|
Vladimir Mikhailovich Alekseev
Vladimir Mikhailovich Alekseev (Владимир Михайлович Алексеев, sometimes transliterated as "Alexeyev" or "Alexeev", 17 June 1932, Bykovo, Ramensky District, Moscow Oblast – 1 December 1980) was a Russian mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and dynamical systems.D. Anosov, V. Arnold, A. N. Kolmogorov, Y. Sinai et al., (Obituary in Russian) Mathematical Surveys, vol. 36, 1981, pp. 201–206Russian on mathnet.ru He attended secondary school in Moscow at one of the special schools of mathematics affiliated with Moscow State University and participated in several mathematical olympiads. From 1950 he studied at the Faculty of Mathematics and Mechanics at the Moscow State University, where he worked as a student of Andrei Kolmogorov on the asymptotic behavior in the three-body problem of celestial mechanics. Already as an undergraduate, Alekseev proved significant new results on quasi-random motion associated with the three-body problem. This was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bykovo, Ramensky District, Moscow Oblast
Bykovo () is an urban locality (a work settlement) in Ramensky District of Moscow Oblast, located southeast of Moscow. Population: History It was founded in 1861–1862 upon construction of the Moscow-Ryazan Ryazan (, ; also Riazan) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the banks of the Oka River in Central Russia, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 C ... railroad, replacing the former village to the south. Work settlement status was granted to it in 1962. Economy The Bykovo Airport and an aircraft repair facility are located here. Notable people Bykovo is a home (and a place of birth) for Pavel Chukhrai, Vladimir Sorokin, and Nikolay Rastorguyev. References {{Authority control Urban-type settlements in Moscow Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Mechanics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, to produce ephemeris data. History Modern analytic celestial mechanics started with Isaac Newton's ''Principia'' (1687). The name celestial mechanics is more recent than that. Newton wrote that the field should be called "rational mechanics". The term "dynamics" came in a little later with Gottfried Leibniz, and over a century after Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace introduced the term ''celestial mechanics''. Prior to Kepler, there was little connection between exact, quantitative prediction of planetary positions, using geometrical or numerical techniques, and contemporary discussions of the physical causes of the planets' motion. Laws of planetary motion Johannes Kepler was the first to closely integrate the predictive geometrical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
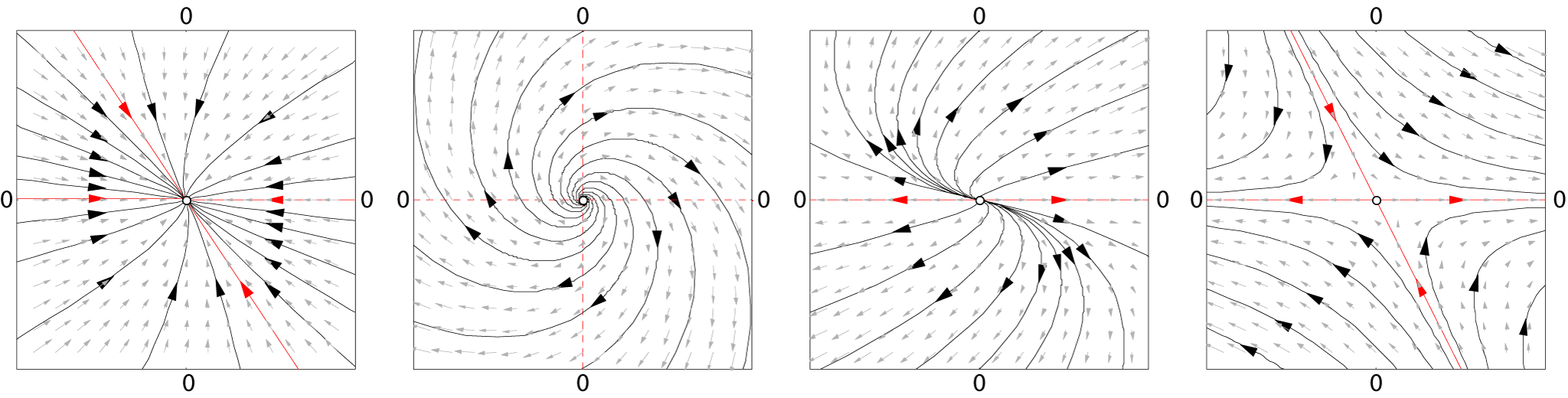
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University
Moscow State University (MSU), officially M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,. is a public university, public research university in Moscow, Russia. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches. Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner were affiliated with the university. History Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov and Mikhail Lomonosov promoted the idea of a university in Moscow, and Elizabeth of Russia, Russian Empress Elizabeth decreed its establishment on . The first lectures were given on . Saint Petersburg State University and MSU each claim to be Russia's oldest university. Though Moscow State University was founded in 1755, St. Petersburg which has had a continuous existence as a "university" since 1819 sees itself as the successor of an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Kolmogorov
Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov ( rus, Андре́й Никола́евич Колмого́ров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ kəlmɐˈɡorəf, a=Ru-Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov.ogg, 25 April 1903 – 20 October 1987) was a Soviet mathematician who played a central role in the creation of modern probability theory. He also contributed to the mathematics of topology, intuitionistic logic, turbulence, classical mechanics, algorithmic information theory and computational complexity. Biography Early life Andrey Kolmogorov was born in Tambov, about 500 kilometers southeast of Moscow, in 1903. His unmarried mother, Maria Yakovlevna Kolmogorova, died giving birth to him. Andrey was raised by two of his aunts in Tunoshna (near Yaroslavl) at the estate of his grandfather, a well-to-do nobleman. Little is known about Andrey's father. He was supposedly named Nikolai Matveyevich Katayev and had been an agronomist. Katayev had been exiled from Saint Petersburg to the Yarosla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Congress Of Mathematicians
The International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM) is the largest conference for the topic of mathematics. It meets once every four years, hosted by the International Mathematical Union (IMU). The Fields Medals, the IMU Abacus Medal (known before 2022 as the Nevanlinna Prize), the Carl Friedrich Gauss Prize, Gauss Prize, and the Chern Medal are awarded during the congress's opening ceremony. Each congress is memorialized by a printed set of Proceedings recording academic papers based on invited talks intended to be relevant to current topics of general interest. Being List of International Congresses of Mathematicians Plenary and Invited Speakers, invited to talk at the ICM has been called "the equivalent ... of an induction to a hall of fame". History German mathematicians Felix Klein and Georg Cantor are credited with putting forward the idea of an international congress of mathematicians in the 1890s.A. John Coleman"Mathematics without borders": a book review. ''CMS Notes'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Sinai
Yakov Grigorevich Sinai (; born September 21, 1935) is a Russian–American mathematician known for his work on dynamical systems. He contributed to the modern metric theory of dynamical systems and connected the world of deterministic (dynamical) systems with the world of probabilistic (stochastic) systems. He has also worked on mathematical physics and probability theory. His efforts have provided the groundwork for advances in the physical sciences. Sinai has won several awards, including the Nemmers Prize, the Wolf Prize in Mathematics and the Abel Prize. He has served as professor of mathematics at Princeton University since 1993 and holds the position of Senior Researcher at the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics in Moscow, Russia. Biography Yakov Grigorevich Sinai was born into a Russian Jewish academic family on September 21, 1935, in Moscow, Soviet Union (now Russia). His parents, Nadezda Kagan and Gregory Sinai, were both microbiologists. His grandfat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Mikhailovich Tikhomirov
Vladimir (, , pre-1918 orthography: ) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, widespread throughout all Slavic nations in different forms and spellings. The earliest record of a person with the name is Vladimir of Bulgaria (). Etymology The Old East Slavic form of the name is Володимѣръ ''Volodiměr'', while the Old Church Slavonic form is ''Vladiměr''. According to Max Vasmer, the name is composed of Slavic владь ''vladĭ'' "to rule" and ''*mēri'' "great", "famous" (related to Gothic element ''mērs'', ''-mir'', cf. Theode''mir'', Vala''mir''). The modern ( pre-1918) Russian forms Владимиръ and Владиміръ are based on the Church Slavonic one, with the replacement of мѣръ by миръ or міръ resulting from a folk etymological association with миръ "peace" or міръ "world". Max Vasmer, ''Etymological Dictionary of Russian Language'' s.v. "Владимир"starling.rinet.ru [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Fomin
Sergei Vasilyevich Fomin (; 9 December 1917 – 17 August 1975) was a Soviet mathematician who was co-author with Andrey Kolmogorov of ''Introductory real analysis'', and co-author with Israel Gelfand of ''Calculus of Variations'' (1963),. both books that are widely read in Russian and in English. Fomin entered Moscow State University at the age of 16. His first paper was published at 19 on infinite abelian groups. After his graduation he worked with Kolmogorov. He was drafted during World War II, after which he returned to Moscow. When the war ended Fomin returned to Moscow State University and joined Andrey Tikhonov's department. In 1951 he was awarded his habilitation for a dissertation on dynamical systems with invariant measure. Two years later he was appointed a professor. Later in life, he became involved with mathematical aspects of biology. The American mathematician Paul Halmos wrote the following about Fomin: ''Some of the mathematical interests of Sergei Vasilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems Theorists
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Systems Scientists
Russian(s) may refer to: *Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *A citizen of Russia *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series *Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 See also * *Russia (other) *Rus (other) *Rossiysky (other) *Russian River (other) *Rushen (other) Rushen may refer to: Places * Rushen, formally Kirk Christ Rushen, a historic parish of the Isle of Man ** Rushen (constituency), a House of Keys constituency of which the parish forms part ** Rushen (sheading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |