|
Verderers
Verderers are forestry officials in England who deal with common land in certain former royal hunting areas which are the property of the Crown. The office was developed in the Middle Ages to administer forest law on behalf of the King. Verderers investigated and recorded minor offences such as the taking of venison and the illegal cutting of woodland, and dealt with the day-to-day forest administration. In the modern era, verderers are still to be found in the New Forest, the Forest of Dean, and Epping Forest, where they serve to protect commoning practices, and conserve the traditional landscape and wildlife. Origins Verderers were originally part of the ancient judicial and administrative hierarchy of the vast areas of English forests and Royal Forests set aside by William the Conqueror for hunting. The title Verderer comes from the Norman word ‘vert’ meaning green and referring to woodland. These forests were divided into provinces each having a Chief Justice who travelled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Forest
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, featuring in the Domesday Book. It is the home of the New Forest Commoners, whose ancient rights of common pasture are still recognised and exercised, enforced by official verderers and agisters. In the 18th century, the New Forest became a source of timber for the Royal Navy. It remains a habitat for many rare birds and mammals. It is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest. Several areas are Geological Conservation Review and Nature Conservation Review sites. It is a Special Area of Conservation, a Ramsar site and a Special Protection Area. Copythorne Common is managed by the Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust, Kingston Great Common is a national nature reserve and New Forest Northern Commons is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
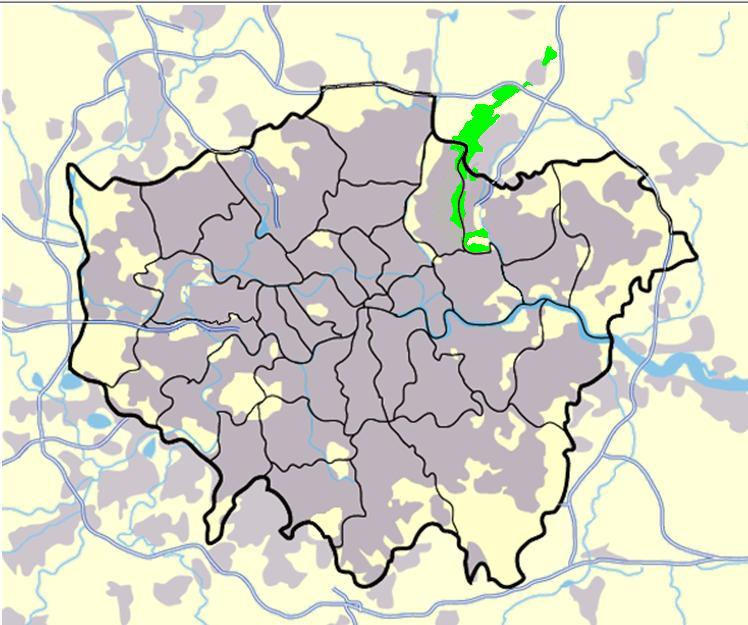
Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London built-up area. South of Chingford the forest narrows, and forms a green corridor that extends deep into East London, as far as Forest Gate; the Forest's position gives rise to its nickname, the ''Cockney Paradise''. It is the largest forest in London. It lies on a ridge between the valleys of the rivers Lea and Roding. It contains areas of woodland, grassland, heath, streams, bogs and ponds, and its elevation and thin gravelly soil (the result of glaciation) historically made it less suitable for agriculture. The Forest was historically managed as a common; the land was held by a number of local landowners who exercised economic rights over aspects such as timber, while local commoners had grazing and other rights. It was designated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
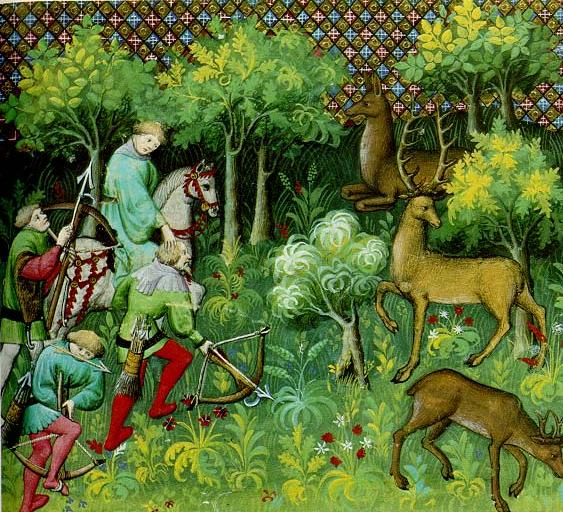
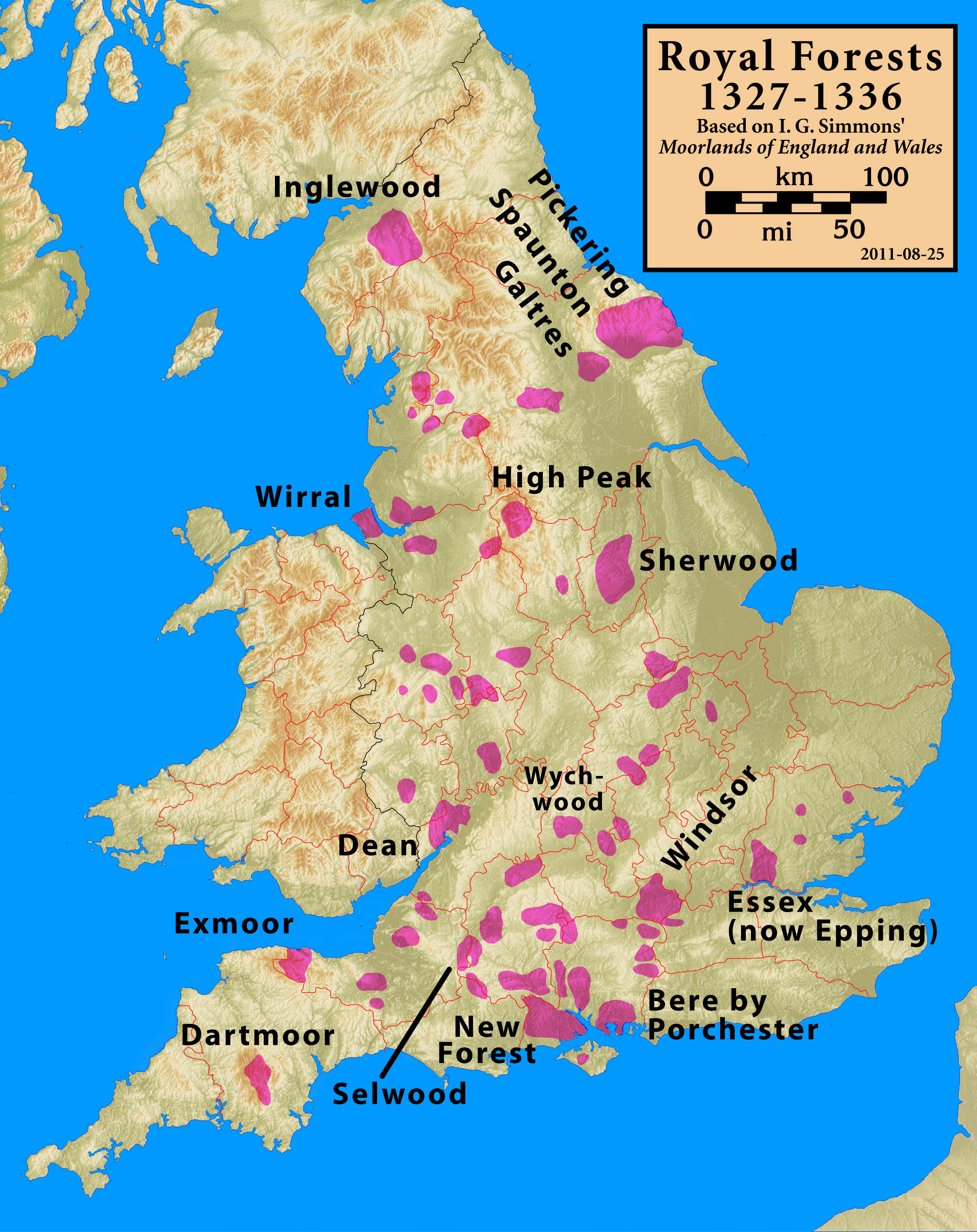
Royal Forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the original medieval sense was closer to the modern idea of a "preserve" – i.e. land legally set aside for specific purposes such as royal hunting – with less emphasis on its composition. There are also differing and contextual interpretations in Continental Europe derived from the Carolingian and Merovingian legal systems. In Anglo-Saxon England, though the kings were great huntsmen, they never set aside areas declared to be "outside" (Latin ''foris'') the law of the land.H. R. Loyn, ''Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest'' 2nd ed. 1991:378-82. Historians find no evidence of the Anglo-Saxon monarchs (c. 500 to 1066) creating forests. However, under the Norman kings (after 1066), by royal prerogative forest law was widely applied. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Of Dean
The Forest of Dean is a geographical, historical and cultural region in the western part of the county of Gloucestershire, England. It forms a roughly triangular plateau bounded by the River Wye to the west and northwest, Herefordshire to the north, the River Severn to the south, and the City of Gloucester to the east. The area is characterised by more than of mixed woodland, one of the surviving ancient woodlands in England. A large area was reserved for royal hunting before 1066, and remained as the second largest crown forest in England, after the New Forest. Although the name is used loosely to refer to the part of Gloucestershire between the Severn and Wye, the Forest of Dean proper has covered a much smaller area since the Middle Ages. In 1327, it was defined to cover only the royal demesne and parts of parishes within the hundred of St Briavels, and after 1668 comprised the royal demesne only. The Forest proper is within the civil parishes of West Dean, Lydb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the original medieval sense was closer to the modern idea of a "preserve" – i.e. land legally set aside for specific purposes such as royal hunting – with less emphasis on its composition. There are also differing and contextual interpretations in Continental Europe derived from the Carolingian and Merovingian legal systems. In Anglo-Saxon England, though the kings were great huntsmen, they never set aside areas declared to be "outside" (Latin ''foris'') the law of the land.H. R. Loyn, ''Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest'' 2nd ed. 1991:378-82. Historians find no evidence of the Anglo-Saxon monarchs (c. 500 to 1066) creating forests. However, under the Norman kings (after 1066), by royal prerogative forest law was widely applied. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Fowell Buxton
Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, 1st Baronet (1 April 1786Olwyn Mary Blouet, "Buxton, Sir Thomas Fowell, first baronet (1786–1845)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online ed., May 201accessed 25 April 2013 – 19 February 1845) was an English Member of Parliament, brewer, abolitionist and social reformer. He had connections with the Gurney family. Early life Buxton was born at Castle Hedingham, Essex. His father, also named Thomas Fowell Buxton, died young, leaving three sons and two daughters. His Quaker mother's maiden name was Anna Hanbury. He completed his education at Trinity College Dublin, graduating in 1807. Through his mother's influence Buxton became associated with the Gurney family of Earlham Hall, Norwich, especially with Joseph John Gurney and Gurney's sister, the prison reformer Elizabeth Fry. He married their sister Hannah in May 1807. He lived at Belfield House, Weymouth, Dorset in the constituency he represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management play essential role of creation and modification of habitats and affect ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as " sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean. The county town is the city of Gloucester and other principal towns and villages include Cheltenham, Cirencester, Kingswood, Bradley Stoke, Stroud, Thornbury, Yate, Tewkesbury, Bishop's Cleeve, Churchdown, Brockworth, Winchcombe, Dursley, Cam, Berkeley, Wotton-under-Edge, Tetbury, Moreton-in-Marsh, Fairford, Lechlade, Northleach, Stow-on-the-Wold, Chipping Campden, Bourton-on-the-Water, Stonehouse, Nailsworth, Minchinhampton, Painswick, Winterbourne, Frampton Cotterell, Coleford, Cinderford, Lydney and Rodborough and Cainscross that are within Stroud's urban area. Gloucestershire borders Herefordshire to the north-west, Worcestershire to the north, Warwickshire to the north-east, Oxfordshire to the east, Wiltshire to the south, Bristol and Somerset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeve (England)
In Anglo-Saxon England, the reeve was a senior official with local responsibilities under the Crown, such as the chief magistrate of a town or district. After the Norman conquest, it was an office held by a man of lower rank, appointed as manager of a manor and overseer of the peasants. In this later role, historian H. R. Loyn observes, "he is the earliest English specialist in estate management." Anglo-Saxon England Before the Conquest, a reeve (Old English '' ġerēfa''; similar to the titles '' greve''/''gräfe'' in the Low Saxon languages of Northern Germany) was an administrative officer who generally ranked lower than the ealdorman or earl. The Old English word ''ġerēfa'' was originally a general term, but soon acquired a more technical meaning. Land was divided into a large number of hides—an area containing enough farmable land to support one household. Ten hides constituted a tithings, and the families living upon it (in theory, ten of them) were obliged to u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loughton
Loughton () is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex. Part of the metropolitan and urban area of London, the town borders Chingford, Waltham Abbey, Theydon Bois, Chigwell and Buckhurst Hill, and is northeast of Charing Cross. The parish of Loughton covers part of Epping Forest, in 1996 some parts of the south of the old parish were transferred to Buckhurst Hill parish, and other small portions to Chigwell and Theydon Bois. It is the most populous civil parish in the Epping Forest district, and within Essex it is the second most populous civil parish (after Canvey Island) and the second largest in the area. At the 2021 census, it had a population of 33,353. Loughton has three conservation areas and there are 56 listed buildings in the town, together with a further 50 that are locally listed. History The earliest structure in Loughton is Loughton Camp, an Iron Age earth fort in Epping Forest dating from around 500 BC. Hidden by dense undergrowt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London from its settlement by the Romans in the 1st century AD to the Middle Ages, but the modern area named London has since grown far beyond the City of London boundary. The City is now only a small part of the metropolis of Greater London, though it remains a notable part of central London. Administratively, the City of London is not one of the London boroughs, a status reserved for the other 32 districts (including Greater London's only other city, the City of Westminster). It is also a separate ceremonial county, being an enclave surrounded by Greater London, and is the smallest ceremonial county in the United Kingdom. The City of London is widely referred to simply as the City (differentiated from the phrase "the city of London" by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |