sills, dike (geology), dikes) and extrusive rock, extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust (geology), crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with extinction event, mass extinctions and abrupt climate change, rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Overview Definition In 1992, Coffin and Eldholm initially defined the term "large igneous province" as representing a variety of mafic igneous provinces with areal extent greater than 100,000 km2 that represented "mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Meteorology
Mesoscale meteorology is the study of weather systems and processes at horizontal scales of approximately to several hundred kilometres. It is smaller than synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic-scale systems (1,000 km or larger) but larger than Microscale meteorology, microscale (less than 1 km). At the small end, it includes storm-scale phenomena (the size of an individual thunderstorm). Examples of mesoscale weather systems are sea breezes, squall lines, and mesoscale convective complexes. Vertical velocity often equals or exceeds horizontal velocities in mesoscale meteorological systems due to nonhydrostatic processes such as buoyant acceleration of a rising thermal or acceleration through a narrow mountain pass. Classification The History of weather forecasting, earliest networks of weather observations in the late 1800s and early 1900s could detect the movement and evolution of larger, synoptic scale, synoptic-scale systems like high pressure area, high and low-pressure area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Clay
Ultisol, commonly known as red clay soil, is one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continuous weathering of minerals in a humid, temperate climate without new soil formation via glaciation. They are defined as mineral soils which contain no calcareous (calcium carbonate containing) material anywhere within the soil, have less than 10% weatherable minerals in the extreme top layer of soil, and have less than 35% base saturation throughout the soil. Ultisols occur in humid temperate or tropical regions. While the term is usually applied to the red clay soils of the Southern United States, Ultisols are also found in regions of Africa, Asia, Australia and South America. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), most Ultisols are known as Acrisols and Alisols. Some belong to the Retisols or to the Nitisols. Aquults are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Thermal Maximum 2
Eocene Thermal Maximum 2 (ETM-2), also called H-1 or Elmo (Eocene Layer of Mysterious Origin), was a transient period of global warming that occurred around 54 Ma. It was the second major hyperthermal that punctuated long-term warming from the Late Paleocene through the Early Eocene (58 to 50 Ma). Timing ETM-2 occurred exactly 4.5 long eccentricity cycles after the PETM. ETM-2 is clearly recognized in sediment sequences by analyzing the stable carbon isotope composition of carbon-bearing material. The 13C/ 12C ratio of calcium carbonate or organic matter drops significantly across the event. This is similar to what happens when one examines sediment across the PETM, although the magnitude of the negative carbon isotope excursion is not as large during ETM-2. The timing of Earth system perturbations during ETM-2 and PETM also appear different. Specifically, the onset of ETM-2 may have been longer (perhaps 30,000 years) while the recovery seems to have been shorter (perhaps <50,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewing Seamount
The Ewing Seamount is a seamount in the southern Atlantic Ocean, which lies on the Tropic of Capricorn.National Geographic Atlas of the World: Revised Sixth Edition, National Geographic Society The National Geographic Society, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest nonprofit scientific and educational organizations in the world. Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, natural sc ..., 1992 Ewing is part of the Walvis Ridge having a mean depth of 4,500 metres and a summit depth of 700 metres. References Seamounts of the Atlantic Ocean {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (stratigraphy), Series, the Cretaceous geologic period, Period or system (stratigraphy), System, and of the Mesozoic geologic era, Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). It is named after the city of Maastricht, the capital and largest city of the Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg province in the Netherlands. The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary period, Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this extinction event, mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |