|
Vanda Vietnamica
''Vanda'', abbreviated in the horticultural trade as ''V.,'' is a genus in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. There are about 87 species, and the genus is commonly cultivated for the marketplace. This genus and its allies are considered to be among the most specifically adapted of all orchids within the Orchidaceae. The genus is highly prized in horticulture for its showy, fragrant, long-lasting, and intensely colorful flowers.The Orchids, Natural History and Classification, Robert L. Dressler. ''Vanda'' species are widespread across East Asia, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea, with a few species extending into Queensland and some of the islands of the western Pacific. Biology The name "Vanda" is derived from the Sanskrit (वन्दाका) name for the species ''Vanda roxburghii'' (a synonym of '' Vanda tessellata''). These mostly epiphytic, but sometimes lithophytic or terrestrial orchids, are distributed in India, Himalaya, Southeast Asia, Indonesia, the Philippines, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaud
Gaur Brahmins (spelling variations: Gor or Gour), also Gauda Brahmins (spelling variations: Gaud, or God), also known as Adi Gauda/Gaur, is a group of Brahmin communities in India. The Gauda Brahmins are one of the five Pancha Gauda Brahmin communities that lives in the north of the Vindhyas. Gaur Brahmins likely originated from Kurukshetra region. Initially inhabiting tracts of land between the Yamuna and Sutlej rivers. Today they are most numerous in the western half of Northern India, particularly in the states of Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan as well as in the western parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh and a significant amount are present in other northern states of India as well. The Gaurs claim that the other four main divisions of North Indian Brahmins were originally Gaur, and have acquired their present designations of Saraswat Brahmins, Kanyakubja Brahmins, Maithil Brahmins and Utkala Brahmin Utkala Brahmins, also known as Utkal Brahmins, are a Brahmin comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in blending inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridisation, which include genetic and morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization and others after it. Similar barriers exist in plants, with differences in flowering t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention On International Trade In Endangered Species
CITES (shorter name for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975. Its aim is to ensure that international trade (import/export) in specimens of animals and plants included under CITES, does not threaten the survival of the species in the wild. This is achieved via a system of permits and certificates. CITES affords varying degrees of protection to more than 38,000 species. , Secretary-General of CITES is Ivonne Higuero. Background CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. There are three working langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labellum (botany)
In botany, the labellum (or lip) is the part of the flower of an orchid or '' Canna'', or other less-known genera, that serves to attract insects, which pollinate the flower, and acts as a landing platform for them. ''Labellum'' (plural: ''labella'') is the Latin diminutive of ''labrum'', meaning lip. The labellum is a modified petal and can be distinguished from the other petals and from the sepals by its large size and its often irregular shape. It is not unusual for the other two petals of an orchid flower to look like the sepals, so that the labellum stands out as distinct. Bailey, L. H. ''Gentes Herbarum: Canna x orchiodes''. (Ithaca), 1 (3): 120 (1923); Khoshoo, T. N. & Guha, I. ''Origin and Evolution of Cultivated Cannas.'' Vikas Publishing House. In orchids, the labellum is the modified median petal that sits opposite from the fertile anther and usually highly modified from the other perianth segments. It is often united with the column and can be hinged or movable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphology (biology), Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of spermatophyte, seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internode (botany), internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a Peduncle (botany), peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a Pedicel (botany) , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
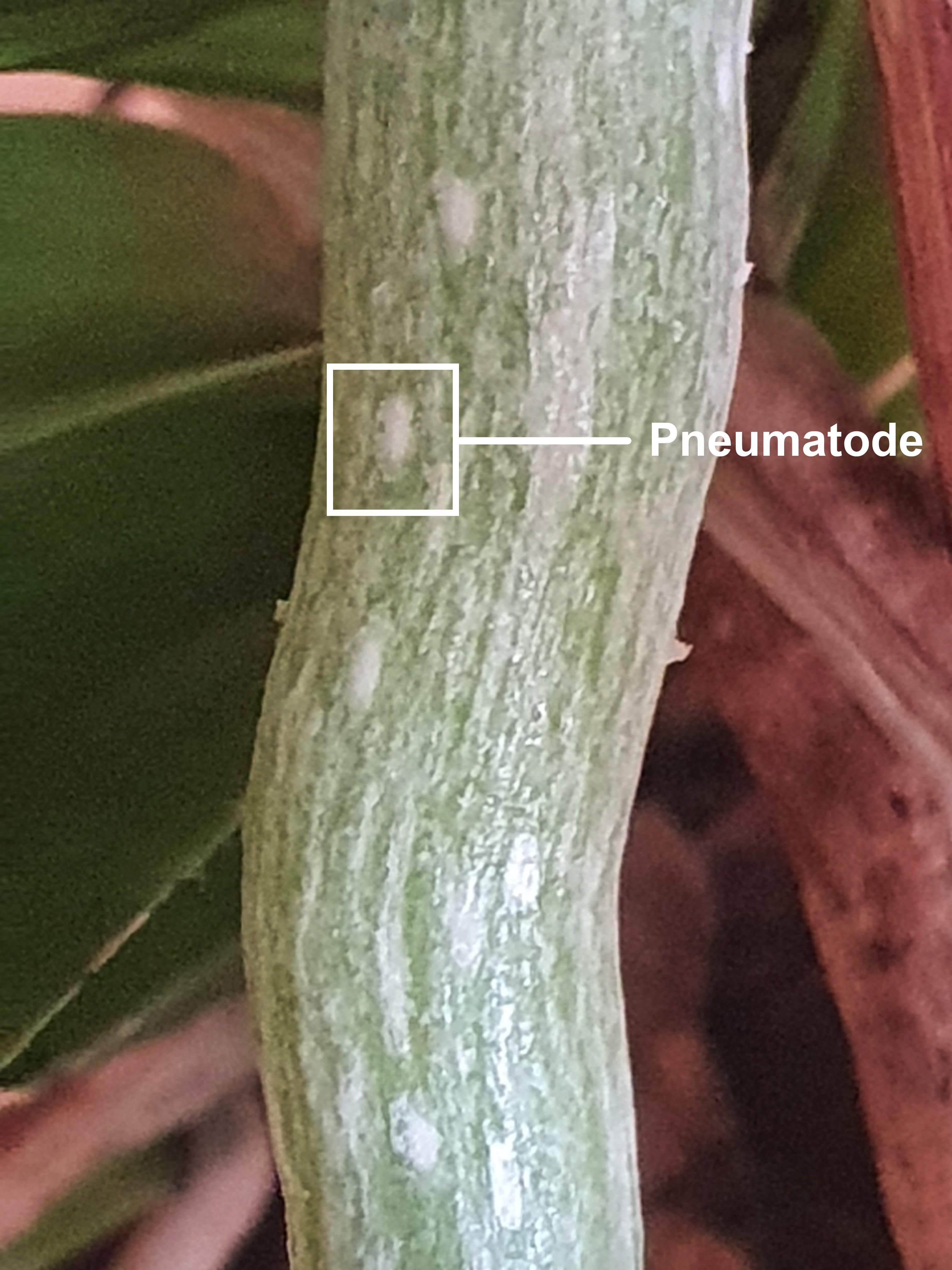
Pneumatode
In botany, pneumatodes are air-containing structures in plant roots. Their function is to allow gaseous exchange in root tissues. This can be beneficial to semi-aquatic plants, such as neo-tropical palms. Plants with photosynthetic roots, such as epiphytic orchids like ''Dendrophylax lindenii'' also possess these structures. They play a role in fungal interactions. Etymology The name of the structure is derived from the Greek word πνεῦμα (pneûma), meaning breath and ὁδός (hodós), meaning pathway. Fungal interactions Fungal infections of plants may begin through penetration of the roots through pneumatodes. Functional analogy to stomata Pneumatodes are considered as a special type of cyclocytic stomata. The entire structure may rise above the adjacent epidermis. The pneumatodes may function as double structures for gas exchange and liquid water elimination (guttation Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papilionanthe
''Papilionanthe'' (abbreviated ''Ple.'') is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, southern China, and the Indian Subcontinent. Species *''Papilionanthe biswasiana'' (Ghose & Mukerjee) Garay – Yunnan, Myanmar, Thailand *''Papilionanthe greenii'' (W.W.Sm.) Garay – Bhutan *'' Papilionanthe hookeriana'' (Rchb.f.) Schltr. – Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra *''Papilionanthe pedunculata'' (Kerr) Garay – Cambodia, Vietnam *''Papilionanthe sillemiana'' (Rchb.f.) Garay – Myanmar *''Papilionanthe cylindrica'' (Lindl.) Seidenf. - India, Sri Lanka *'' Papilionanthe teres'' (Roxb.) Schltr. – Yunnan, Bangladesh, Assam, Bhutan, India, Laos, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, Vietnam; naturalized in Fiji and Caroline Islands *''Papilionanthe tricuspidata'' (J.J.Sm.) Garay – Bali, Lombok, Timor *'' Papilionanthe uniflora'' (Lindl.) Garay – Himalayas, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam *''Papilionanthe vandarum'' (Rchb.f.) Garay – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopodial
Vascular plants with monopodial growth habits grow upward from a single point. They add leaves to the apex each year and the stem grows longer accordingly. The word ''Monopodial'' is derived from Greek "mono-", ''one'' and "podial", "foot", in reference to the fact that monopodial plants have a single trunk or stem. Orchids with monopodial growth often produce copious aerial roots that often hang down in long drapes and have green chlorophyll underneath the grey root coverings, which are used as additional photosynthetic organs. They do not have a rhizome or pseudobulbs so species adapted to dry periods have fleshy succulent leaves instead. Flowers generally come from the stem between the leaves. With some monopodial species, the stem (the rhizome) might fork into two, but for all monopodial orchids this is not necessary for continued growth, as opposed to orchids with sympodial Sympodial growth is a bifurcating branching pattern where one branch develops more strongly than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |