|
Vladimir Jochelson
Vladimir Ilyich Jochelson (russian: Владимир Ильич Иохельсон) (January 14 ( N.S. January 26), 1855, Vilnius - November 2, 1937, New York City) was a Russian ethnographer and researcher of the indigenous peoples of the Russian North. Biography Jochelson came from a wealthy, religious Jewish family. He attended the Vilna Rabbinical Seminary, where he participated in the socialist, revolutionary group Narodnaya Volya. Compelled to leave Russia in 1875, he went first to Berlin and then in 1879 to Switzerland, where he remained four years, studying at Zurich and then teaching at a school on the Lake of Geneva, while keeping in touch with the revolutionary movement as editor of the ''Vyestnik Narodnoi Voli'', which had a clandestine circulation in Russia. On his return to Russia in 1884 he was recognised, arrested and confined for three years in the Petro-Pavlovsk fortress in St. Petersburg, and in 1887 was sentenced by order of the czar to exile for ten years i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Iochel'son
Vladimir may refer to: Names * Vladimir (name) for the Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Macedonian, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak and Slovenian spellings of a Slavic name * Uladzimir for the Belarusian version of the name * Volodymyr for the Ukrainian version of the name * Włodzimierz (given name) for the Polish version of the name * Valdemar for the Germanic version of the name * Wladimir for an alternative spelling of the name Places * Vladimir, Russia, a city in Russia * Vladimir Oblast, a federal subject of Russia * Vladimir-Suzdal, a medieval principality * Vladimir, Ulcinj, a village in Ulcinj Municipality, Montenegro * Vladimir, Gorj, a commune in Gorj County, Romania * Vladimir, a village in Goiești Commune, Dolj County, Romania * Vladimir (river), a tributary of the Gilort in Gorj County, Romania * Volodymyr (city), a city in Ukraine Religious leaders * Metropolitan Vladimir (other), multiple * Jovan Vladimir (d. 1016), ruler of Doclea and a saint of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
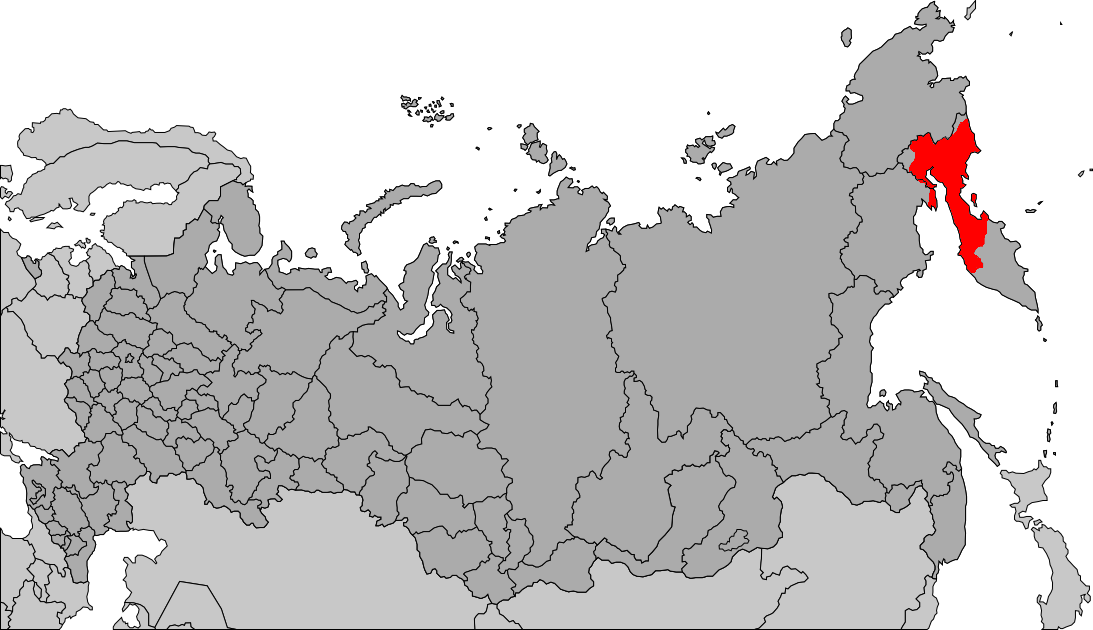
Yukaghirs
The Yukaghirs, or Yukagirs ( (), russian: юкаги́ры) are a Siberian ethnic group people in the Russian Far East, living in the basin of the Kolyma River. Geographic distribution The Tundra Yukaghirs live in the Lower Kolyma region in the Sakha Republic; the Taiga Yukaghirs in the Upper Kolyma region in the Sakha Republic and in Srednekansky District of Magadan Oblast. By the time of Russian colonization in the 17th century, the Yukaghir tribal groups occupied territories from the Lena River to the mouth of the Anadyr River. The number of the Yukaghirs decreased between the 17th and 19th centuries due to epidemics, internecine wars and Tsarist colonial policy which may have included genocide against the sedentary hunter-fisher Anaouls. Some of the Yukaghirs have assimilated with the Yakuts, Evens, and Russians. Currently, Yukaghirs live in the Sakha Republic and the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug of the Russian Federation. According to the 2002 Census, their total number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million.Eric Isaacs is president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and now feature his surname. They perform work involving topics as diverse as art, education, international affairs, world peace, and scientific research. In 2007, the Carnegie Institution of Washington adopted the public name "Carnegie Institution for Science" to distinguish itself from other organizations established by and named for Andrew Carnegie. The Institution remains officially and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the Academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the Academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the Academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The Academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great Museum Of Anthropology And Ethnography
The Kunstkamera (russian: Кунсткамера) or Kunstkammer (German for "Culture Room" (literally) or "Art Chamber", typically used for a " cabinet of curiosities") is a public museum located on the Universitetskaya Embankment in Saint Petersburg, facing the Winter Palace. Its collection was first opened to the public at the Summer Palace by Peter the Great in 1714, making it Russia's first museum. Enlarged by purchases from the Dutch collectors Albertus Seba and Frederik Ruysch, the museum was moved to its present location in 1727. Having expanded to nearly 2,000,000 items, it is formally organized as the Russian Academy of Science's Peter the Great Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography (russian: Музей антропологии и этнографии имени Петра Великого Российской академии наук, ''Muzey antropologii i etnografii imeni Petra Velikogo Rossiyskoy akademii nauk''), abbreviated in Russian as the or . History As p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude ( Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( Semisopochnoi Island). The westernmost U.S. islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and the Karaginsky Island, constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, although about 13,000 are Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for spade.) The circular bay to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakha People
The Yakuts, or the Sakha ( sah, саха, ; , ), are a Turkic ethnic group who mainly live in the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation, with some extending to the Amur, Magadan, Sakhalin regions, and the Taymyr and Evenk Districts of the Krasnoyarsk region. The Yakut language belongs to the Siberian branch of the Turkic languages. The Russian word was taken from Evenk . The Yakuts call themselves , or (Yakut: Уран Саха, ''Uran Sakha'') in some old chronicles. Origin Early scholarship An early work on the Yakut ethnogenesis was drafted by the Russian Collegiate Assessors I. Evers and S. Gornovsky in the late 18th century. At an unspecified time in the past certain tribes resided around the western shore of the Aral Sea. These peoples later migrated eastward and settled near the Tunka Goltsy mountains of modern Buryatia. Pressure from the expansionist Mongolian Empire later made many of those around the Tunka Goltsy relocate to the Lena River. Several a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koryaks
Koryaks () are an indigenous people of the Russian Far East, who live immediately north of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Kamchatka Krai and inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea. The cultural borders of the Koryaks include Tigilsk in the south and the Anadyr basin in the north. The Koryaks are culturally similar to the Chukchis of extreme northeast Siberia. The Koryak language and Alutor (which is often regarded as a dialect of Koryak), are linguistically close to the Chukchi language. All of these languages are members of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. They are more distantly related to the Itelmens on the Kamchatka Peninsula. All of these peoples and other, unrelated minorities in and around Kamchatka are known collectively as Kamchadals. Neighbors of the Koryaks include the Evens to the west, the Alutor to the south (on the isthmus of Kamchatka Peninsula), the Kerek to the east, and the Chukchi to the northeast. The Koryak are typically split into two gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Imperial Academy Of Science
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the Academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the Academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the Academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The Academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
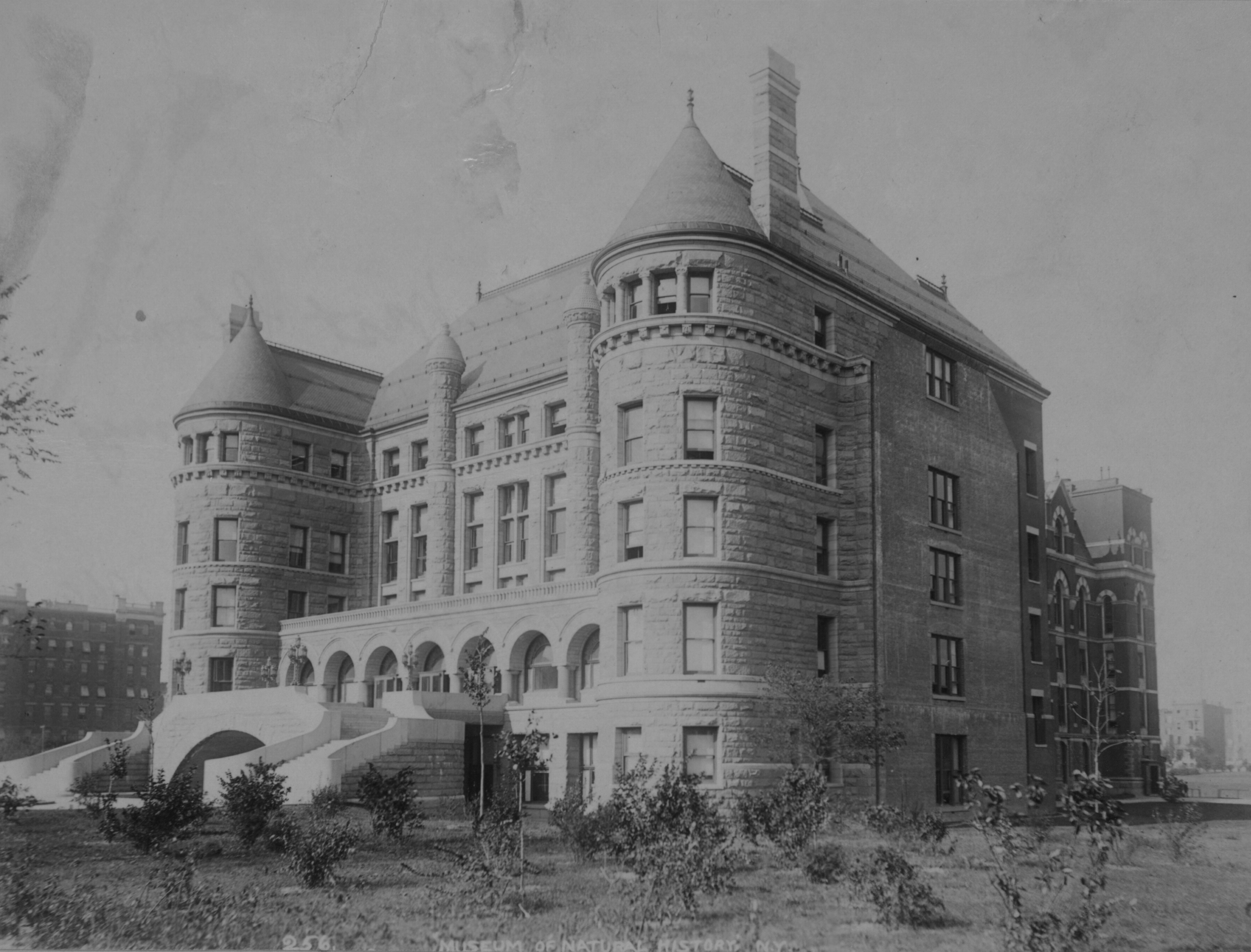
American Museum Of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 interconnected buildings housing 45 permanent exhibition halls, in addition to a planetarium and a library. The museum collections contain over 34 million specimens of plants, animals, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, of which only a small fraction can be displayed at any given time. The museum occupies more than . AMNH has a full-time scientific staff of 225, sponsors over 120 special field expeditions each year, and averages about five million visits annually. The AMNH is a private 501(c)(3) organization. Its mission statement is: "To discover, interpret, and disseminate—through scientific research and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesup North Pacific Expedition
The Jesup North Pacific Expedition (1897–1902) was a major anthropological expedition to Siberia, Alaska, and the northwest coast of Canada. The purpose of the expedition was to investigate the relationships among the peoples at each side of the Bering Strait. The multi-year expedition was sponsored by American industrialist-philanthropist Morris Jesup (who was among other things the president of the American Museum of Natural History). It was planned and directed by the American anthropologist Franz Boas. The participants included a number of significant figures in American and Russian anthropology, as well as Bernard Fillip Jacobsen (brother of Johan Adrian Jacobsen), a Norwegian, who settled in the Northwest coast in 1884 where he collected artifacts as well as the stories of the local indigenous people. Local people of the tribes, such as George Hunt ( Tlingit), served as interpreters and guides. The expedition resulted in the publication of numerous important ethnographies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |