|
Vladimir Pavlecka
Vladimir Pavlecka (May 20, 1901 – June 28, 1980) was a Czech-American inventor and aircraft designer. He was the chief inventor of Flush riveted, flush riveting and held other important patents. Biography Pavlecka was born May 20, 1901, in the village of Charvatce in Austria-Hungary (today in the Czech Republic). One of the factories in the town considered branching out into aircraft production and acquired a Blériot XI. Examining this machine inspired the teenaged Pavlecka with a lifelong interest in aviation. In 1919, Pavlecka entered Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague Technical University. With his brother, he emigrated to the United States in 1923, and was graduated from Union College in 1925. He moved to Detroit and went to work for Buick, then for the Detroit Aircraft Corporation, Aircraft Development Corporation of Detroit. Here, he became chief of hull design for the revolutionary ZMC-2 metal-clad airship, which first flew in 1929. Although the single ship bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Pavlecka Portrait
Vladimir (, , pre-1918 orthography: ) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, widespread throughout all Slavic nations in different forms and spellings. The earliest record of a person with the name is Vladimir of Bulgaria (). Etymology The Old East Slavic form of the name is Володимѣръ ''Volodiměr'', while the Old Church Slavonic form is ''Vladiměr''. According to Max Vasmer, the name is composed of Slavic владь ''vladĭ'' "to rule" and ''*mēri'' "great", "famous" (related to Gothic element ''mērs'', ''-mir'', cf. Theode''mir'', Vala''mir''). The modern ( pre-1918) Russian forms Владимиръ and Владиміръ are based on the Church Slavonic one, with the replacement of мѣръ by миръ or міръ resulting from a folk etymological association with миръ "peace" or міръ "world". Max Vasmer, ''Etymological Dictionary of Russian Language'' s.v. "Владимир"starling.rinet.ru [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross section (geometry), cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a Die (manufacturing), die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive stress, compressive and shear stress, shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process. Drawing (manufacturing), Drawing is a similar process, using the tensile strength of the material to pull it through the die. It limits the amount of change that can be performed in one step, so it is limited to simpler shapes, and multiple stages are usually needed. Drawing is the main way to produce wire. Metal Bar stock, bars and tube (fluid conveyance), tubes are also often drawn. Extrusion may be continuous (theoretically producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet
The Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet is a unique prototype fighter interceptor built by the Northrop Corporation. It was one of the most radical of the experimental aircraft built during World War II. Ultimately, it was unsuccessful and did not enter production. Design and development The initial idea for the XP-56 was quite radical for 1939. It was to have no horizontal tail, only a small vertical tail, used an experimental engine, and be produced using a novel metal, magnesium. The aircraft was to be a wing with a small central fuselage added to house the engine and pilot. It was hoped that this configuration would have less aerodynamic drag than a conventional airplane. The idea for this single-seat aircraft originated in 1939 as the Northrop N2B model. It was designed around the Pratt & Whitney liquid-cooled X-1800 engine in a pusher configuration driving contra-rotating propellers. The U.S. Army ordered Northrop to begin design work on 22 June 1940, and after reviewing the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet 061024-F-1234P-008
Northrop may refer to: Businesses * Northrop Corporation, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1939 * Northrop Grumman, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1994 as a merger of the above company with Grumman * Northrop Loom, an American designed weaving loom Places United States * Northrop, Minnesota, a town * Northrop, Minneapolis, Minnesota, a neighborhood * Northrop Auditorium, on the Minneapolis campus of the University of Minnesota * Northrop Field, a former stadium for the University of Minnesota * Northrop High School, Fort Wayne, Indiana * Northrop University, a former aviation institute * Mount Northrop, Minnesota People * Northrop (surname), including a list of people with the name * Northrop Frye (1912–1991), Canadian literary theorist * Suzane Northrop Suzane Northrop is an American writer, podcaster, TV show host, and psychic medium. She has written at least four books, and hosted the television show, '' The Afterlife with Suzane Northrop''. She p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Fighter
A night fighter (later known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor post-Second World War) is a largely historical term for a fighter aircraft, fighter or interceptor aircraft adapted or designed for effective use at night, during periods of adverse meteorological conditions, or in otherwise poor visibility. Such designs were in direct contrast to day fighter, day fighters: fighters and interceptors designed primarily for use during the day or during good weather. The concept of the night fighter was developed and experimented with during the First World War but would not see widespread use until WWII. The term would be supplanted by “all-weather fighter/interceptor” post-WWII, with advancements in various technologies permitting the use of such aircraft in virtually all conditions. During the Second World War, night fighters were either purpose-built night fighter designs, or more commonly, heavy fighters or light bombers adapted for the mission, often employing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
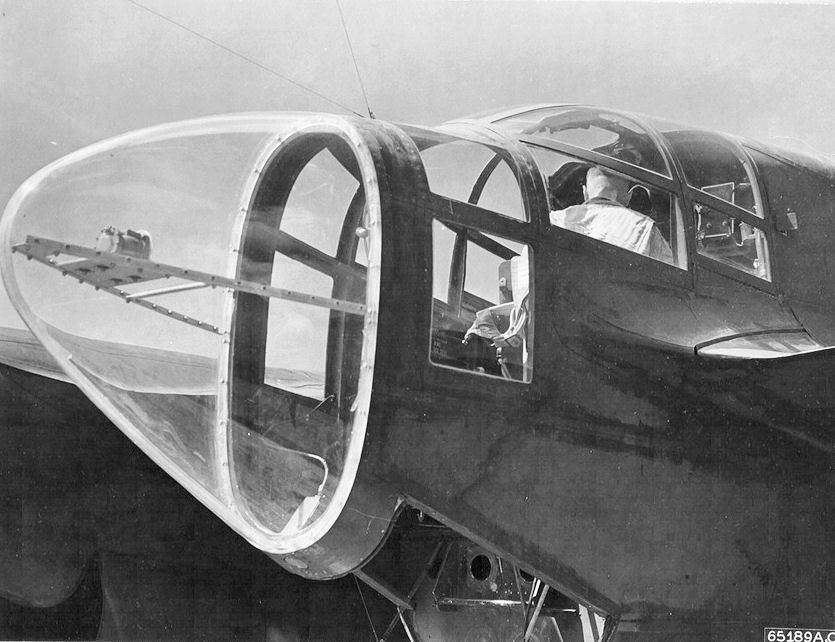
Northrop P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider '' Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on 26 May 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier British-designed night-fighter aircraft that had been up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop Corporation
Northrop Corporation was an American aircraft manufacturer from its formation in 1939 until its 1994 merger with Grumman to form Northrop Grumman. The company is known for its development of the flying wing design, most successfully the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 93-106, Cypress, CA, 2013. . History Jack Northrop founded three companies using his name. The first was the Avion Corporation in 1928, which was absorbed in 1929 by the United Aircraft and Transport Corporation as a subsidiary named "Northrop Aircraft Corporation" (and later became part of Boeing). The parent company moved its operations to Kansas in 1931, and so Northrop, along with Donald Wills Douglas Sr., Donald Douglas, established a "Northrop Corporation" located in El Segundo, California, which produced several successful designs, including the Northrop Gamma and Northrop Delta. However, labor difficulties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop-Hendy XT37
The Northrop-Hendy T37 Turbodyne (company designation N-10) was an American turboprop engine developed by the Turbodyne Division of Northrop in the late 1940s. Design and development Turbodyne I Northrop undertook a private venture to develop a turboprop engine from 1939 and was awarded a joint US Army/US Navy contract in 1941 for design, analysis and fabrication of a research compressor for the proposed engine. The contract was amended later to call for construction of two complete engine prototypes. Northrop had neither the space or expertise to fabricate the engines in a reasonable time-scale so they joined forces with the Joshua Hendy Iron Works in 1944 to form the Northrop-Hendy company. the two prototype engines were completed and test run in late 1944, but the first engine compressor failed, destroying the engine. Meanwhile the USN cancelled their interest in the engine in 1945, leaving the US Army to carry on. Testing continued with the second engine until that too fail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Northrop
John Knudsen Northrop (November 10, 1895 – February 18, 1981) was an American aircraft industrialist and designer who founded the Northrop Corporation in 1939. His career began in 1916 as a draftsman for Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company (founded 1912). He joined the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1923 and worked on the Douglas World Cruiser, where in time he became a project engineer. In 1927 he joined the Lockheed Corporation, where he was a chief engineer on the Lockheed Vega transport. He left in 1929 to found Avion Corporation, which he sold in 1930. Two years later, he founded the Northrop Corporation. This firm became a subsidiary of Douglas Aircraft in 1939, so he co-founded a second company named Northrop. Early life and entering aviation Born in Newark, New Jersey, in 1895, Northrop grew up in Santa Barbara, California. In 1916, Northrop's first job in aviation was in working as a draftsman for the Santa Barbara-based Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a Gas turbine, gas turbine engine that drives an aircraft Propeller (aeronautics), propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction drive, reduction gearbox, gas compressor, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the Fuel mixture, fuel-air mixture then Combustion, combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough power to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the direction of flow: * a rotating gas compressor * a combustor * a compressor-driving turbine. Additional components have to be added to the gas generator to suit its application. Common to all is an air inlet but with different configurations to suit the requirements of marine use, land use or flight at speeds varying from stationary to supersonic. A propelling nozzle is added to produce thrust for flight. An extra turbine is added to drive a propeller (turboprop) or ducted fan (turbofan) to reduce fuel consumption (by increasing propulsive efficiency) at subsonic flight speeds. An extra turbine is also required to drive a helicopter rotor or land-vehicle transmission (turboshaft), marine propeller or electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop P-61 Green Airborne
Northrop may refer to: Businesses * Northrop Corporation, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1939 * Northrop Grumman, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1994 as a merger of the above company with Grumman * Northrop Loom, an American designed weaving loom Places United States * Northrop, Minnesota, a town * Northrop, Minneapolis, Minnesota, a neighborhood * Northrop Auditorium, on the Minneapolis campus of the University of Minnesota * Northrop Field, a former stadium for the University of Minnesota * Northrop High School, Fort Wayne, Indiana * Northrop University, a former aviation institute * Mount Northrop, Minnesota People * Northrop (surname), including a list of people with the name * Northrop Frye (1912–1991), Canadian literary theorist * Suzane Northrop Suzane Northrop is an American writer, podcaster, TV show host, and psychic medium. She has written at least four books, and hosted the television show, '' The Afterlife with Suzane Northrop''. She p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |