|
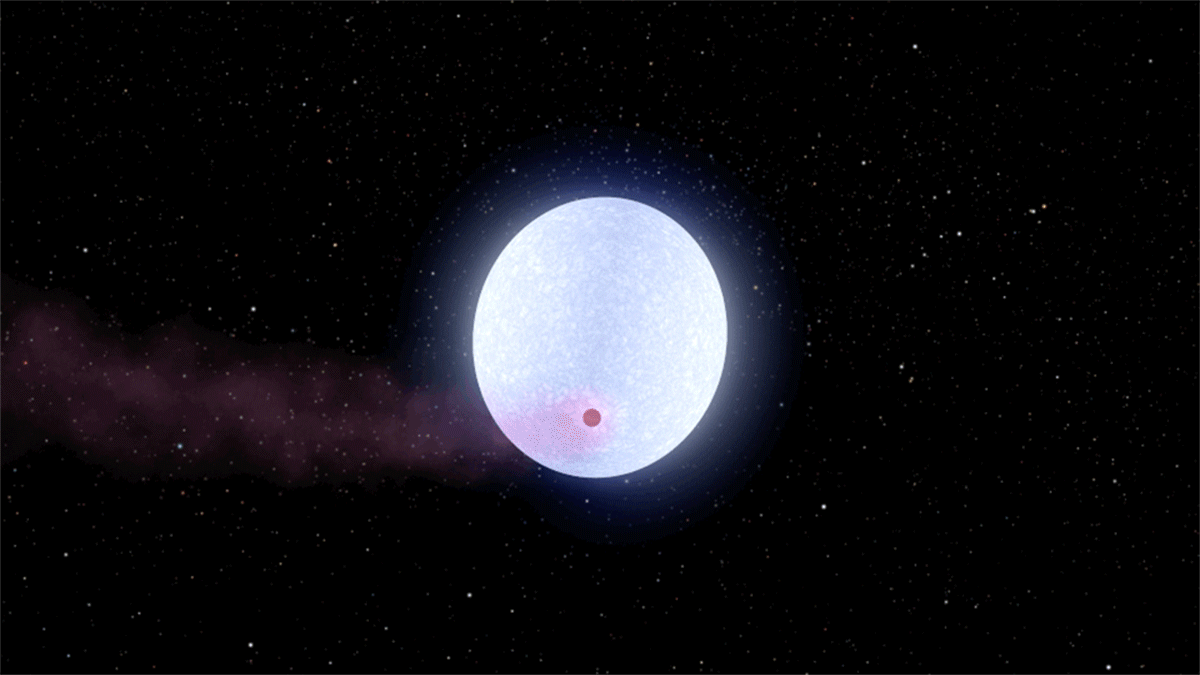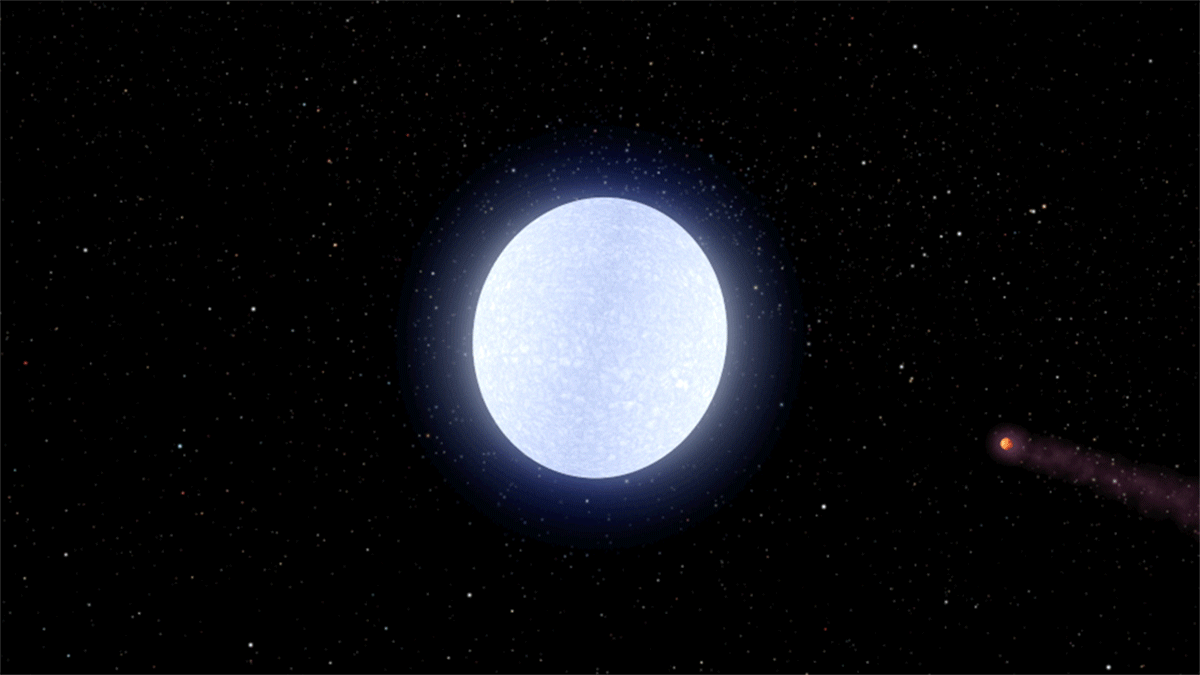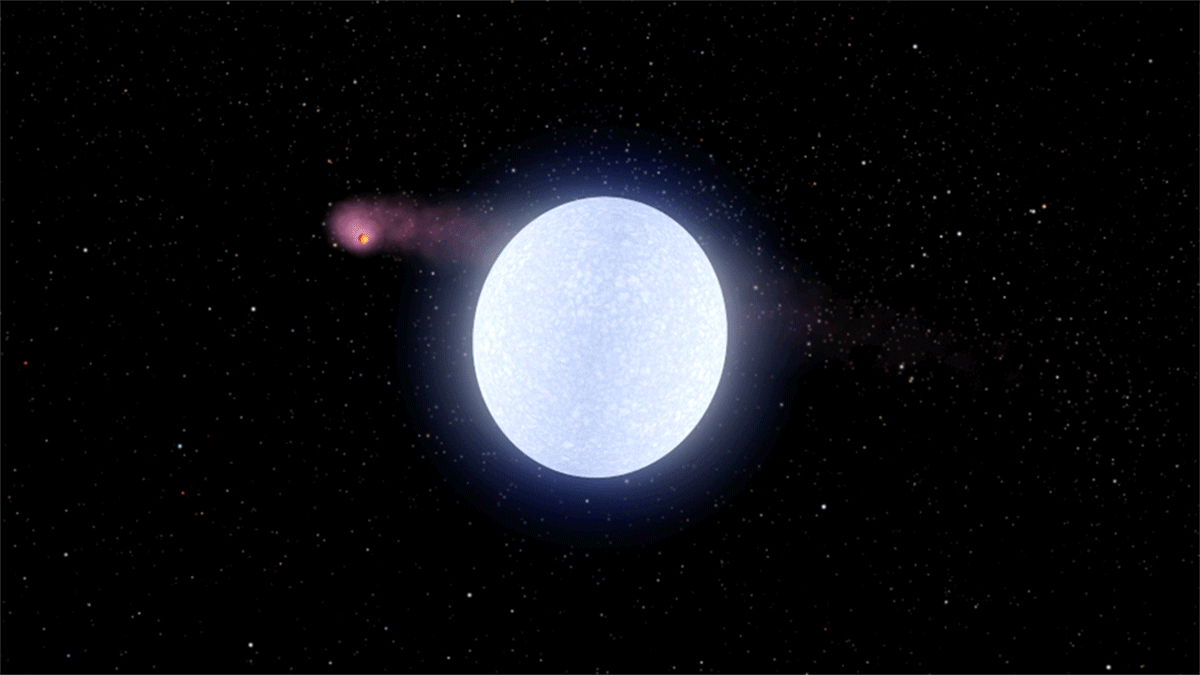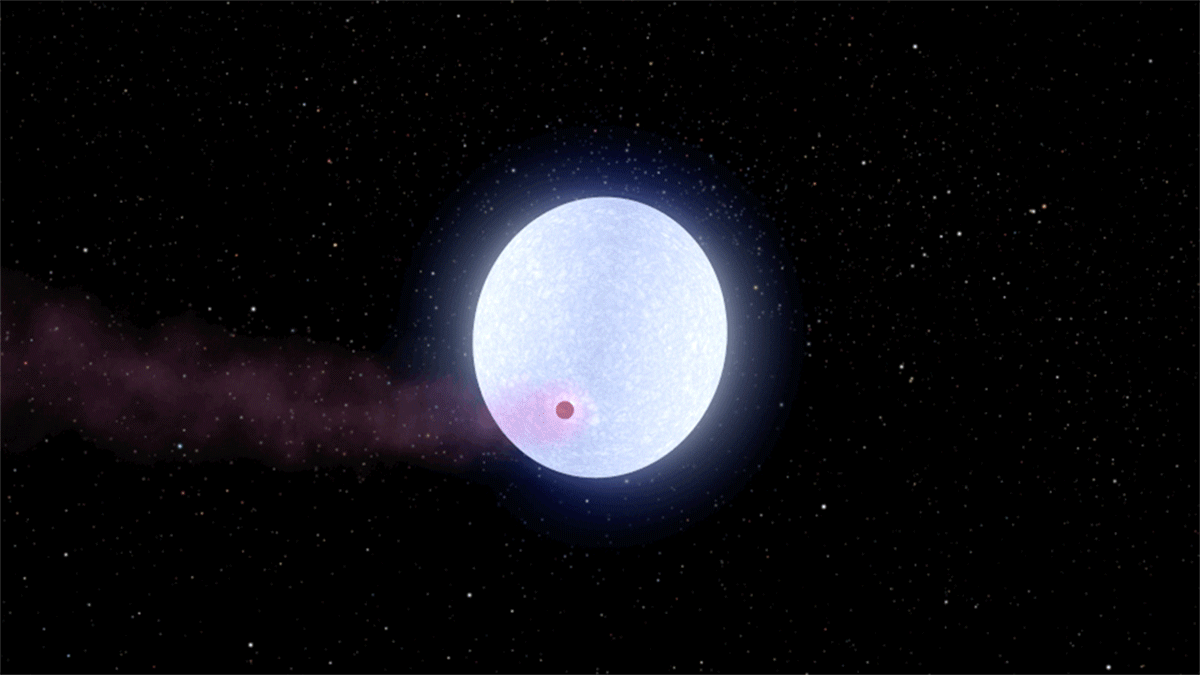
WASP-178
WASP-178, also known as KELT-26 and HD 134004, is a star located about away in the Southern celestial hemisphere, southern constellation of Lupus (constellation), Lupus. It is a hot A-type main sequence star or subgiant, a likely Am star, and a possible Delta Scuti variable, about twice as massive as the Sun and twenty times as luminous. In late 2019, the star was discovered to be orbited by an ultra-hot Jupiter planet, WASP-178b, making it one of the hottest stars known to host a hot Jupiter. Physical properties WASP-178 has a spectral type of A1IV-V, indicating that it is in an stellar evolution, evolutionary stage between a main sequence star and a subgiant. The star is comparable to Sirius, Sirius A in mass and radius, but slightly cooler, older, and less luminous. It is about twice as massive as the Sun and has a radius of 1.67 or 1.80 , with an effective temperature of roughly 9,000 Kelvin (unit), K. A 2019 estimate of makes WASP-178 the second-hottest host to a hot J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WASP-178b
WASP-178b, also known as KELT-26b and HD 134004 b, is an ultra-hot Jupiter exoplanet discovered in 2019 orbiting WASP-178, a hot Stellar classification#Class A, A-type star located about away in the constellation of Lupus (constellation), Lupus. At over 1.8 times the radius of Jupiter, it is among the List of largest exoplanets, largest exoplanets. The planet is Tidal locking, tidally locked, heating up one side of the planet to such a degree that silicate rock and metal evaporate. Supersonic speed, Supersonic winds blow constantly towards the dark, cooler nighttime side, where the vaporized minerals condense and fall as rain. Discovery and nomenclature The planet was discovered by a team of astronomers led by Coel Hellier, who published their findings in November 2019, alongside the detection of three other planets, designated WASP-184b, WASP-185b, and WASP-192b. The four planets were all found through photometry (astronomy), photometric analysis of astronomical transit data c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope
The Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope (or KELT) is an astronomical observation system formed by two robotic telescopes that are conducting a survey for transiting exoplanets around bright stars. The project is jointly administered by members of Ohio State University Department of Astronomy, the Vanderbilt University Department of Physics and Astronomy Astronomy Group, the Lehigh University Department of Physics, and the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO). KELT Telescopes KELT consists of two telescopes, KELT-North in Arizona in the United States, and KELT-South at the SAAO observing station near Sutherland, South Africa. Each KELT telescope consists of a wide field (26 degrees by 26 degrees) medium format telephoto lens with a 4.2 cm aperture, mounted in front of a 4k x 4k Apogee CCD. Each can also be equipped with an alternative narrower field (10.8 degrees by 10.8 degrees) lens with a 7.1 cm aperture for a narrow angle campaign mode. KELT-N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus (constellation)
Lupus is a constellation of the mid-Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for wolf. Lupus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations but was long an asterism associated with the just westerly, larger constellation Centaurus. History and mythology In ancient times, the constellation was considered an asterism within Centaurus, and was considered to have been an arbitrary animal, killed, or about to be killed, on behalf of, or for, Centaurus. An alternative visualization, attested by Eratosthenes, saw this constellation as a wineskin held by Centaurus. It was not separated from Centaurus until Hipparchus of Bithynia named it ( meaning "beast") in the 2nd century BC. The Greek constellation is probably based on the Babylonian figure known as the Mad Dog (UR.IDIM). This was a strange hybrid creature that combined the head and torso of a man with the legs and tail of a lion (the cuneiform sign 'UR' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KELT-9
KELT-9b is an exoplanet—more specifically, an ultra-hot Jupiter—that orbits the late B-type/early A-type star KELT-9, located about 670 light-years from Earth. Detected using the Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope, the discovery of KELT-9b was announced in 2016. , it is the hottest known exoplanet. Host star The star is 2-3 times bigger and 2–5 times more massive than the sun. The surface temperature of the host star, KELT-9, is 10,170 K, unusually hot for a star with a transiting planet. Prior to the discovery of KELT-9b, only six A-type stars were known to have planets, of which the warmest, WASP-33, is significantly cooler at 7,430 K; no B-type stars were previously known to host planets. KELT-9, classified as B9.5-A0 could be the first B-type star known to have a planet. KELT-9b occupies a circular but strongly inclined orbit a mere 0.03462 AU from KELT-9 with an orbital period of less than 1.5 days. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures. The diagram was created independently in 1911 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and by Henry Norris Russell in 1913, and represented a major step towards an understanding of stellar evolution. Historical background In the nineteenth century large-scale photographic spectroscopic surveys of stars were performed at Harvard College Observatory, producing spectral classifications for tens of thousands of stars, culminating ultimately in the Henry Draper Catalogue. In one segment of this work Antonia Maury included divisions of the stars by the width of their spectral lines. Hertzsprung noted that stars described with narrow lines tended to have smaller proper motions than the others of the same spectral classification. He took this as an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instability Strip
The unqualified term instability strip usually refers to a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram largely occupied by several related classes of pulsating variable stars: Delta Scuti variables, SX Phoenicis variables, and rapidly oscillating Ap stars (roAps) near the main sequence; RR Lyrae variables where it intersects the horizontal branch; and the Cepheid variables where it crosses the supergiants. RV Tauri variables are also often considered to lie on the instability strip, occupying the area to the right of the brighter Cepheids (at lower temperatures), since their stellar pulsations are attributed to the same mechanism. Position on the HR diagram The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram plots the real luminosity of stars against their effective temperature (their color, given by the temperature of their photosphere). The instability strip intersects the main sequence, (the prominent diagonal band that runs from the upper left to the lower right) in the region of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (astronomy)
In astronomy, magnitude is a unitless measure of the brightness of an object in a defined passband, often in the visible or infrared spectrum, but sometimes across all wavelengths. An imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by Hipparchus. The scale is logarithmic and defined such that a magnitude 1 star is exactly 100 times brighter than a magnitude 6 star. Thus each step of one magnitude is \sqrt \approx 2.512 times brighter than the magnitude 1 higher. The brighter an object appears, the lower the value of its magnitude, with the brightest objects reaching negative values. Astronomers use two different definitions of magnitude: apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The ''apparent'' magnitude () is the brightness of an object as it appears in the night sky from Earth. Apparent magnitude depends on an object's intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and the extinction reducing its brightness. The ''absolute'' magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in 1879 by spectral analysis of the minerals euxenite and gadolinite from Scandinavia. Scandium is present in most of the deposits of rare-earth and uranium compounds, but it is extracted from these ores in only a few mines worldwide. Because of the low availability and difficulties in the preparation of metallic scandium, which was first done in 1937, applications for scandium were not developed until the 1970s, when the positive effects of scandium on aluminium alloys were discovered, and its use in such alloys remains its only major application. The global trade of scandium oxide is 15–20 tonnes per year. The properties of scandium compounds are intermediate between those of aluminium and yttrium. A diagonal relationship exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element. The most common minerals of barium are baryte (barium sulfate, BaSO4) and witherite ( barium carbonate, BaCO3). The name ''barium'' originates from the alchemical derivative "baryta", from Greek (), meaning 'heavy'. ''Baric'' is the adjectival form of barium. Barium was identified as a new element in 1774, but not reduced to a metal until 1808 with the advent of electrolysis. Barium has few industrial applications. Historically, it was used as a getter for vacuum tubes and in oxide form as the emissive coating on indirectly heated cathodes. It is a component of YBCO ( high-temperature superconductors) and electroceramics, and is added to steel and cast iron to reduce the size of carbon grains within the microstructure. Barium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a " rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals, and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope, and the only isotope found in the Earth's crust. The most important uses of yttrium are LEDs and phosphors, particularly the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Yttrium has no known biological role. Exposure to yttrium compounds can cause lung disease in humans. The element is named after ''ytterbite'', a mineral first identified in 1787 by the chemist Carl Axel Arrheni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |