|
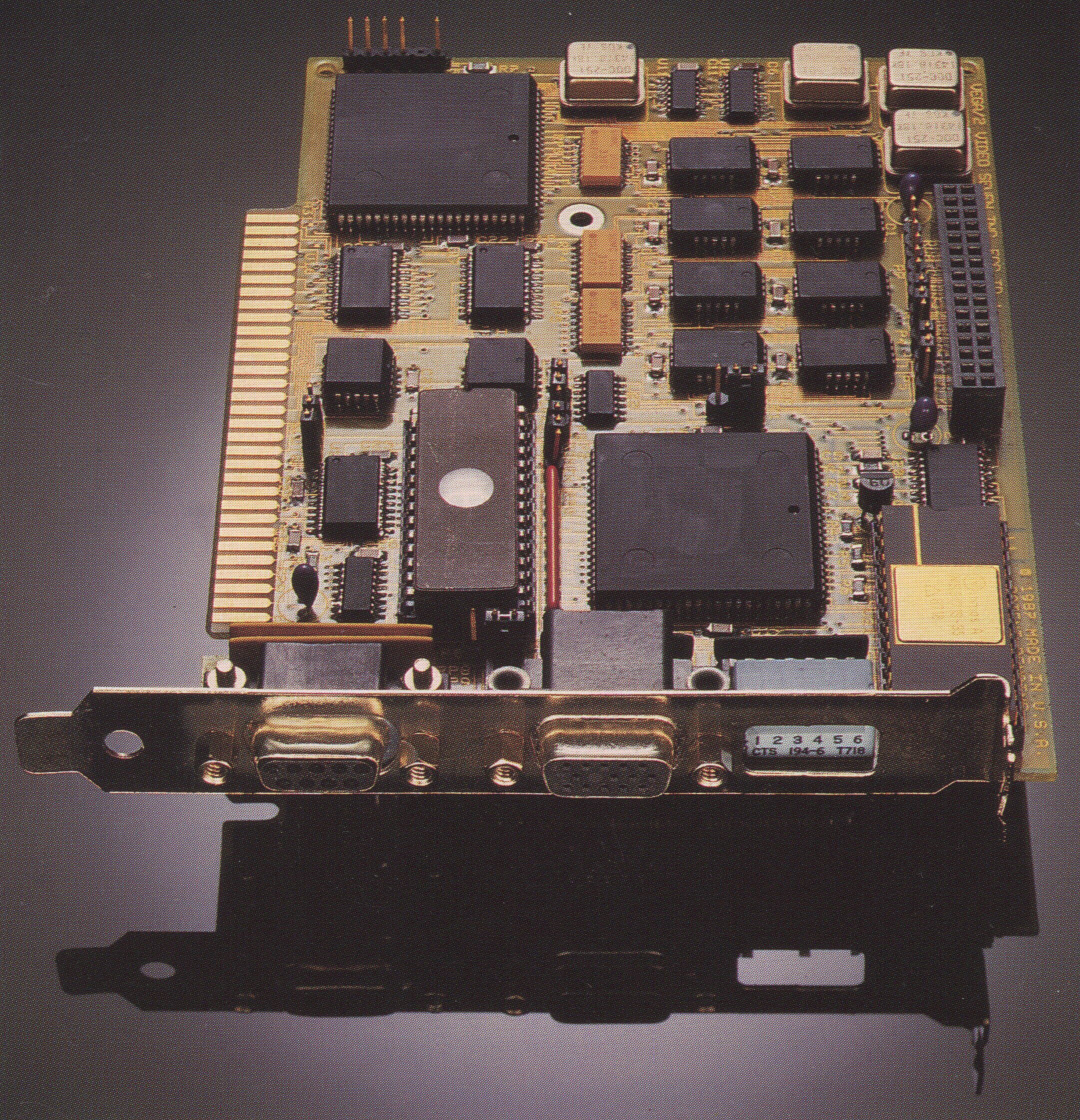
Video Seven
Video Seven, Inc., also typeset as Video-7, later Headland Technology, Inc., was a public American computer hardware company independently active from 1984 to 1989. The company manufactured expansion cards for personal computers, mainly graphics cards for the IBM PC through their Vega brand. It was founded by Paul Jain as his second venture in the graphics card market; after his departure in 1990, he founded Media Vision. Video Seven delivered both the first graphics card compatible with IBM's Enhanced Graphics Adapter (EGA), in 1985, and one of the first cards compatible with IBM's Video Graphics Array (VGA) standard, in 1987. In 1989, Video Seven merged with G-2 Inc., a subsidiary of LSI Logic Corporation, becoming Headland Technology. History Foundation (1984–1987) Video Seven, Inc. was founded by Paul Jain in Milpitas, California, in 1984. Before starting Video Seven, Jain had been the founder of Paradise Systems, another graphics card manufacturer that was an early v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to integrated graphics. A graphics processing unit that performs the necessary computations is the main component of a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the central processing unit. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and CUDA allow using graphics cards for general-purpose computing. Applications of general-purpose computing on graphics cards include AI training, cryptocurrency mining, and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in one or more integrated circuits known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance. Computers In computing, the term ''chipset'' commonly refers to a set of specialized chips on a computer's motherboard or an expansion card. In personal computers, the first chipset for the IBM PC AT of 1984 was the NEAT chipset developed by Chips and Technologies for the Intel 80286 CPU. In home computers, game consoles, and arcade-game hardware of the 1980s and 1990s, the term chipset was used for the custom audio and graphics chips. Examples include the Commodore Amiga's Original Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Designs
Sigma Designs was an American public corporation that designed and built high-performance system-on-a-chip semiconductor technologies for Internet-based set-top boxes, DVD players/recorders, high-definition televisions, media processors, digital media adapters, portable media players and home connectivity products. In addition to platform processing and home network hardware, Sigma Designs also offered engineering support services and customized integrated circuit development. The company developed products for the following connected media platforms: IPTV (video over IP) set-top boxes, TV media players (such as Blu-ray), HDTVs, multimedia players, digital media adapters, portable media players, and home networking products, such as HomePlug AV, HomePNA and G.hn. Sigma Designs owns the intellectual property and was one of two chip makers for the Z-Wave home control technology. Sigma had alliances with other technology companies, including Microsoft, and their products are foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC Compatibles
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones. The term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, since IBM no longer sells personal computers after it sold its personal computer division in 2005 to Chinese technology company Lenovo. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "personal computer" generally, but rather an x86 computer capable of running the same software that a contemporary IBM PC could. The term was initially in contrast to the variety of home computer systems available in the early 1980s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore 64. Later, the term was primarily used in contrast to Apple's Macintosh computers. These "clones" duplicated almost all the significant features of the original IBM PC architectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. Originally referred to as the PC bus (8-bit) or AT bus (16-bit), it was also termed ''I/O Channel'' by IBM. The ISA term was coined as a retronym by competing PC-clone manufacturers in the late 1980s or early 1990s as a reaction to IBM attempts to replace the AT-bus with its new and incompatible Micro Channel architecture. The 16-bit ISA bus was also used with 32-bit processors for several years. An attempt to extend it to 32 bits, called Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA), was not very successful, however. Later buses such as VESA Local Bus and PCI were used instead, often along with ISA slots on the same mainboard. Derivatives of the AT bus structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Channel Architecture
Micro Channel architecture, or the Micro Channel bus, is a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers until the mid-1990s. Its name is commonly abbreviated as "MCA", although not by IBM. In IBM products, it superseded the ISA bus and was itself subsequently superseded by the PCI bus architecture. Background The development of Micro Channel was driven by both technical and business pressures. Technology The IBM AT bus, which later became known as the Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus, had a number of technical design limitations, including: * A slow bus speed. * A limited number of interrupts, fixed in hardware. * A limited number of I/O device addresses, also fixed in hardware. * Hardwired and complex configuration with no conflict resolution. * Deep links to the architecture of the 80x86 chip familyUse of the ISA bus outside of machines employing the 80x86 CPU family was rare. Notable non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IBM Personal Computer Models
The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, spanned multiple models in its first generation (including the PCjr, the Portable PC, the XT, the AT, the Convertible, and the /370 systems, among others), from 1981 to 1987. It eventually gave way to many splintering product lines after IBM introduced the Personal System/2 in April 1987. Notes ; Legend Models Original line Successor lines * Personal System/2 ( list of models) * Industrial System ( list of models) * PCradio ( list of models) * Ambra ( list of models) * PS/note ( list of models) * EduQuest ( list of models) * ThinkPad * PS/ValuePoint ( list of models) * Aptiva ( list of models) * PC Series ( list of models) * NetVista * ThinkCentre Timeline See also * Predecessors to the IBM PC: ** IBM 5100 (1975) ** IBM 5110 (1978) ** IBM 5120 (1980) ** IBM System/23 Datamaster (1981) * Japan-only IBM PC variants: ** IBM 5550 ** IBM JX ** IBM PS/55 ** IBM Palm Top PC 110 * IBM IntelliStation * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PS/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM PC, XT, AT, and PC Convertible in IBM's lineup. Many of the PS/2's innovations, such as the 16550 UART (serial port), 1440 KB 3.5-inch floppy disk format, 72-pin SIMMs, the PS/2 port, and the VGA video standard, went on to become standards in the broader PC market. The PS/2 line was created by IBM partly in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing the advanced yet proprietary Micro Channel architecture (MCA) on higher-end models. These models were in the strange position of being incompatible with the IBM-compatible hardware standards previously established by IBM and adopted in the PC industry. However, IBM's initial PS/2 computers were popular with target market corporate buyers, and by September 1988 IBM reported that it had sold 3 million PS/2 machines. This was only 18 months after the new range had been introduced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initial Public Offering
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment banks, who also arrange for the shares to be listed on one or more stock exchanges. Through this process, colloquially known as ''floating'', or ''going public'', a privately held company is transformed into a public company. Initial public offerings can be used to raise new equity capital for companies, to monetize the investments of private shareholders such as company founders or private equity investors, and to enable easy trading of existing holdings or future capital raising by becoming publicly traded. After the IPO, shares are traded freely in the open market at what is known as the free float. Stock exchanges stipulate a minimum free float both in absolute terms (the total value as determined by the share price multiplied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
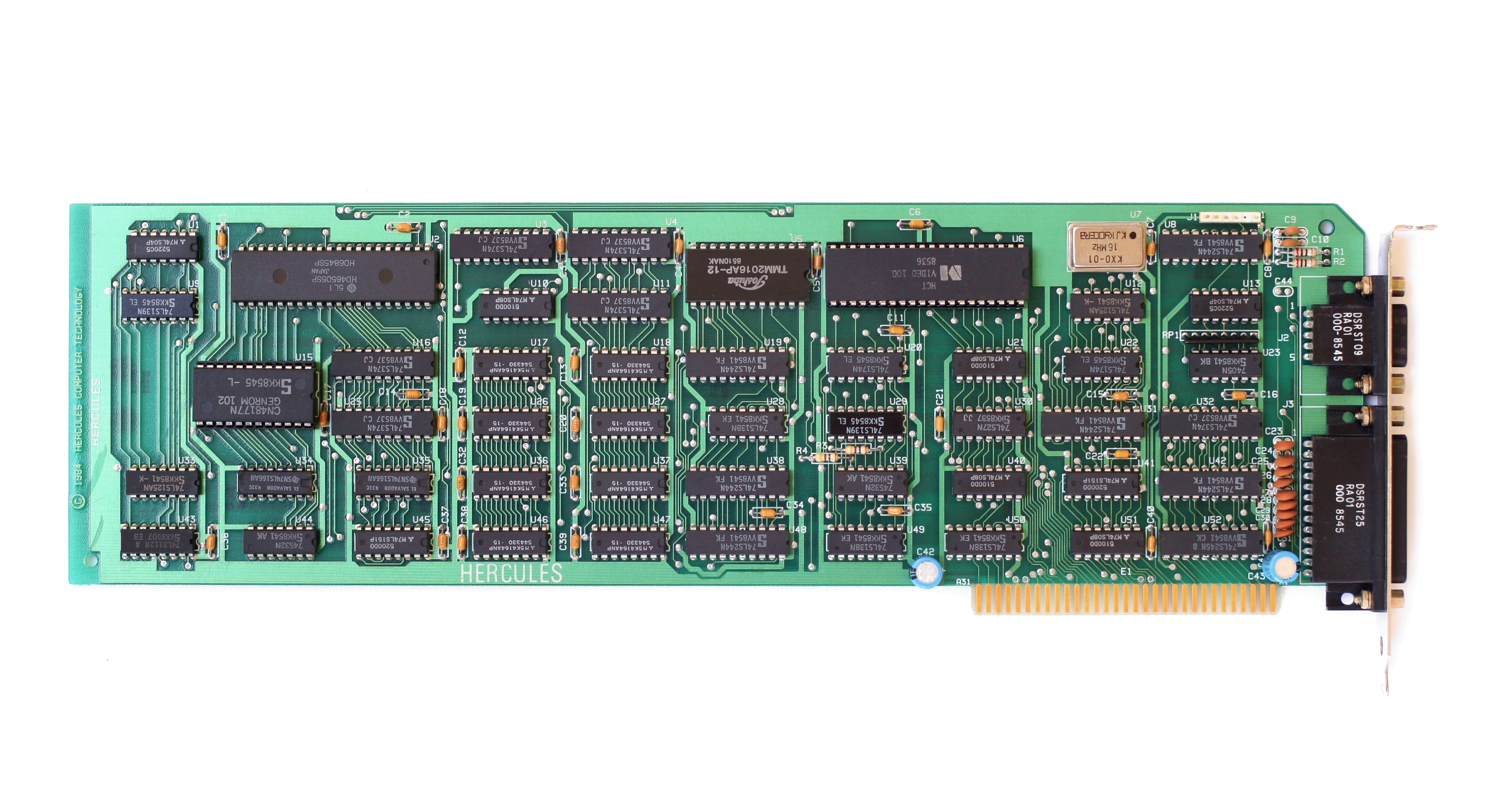
Hercules Computer Technology
Hercules Computer Technology, Inc. was a manufacturer of computer peripherals for PCs and Macs founded in 1982. History Hercules was formed in 1982 in Hercules, California, by Van Suwannukul and Kevin Jenkins and was one of the major graphics card companies of the 1980s. Its biggest products were the MDA-compatible Hercules Graphics Card (HGC) and Hercules Graphics Card Plus (HGC+) and the associated standard, which was widely copied and survived into the 1990s. The Hercules Graphics Card included a " Centronics compatible" parallel printer port, the same as the IBM Monochrome Display and Printer Adapter board that the card was based on. The company also produced CGA compatible cards, and with the unsuccessful Hercules InColor Card, it tried to go head-to-head with the Enhanced Graphics Adapter (EGA). After low sales with InColor, Hercules stopped making its own graphics core and bought graphics chipsets from other manufacturers. The company name gradually declined thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Seven Vega VGA
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems which, in turn, were replaced by flat panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcast, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. History Analog video Video technology was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) television systems, but several new technologies for video display devices have since been invented. Video was originally exclusively a live technology. Charles Ginsburg led an Ampex research team developing one of the first practical vid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadram Corporation
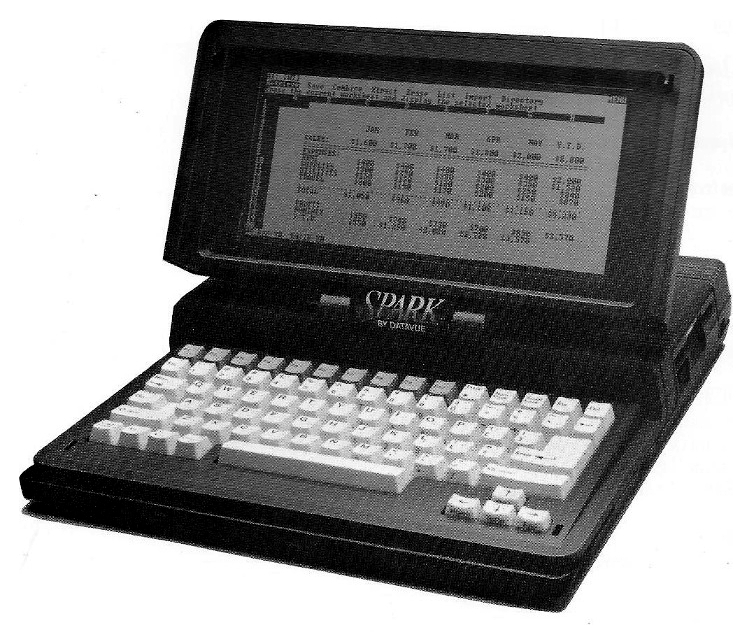
Intelligent Systems Corporation (ISC) was an American technology company that sold portable computers, video terminals, expansion cards, and other peripherals through a variety of manufacturing subsidiaries. Founded in 1973, the company restructured as a master limited partnership in 1987, becoming Intelligent Systems Master Limited Partnership. Notable subsidiaries included Datavue Corporation, which manufactured portable computers; Quadram Corporation, which manufactured expansion cards, mostly for the IBM PC, including memory and video cards; Princeton Graphics Systems, a maker of computer monitors; Intecolor Corporation, which took over Intelligent Systems's terminal manufacturing operations; and more. In the 1990s, Intelligent Systems pivoted into providing venture capital for start-up technology firms, changing its name back to Intelligent Systems Corporation. In 2021, the company changed its name to CoreCard Corporation, following another pivot to fintech. History Intec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)