|
Vinyl Bromide
Vinyl bromide is the organobromine compound with the formula . Classified as a vinyl halide, it is a colorless gas at room temperature. It is used as a reagent and a comonomer. Synthesis, reactions, and applications It is produced from ethylene dibromide: : is mainly consumted as a comonomer to confer fire retardant properties to acrylate polymers. Vinyl bromide reacts with magnesium to give the corresponding Grignard reagent . Safety precautions Vinyl bromide is listed in List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens as a suspected human carcinogen. See also * Vinyl chloride * Allyl bromide * Bromoethane Bromoethane, also known as ethyl bromide, is a chemical compound of the haloalkanes group. It is abbreviated by chemists as EtBr (which is also used as an abbreviation for ethidium bromide). This volatile compound has an ether-like odor. Prepara ... References External links * *MSDS at Oxford University [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyl Halide
In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH2=CHX (X = halide). The term vinyl group, vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl halides. From the perspective of applications, the dominant member of this class of compounds is vinyl chloride, which is produced on the scale of millions of tons per year as a precursor to polyvinyl chloride. Polyvinyl fluoride is another commercial product. Related compounds include 1,1-Dichloroethene, vinylidene chloride and vinylidene fluoride. Synthesis Vinyl chloride is produced by dehydrochlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane. Due to their high utility, many approaches to vinyl halides have been developed, such as: * reactions of vinyl organometallic species with halogens * Takai olefination * Stork-Zhao olefination with, e.g., (Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane - a modification of the Wittig reaction * Olefin metathesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
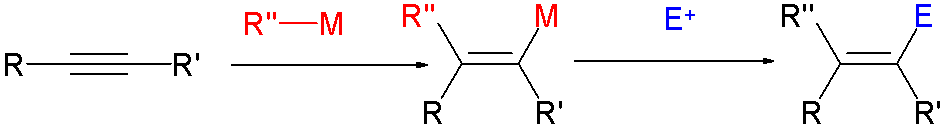
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comonomer
In polymer chemistry, a comonomer refers to a polymerizable precursor to a copolymer aside from the principal monomer. In some cases, only small amounts of a comonomer are employed, in other cases substantial amounts of comonomers are used. Furthermore, in some cases, the comonomers are statistically incorporated within the polymer chain, whereas in other cases, they aggregate. The distribution of comonomers is referred to as the " blockiness" of a copolymer. Polyolefins 1-Octene, 1-hexene, and 1-butene are used comonomers in the manufacture of polyethylene Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bott ...s. The advantages to such copolymers has led to a focus on catalysts that facilitate the incorporation of these comonomers, e.g., constrained geometry complexes. Comonome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Dibromide
1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula . Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is probably formed by algae and kelp, substantial amounts are produced industrially. It is a dense colorless liquid with a faint, sweet odor, detectable at 10 ppm. It is a widely used and sometimes-controversial fumigant. The combustion of 1,2-dibromoethane produces hydrogen bromide gas that is significantly corrosive. Preparation and use It is produced by the reaction of ethylene gas with bromine, in a classic halogen addition reaction: :CH=CH + Br → BrCH–CHBr Historically, 1,2-dibromoethane was used as a component in anti-knock additives in leaded fuels. It reacts with lead residues to generate volatile lead bromides, thereby preventing fouling of the engine with lead deposits. Pesticide It has been used as a pesticide in soil and on various crops. The applications were initiated after the forced re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Retardant
A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants may also cool the fuel through physical action or endothermic chemical reactions. Fire retardants are available as powder, to be mixed with water, as fire-fighting foams and fire-retardant gels. Fire retardants are commonly used in fire fighting, where they may be applied aerially or from the ground. Principles of operation In general, fire retardants reduce the flammability of materials by either blocking the fire physically or by initiating a chemical reaction that stops the fire. Physical action There are several ways in which the combustion process can be retarded by physical action: * By cooling: Some chemical reactions actually cool the material down. * By forming a protective layer that prevents the underlying material from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylate Polymer
An acrylate polymer (also known as acrylic or polyacrylate) is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity. Acrylate polymer is commonly used in cosmetics, such as nail polish, as an adhesive. History The first synthesis of acrylic polymer was reported by G. W. A. Kahlbaum in 1880. Acrylic elastomers Acrylic elastomer is a general term for a type of synthetic rubber whose primary component is acrylic acid alkylester ( ethyl or butyl ester). Acrylic elastomer possesses characteristics of heat and oil resistance, with the ability to withstand temperatures of 170–180 °C. It is used primarily for producing oil seals and packaging related to automobiles. Acrylic elastomer can generally be characterized as one of two types. "Old" types include ACM ( copolymer of acrylic acid ester and 2-chloroethyl vinyl ether) containing chlorine and ANM (copolymer of acrylic acid e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagent
Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon–carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. Grignard reagents are rarely isolated as solids. Instead, they are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran using air-free techniques. Grignard reagents are complex with the magnesium atom bonded to two ether ligands as well as the halide and organyl ligands. The discovery of the Grignard reaction in 1900 was recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IARC Group 2A Carcinogens
IARC group 2A agents are substances and exposure circumstances that have been classified as probable carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This designation is applied when there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans, as well as ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some cases, an agent may be classified in this group when there is ''inadequate evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans along with ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and ''strong evidence'' that the carcinogenesis is mediated by a mechanism that also operates in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be classified in this group solely on the basis of ''limited evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans. This list is focusing on the hazard linked to the agents. This means that the carcinogenic agents are capable of causing cancer, but this does not take their risk into account, which is the probability of causing a can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division. The specific mechanisms for carcinogenic activity is unique to each agent and cell type. Carcinogens can be broadly categorized, however, as activation-dependent and activation-independent which relate to the agent's ability to engage dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyl Chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C =CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. It is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Vinyl chloride is a colourless flammable gas that has a sweet odor and is carcinogenic. Vinyl chloride monomer is among the top twenty largest petrochemicals (petroleum-derived chemicals) in world production. The United States remains the largest vinyl chloride manufacturing region because of its low-production-cost position in chlorine and ethylene raw materials. China is also a large manufacturer and one of the largest consumers of vinyl chloride. It can be formed in the environment when soil organisms break down chlorinated solvents. Vinyl chloride that is released by industries or formed by the breakdown of other chlorinated chemicals can enter the air and drinking water supplies. Vinyl chloride is a common contaminant found near landfills. Before the 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Bromide
Allyl bromide (3-bromopropene) is an organic halide. It is an alkylating agent used in synthesis of polymers, pharmaceuticals, perfumes and other organic compounds. Allyl bromide is a colorless liquid, although commercial samples appear yellow or brown. It is an irritant and a potentially dangerous alkylating agent. Allyl bromide is more reactive but more expensive than allyl chloride, and these considerations guide its use. Preparation Hydrohalogenation Allyl bromide is produced commercially from allyl alcohol and hydrobromic acid: :CH2=CHCH2OH + HBr → CH2=CHCH2Br + H2O It can also be prepared by the halogen-exchange reaction between allyl chloride and hydrobromic acid or by the allylic bromination of propene. Reactions and uses Allyl bromide is an electrophilic alkylating agent. It reacts with nucleophiles, such as amines, carbanions, alkoxides, etc., to introduce the allyl group: :CH2=CHCH2Br + Nu− → CH2=CHCH2Nu + Br− (Nu− is a nucleophile) It is used in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoethane
Bromoethane, also known as ethyl bromide, is a chemical compound of the haloalkanes group. It is abbreviated by chemists as EtBr (which is also used as an abbreviation for ethidium bromide). This volatile compound has an ether-like odor. Preparation The preparation of EtBr stands as a model for the synthesis of bromoalkanes in general. It is usually prepared by the addition of hydrogen bromide to ethene: :H2C=CH2 + HBr → H3C-CH2Br Bromoethane is inexpensive and would rarely be prepared in the laboratory. A laboratory synthesis includes reacting ethanol with a mixture of hydrobromic and sulfuric acids. An alternate route involves refluxing ethanol with phosphorus and bromine; phosphorus tribromide is generated ''in situ''. Uses In organic synthesis, EtBr is the synthetic equivalent of the ethyl carbocation (Et+) synthon. In reality, such a cation is not actually formed. For example, carboxylates salts are converted to ethyl esters, carbanions to ethylated derivatives, thioure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |