|
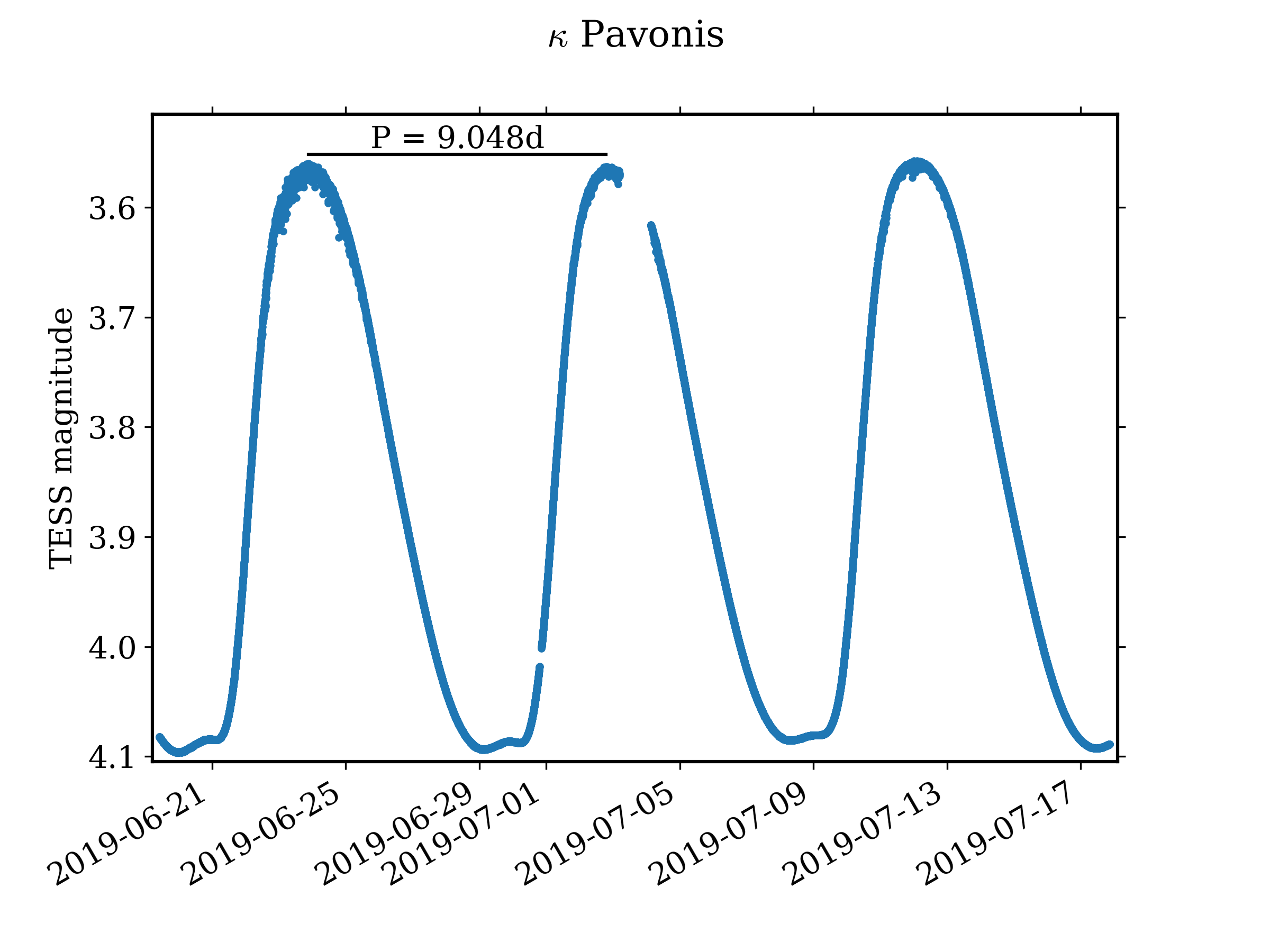
W Virginis
W Virginis is the prototype W Virginis variable, a subclass of the Cepheid variable stars. It is located in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo, and varies between magnitudes 9.46 and 10.75 over a period of approximately 17 days. There are variations in the light curve apparently due to multiple pulsation periods rather than inherent instabilities in the pulsation. The dominant pulsation mode has a period of 17.27134 days with a period decrease detected over a 75-year period. The pulsations cause changes in both temperature and size, leading to large changes in the luminosity and brightness. The maximum temperature occurs when the star is at its brightest visually, when the star is also at its smallest. The minimum temperature and maximum radius occur at around phase 0.5 when the brightness is decreasing and nearly at minimum. Because relatively more infrared radiation is produced when the star is cooler, the maximum brightness in the infrared occurs when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheid Variable
A Cepheid variable () is a type of variable star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature. It changes in brightness, with a well-defined stable period (typically 1–100 days) and amplitude. Cepheids are important cosmic benchmarks for scaling galactic and extragalactic distances; a strong direct relationship exists between a Cepheid variable's luminosity and its pulsation period. This characteristic of classical Cepheids was discovered in 1908 by Henrietta Swan Leavitt after studying thousands of variable stars in the Magellanic Clouds. The discovery establishes the ''true luminosity'' of a Cepheid by observing its pulsation period. This in turn gives the distance to the star by comparing its known luminosity to its observed brightness, calibrated by directly observing the parallax distance to the closest Cepheids such as RS Puppis and Polaris. Cepheids change brightness due to the κ–mechanism, which occurs when opacity in a star increases wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparcos Objects
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions and distances of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the luminosity, intrinsic brightnesses, proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting ''Hipparcos Catalogue'', a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision ''Tycho Catalogue'' of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. ''Hipparcos'' follow-up mission, ''Gaia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-type Supergiants
F-type may refer to: *F-type asteroid, a type of carbonaceous asteroid *F-ATPase, a membrane protein *F-type main-sequence star, a hydrogen-fusing star * F-type Prisons, high-security prisons in Turkey * MG F-type Magna, six-cylinder-engined car produced by the MG Car company from October 1931 to 1932 *Jaguar F-Type, a two-seat sports car manufactured by Jaguar Cars * Renault F-Type engine, straight-4 automobile engine from Renault * Empire F type coaster, a type of prefabricated coastal tanker built in the UK during the Second World War *F connector, a commonly used connector for coaxial cable * F type Adelaide tram Type F may refer to: * Type F AC power plugs and sockets *the Avro Type F The Avro Type F was an early single seat British aircraft from Avro. On 1 May 1912 it became the first aircraft in the world to fly with a completely enclosed cabin for the pilot as an integral part of the design. Design and development It wa ..., an aircraft * Type-F couplers in rail tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue Objects
Henry may refer to: People and fictional characters * Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters * Henry (surname) * Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone Arts and entertainment * Henry (2011 film), ''Henry'' (2011 film), a Canadian short film * Henry (2015 film), ''Henry'' (2015 film), a virtual reality film * ''Henry: Portrait of a Serial Killer'', a 1986 American crime film * Henry (comics), ''Henry'' (comics), an American comic strip created in 1932 by Carl Anderson * "Henry", a song by New Riders of the Purple Sage Places Antarctica * Henry Bay, Wilkes Land Australia *Henry River (New South Wales) *Henry River (Western Australia) Canada * Henry Lake (Vancouver Island), British Columbia * Henry Lake (Halifax County), Nova Scotia * Henry Lake (District of Chester), Nova Scotia New Zealand * Lake Henry (New Zealand) * Henry River (New Zealand) United States * Henry, Illinois * Henry, Indiana * Henry, Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W Virginis Variables
W Virginis variables are a subclass of Type II Cepheids which exhibit pulsation periods between 10–20 days, and are of spectral class F6 – K2. They were first recognized as being distinct from classical Cepheids by Walter Baade in 1942, in a study of Cepheids in the Andromeda Galaxy that proposed that stars in that galaxy were of two populations. See also *Low-dimensional chaos in stellar pulsations Stellar pulsations are caused by expansions and contractions in the outer layers as a star seeks to maintain stellar equilibrium, equilibrium. These fluctuations in stellar radius cause corresponding changes in the stellar luminosity, luminosity o ... References External links * AAVSO Variable Star of the Month. W Virginis: Spring 200PDFHTML {{var-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolometric Luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical objects. In SI units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the Sun, ''L''⊙. Luminosity can also be given in terms of the astronomical magnitude system: the absolute bolometric magnitude (''M''bol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate, while absolute magnitude is a logarithmic measure of the luminosity within some specific wavelength range or filter band. In contrast, the term ''brightness'' in astronomy is generally used to refer to an object's apparent brightness: that is, how bright an object appears to an observer. Apparent brightness depen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue
The ''Henry Draper Catalogue'' (HD) is an astronomical star catalogue published between 1918 and 1924, giving spectroscopic classifications for 225,300 stars; it was later expanded by the ''Henry Draper Extension'' (HDE), published between 1925 and 1936, which gave classifications for 46,850 more stars, and by the ''Henry Draper Extension Charts'' (HDEC), published from 1937 to 1949 in the form of charts, which gave classifications for 86,933 more stars. In all, 359,083 stars were classified as of August 2017. The HD catalogue is named after Henry Draper, an amateur astronomer, and covers the entire sky almost completely down to an apparent photographic magnitude of about 9; the extensions added fainter stars in certain areas of the sky. The construction of the ''Henry Draper Catalogue'' was part of a pioneering effort to classify stellar spectra, and its catalogue numbers are commonly used as a way of identifying stars. History The origin of the ''Henry Draper Catalogue'' d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometric System
In astronomy, a photometric system is a set of well-defined passbands (or optical filters), with a known sensitivity to incident radiation. The sensitivity usually depends on the optical system, detectors and filters used. For each photometric system a set of primary standard stars is provided. A commonly adopted standardized photometric system is the Johnson-Morgan or UBV photometric system (1953). At present, there are more than 200 photometric systems. Photometric systems are usually characterized according to the widths of their passbands: * broadband (passbands wider than 30 nm, of which the most widely used is Johnson-Morgan UBV system) * intermediate band (passbands between 10 and 30 nm wide) * narrow band (passbands less than 10 nm wide) Photometric letters Each letter designates a section of light of the electromagnetic spectrum; these cover well the consecutive major groups, near-ultraviolet (NUV), visible light (centered on the V band), near-infra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durchmusterung
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, published by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1863, with an extension published in Bonn in 1886. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for a systematic survey of objects or data. The term has sometimes been used for other astronomical surveys, including not only stars, but also the search for other celestial objects. Special tasks include celestial scanning in electromagnetic wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light waves. Original catalog The Bonner Durchmusterung (abbreviated BD), was initiated by Friedrich Argelander and using observations largely carried out by his assistants, which resulted in a catalogue of the positions and apparent magnitudes of 342,198 stars down to approximate apparent magnitude 9.5 and covering the sky from 90°N to 2°S declination. The catalogue, published in three parts, was accompanied by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog is an astrometric star catalogue, created by Smithsonian Institution, a research institute. It was published by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in 1966 and contains 258,997 stars. The catalogue was compiled from various previous astrometric catalogues, and contains only stars to about ninth magnitude for which accurate proper motions were known. Names in the SAO catalogue start with the letters SAO, followed by a number. The numbers are assigned following 18 ten-degree bands of declination, with stars sorted by right ascension within each band. Online version of the SAO Catalog was created by the HEASARC in March 2001 based on ADC/CDS Catalog I/131A, which itself is originally derived from a character-coded machine-readable version of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog (SAO, SAO Staff 1966) prepared by T.A. Nagy in 1979, and subsequently modified over the next decade or so. Examples of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |