|
WASP-193b
WASP-193b is a hot, transiting gas giant planet located approximately away in the constellation of Hydra, orbiting the F-type star WASP-193. Its discovery was made by the WASP-South transit survey and announced in 2023. The planet is extremely bloated, with a radius nearly 50% larger than Jupiter, despite having only 14% of its mass. This places its density at , the second lowest of any known exoplanet as of May 2024 after Kepler-51d, and comparable to that of cotton candy (about ). Discovery The planet was discovered in July 2023 by a team of astronomers led by Khalid Barkaoui, a researcher at the University of Liège, from observational data taken by WASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) in 2006–2008 and 2011–2012. It is one of hundreds discovered in the WASP mission, which uses transit photometry to find exoplanets, observing the dimming of a star caused by the astronomical transit of planets passing in front of them. The discovery was subsequently confirmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Angle Search For Planets
WASP or Wide Angle Search for Planets is an international consortium of several academic organisations performing an ultra-wide angle search for exoplanets using transit photometry. The array of robotic telescopes aims to Astronomical survey, survey the entire sky, simultaneously monitoring many thousands of stars at an apparent visual magnitude from about 7 to 13. WASP is the detection program composed of the Isaac Newton Group, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, IAC and six universities from the United Kingdom. The two continuously operating, robotic observatories cover the Northern and Southern Hemisphere, respectively. SuperWASP-North is at Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the mountain of that name which dominates La Palma in the Canary Islands. WASP-South is at the South African Astronomical Observatory, Sutherland, South Africa, Sutherland in the arid Roggeveld Mountains of South Africa. These use eight wide-angle cameras that simultaneously monitor the sky for pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
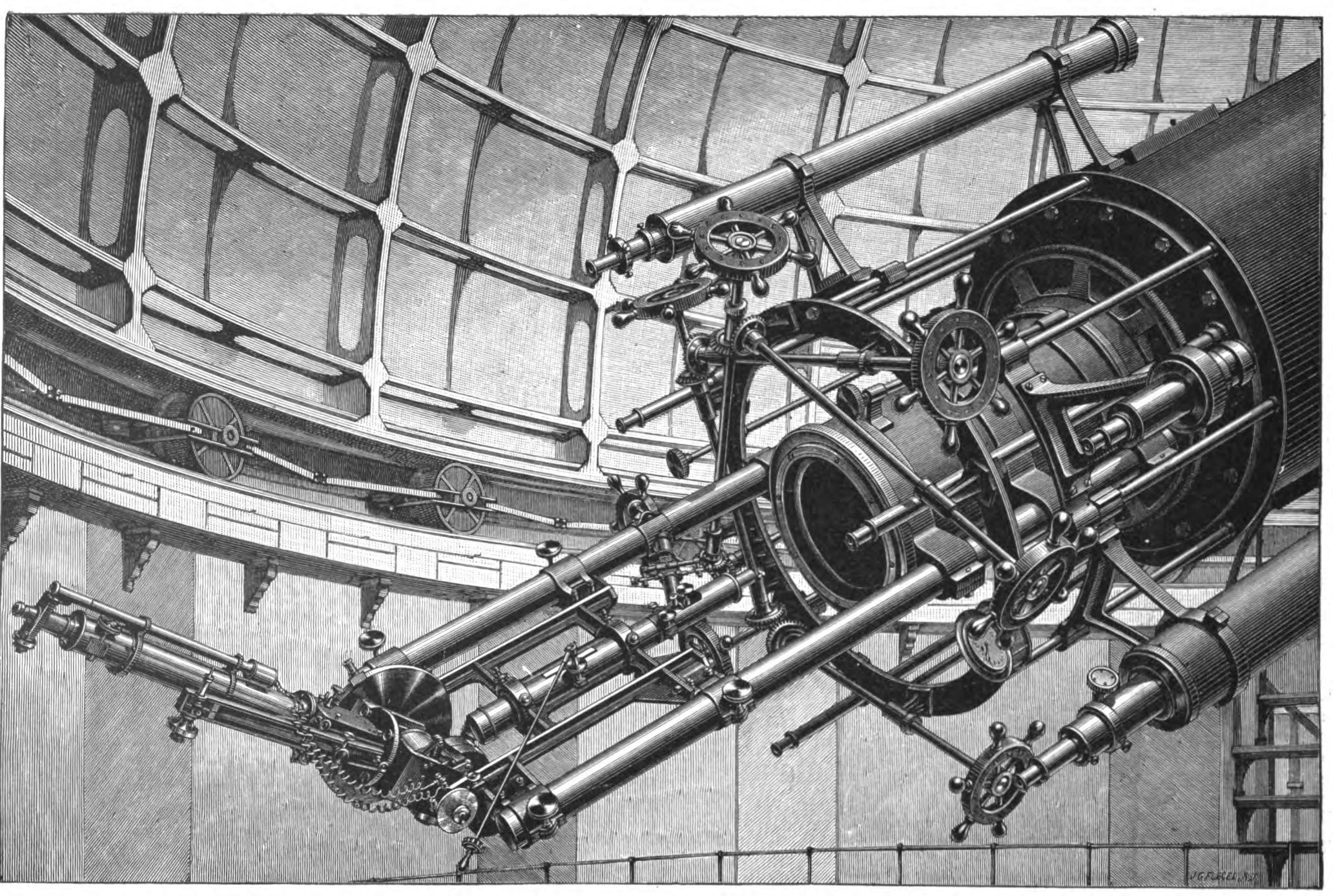
Transit Method
Methods of detecting exoplanets usually rely on indirect strategies – that is, they do not directly image the planet but deduce its existence from another signal. Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the glare from the parent star washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported have been detected directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star. Established detection methods The following methods have proven successful at least once for discovering a new planet or detecting an already discovered planet: Radial velocity A star with a planet will move in its own small orbit in response to the planet's gravity. This leads to variations in the speed with which the star moves toward or away from E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Transit
In astronomy, a transit (or astronomical transit) is the passage of a astronomical object, celestial body directly between a larger body and the observer. As viewed from a particular vantage point, the transiting body appears to move across the face of the larger body, eclipse, covering a small portion of it. The word "transit" refers to cases where the nearer object apparent size, appears smaller than the more distant object. Cases where the nearer object appears larger and completely hides the more distant object are known as occultation, ''occultations''. However, the probability of seeing a transiting planet is low because it is dependent on the alignment of the three objects in a nearly perfectly straight line. Many parameters of a planet and its parent star can be determined based on the transit. In the Solar System One type of transit involves the motion of a planet between a Earth, terrestrial observer and the Sun. This can happen only with inferior and superior pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image of the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that comes to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many structures that limit ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the cone of rays that an optical system accepts (see entrance pupil). As a result, it also determines the ray cone angle and brightne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, astronomical objects. In SI units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the Solar luminosity, luminosity of the Sun, ''L''⊙. Luminosity can also be given in terms of the astronomical Magnitude (astronomy), magnitude system: the Absolute magnitude#Bolometric magnitude, absolute bolometric magnitude (''M''bol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate, while absolute magnitude is a logarithmic measure of the luminosity within some specific wavelength range or Passband, filter band. In contrast, the term ''brightness'' in astronomy is gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-type Main-sequence Star
An F-type main-sequence star (F V) is a main-sequence, hydrogen-fusing star of spectral type F and luminosity class V. These stars have from 1.0 to 1.4 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 6,000 and 7,600 K.Tables VII and VIII. This temperature range gives the F-type stars a whitish hue when observed by the atmosphere. Because a main-sequence star is referred to as a dwarf star, this class of star may also be termed a yellow-white dwarf (not to be confused with white dwarfs, remnant stars that are a possible final stage of stellar evolution). Notable examples include Procyon A, Gamma Virginis A and B, and KIC 8462852. Spectral standard stars The revised Yerkes Atlas system (Johnson & Morgan 1953) listed a dense grid of F-type dwarf spectral standard stars; however, not all of these have survived to this day as stable standards. The ''anchor points'' of the MK spectral classification system among the F-type main-sequence dwarf stars, i.e. thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including Visible light astronomy, visible light, Ultraviolet astronomy, ultraviolet, X-ray astronomy, X-ray, Infrared astronomy, infrared and Radio astronomy, radio waves that radiant energy, radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler effect, Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, Galaxy, galaxies, and Active galactic nucleus, active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Spectroscopy
Doppler spectroscopy (also known as the radial-velocity method, or colloquially, the wobble method) is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in the spectrum of the planet's parent star. As of June 2025, over 1,100 known extrasolar planets (about 19.0% of the total) have been discovered using Doppler spectroscopy. History Otto Struve proposed in 1952 the use of powerful spectrographs to detect distant planets. He described how a very large planet, as large as Jupiter, for example, would cause its parent star to wobble slightly as the two objects orbit around their center of mass. He predicted that the small Doppler shifts to the light emitted by the star, caused by its continuously varying radial velocity, would be detectable by the most sensitive spectrographs as tiny redshifts and blueshifts in the star's emission. However, the technology of the time produced radial-veloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force between objects and the Earth. This force is dominated by the combined gravitational interactions of particles but also includes effect of the Earth's rotation. Gravity gives weight to physical objects and is essential to understanding the mechanisms responsible for surface water waves and lunar tides. Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circulation of fluids in multicellular organisms. The gravitational attraction between primordial hydrogen and clumps of dark matter in the early universe caused the hydrogen gas to coalesce, eventually condensing and fusing to form stars. At larger scales this results in galaxies and clust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss 1
Swiss most commonly refers to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland *Swiss people Swiss may also refer to: Places * Swiss, Missouri * Swiss, North Carolina * Swiss, West Virginia * Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses * Swiss Café, an old café located in Baghdad, Iraq * Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports * Swiss International Air Lines **Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary *Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland * .swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also *Swiss made, label for Swiss products *Swiss cheese (other) *Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer Schweitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Albert Schweitzer (1875–1965), German theologian, musician, physician, and medical missionary, winner of the 1952 Nobel Peace Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher
The High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) is a high-precision echelle planet-finding spectrograph installed in 2002 on the ESO's 3.6m telescope at La Silla Observatory in Chile. The first light was achieved in February 2003. HARPS has discovered over 130 exoplanets to date, with the first one in 2004, making it the most successful planet finder behind the Kepler space telescope. It is a second-generation radial-velocity spectrograph, based on experience with the ELODIE and CORALIE instruments. Characteristics The HARPS can attain a precision of 0.97 m/s (3.5 km/h), making it one of only two instruments worldwide with such accuracy. This is due to a design in which the target star and a reference spectrum from a thorium lamp are observed simultaneously using two identical optic fibre feeds, and to careful attention to mechanical stability: the instrument sits in a vacuum vessel which is temperature-controlled to within 0.01 kelvins. The precision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |