|
Vernier Spectroscopy
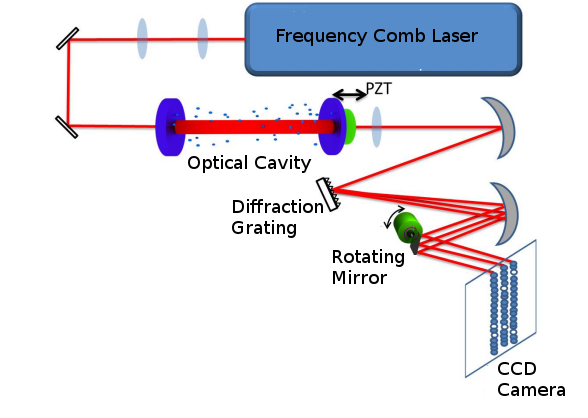
Vernier spectroscopy is a type of cavity enhanced laser absorption spectroscopy that is especially sensitive to trace gases. The method uses a frequency comb laser combined with a high finesse optical cavity to produce an absorption spectrum in a highly parallel manner. The method is also capable of detecting trace gases in very low concentration due to the enhancement effect of the optical resonator on the effective optical path length. Overview of method Understanding of the principle of operation of Vernier spectroscopy requires an understanding of frequency comb lasers. The oscillating electric field of a laser (or any time dependent signal) can be represented by a sum of sinusoidal signals in the frequency domain using the Fourier series. The oscillating electric field of a coherent, continuous-wave (cw) laser is represented as a single narrow peak in the frequency domain representation. If the laser is amplitude-modulated to produce a stable train of very short pulses (usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common arrangement is to dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Comb
In optics, a frequency comb is a laser source whose spectrum consists of a series of discrete, equally spaced frequency lines. Frequency combs can be generated by a number of mechanisms, including periodic modulation (in amplitude and/or phase) of a continuous-wave laser, four-wave mixing in nonlinear media, or stabilization of the pulse train generated by a mode-locked laser. Much work has been devoted to this last mechanism, which was developed around the turn of the 21st century and ultimately led to one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics being shared by John L. Hall and Theodor W. Hänsch in 2005. The frequency domain representation of a perfect frequency comb is a series of delta functions spaced according to : f_n = f_0 + n\,f_r, where n is an integer, f_r is the comb tooth spacing (equal to the mode-locked laser's repetition rate or, alternatively, the modulation frequency), and f_0 is the carrier offset frequency, which is less than f_r. Combs spanning an octave in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that forms a cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing modes with certain resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross-section of the beam. Many types of optical cavity produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The geometry (resonator type) must be chosen so that the beam remains sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Series
A Fourier series () is a summation of harmonically related sinusoidal functions, also known as components or harmonics. The result of the summation is a periodic function whose functional form is determined by the choices of cycle length (or ''period''), the number of components, and their amplitudes and phase parameters. With appropriate choices, one cycle (or ''period'') of the summation can be made to approximate an arbitrary function in that interval (or the entire function if it too is periodic). The number of components is theoretically infinite, in which case the other parameters can be chosen to cause the series to converge to almost any ''well behaved'' periodic function (see Pathological and Dirichlet–Jordan test). The components of a particular function are determined by ''analysis'' techniques described in this article. Sometimes the components are known first, and the unknown function is ''synthesized'' by a Fourier series. Such is the case of a discrete-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (signal strength) of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the sidebands a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that forms a cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing modes with certain resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross-section of the beam. Many types of optical cavity produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The geometry (resonator type) must be chosen so that the beam remains sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Spectral Range
Free spectral range (FSR) is the spacing in optical frequency or wavelength between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element. The FSR is not always represented by \Delta\nu or \Delta\lambda, but instead is sometimes represented by just the letters FSR. The reason is that these different terms often refer to the bandwidth or linewidth of an emitted source respectively. In general The free spectral range (FSR) of a cavity in general is given by :\left, \Delta\lambda_\text\ = \frac\left, \left(\frac\right)^ \ or, equivalently, :\left, \Delta\nu_\text\ = \frac\left, \left(\frac\right)^\ These expressions can be derived from the resonance condition \Delta \beta L = 2\pi by expanding \Delta \beta in Taylor series. Here, \beta = k_0 n(\lambda) = \fracn(\lambda) is the wavevector of the light inside the cavity, k_0 and \lambda are the wavevector and wavelength in vacuum, n is the refractive index of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernier Scale
A vernier scale, named after Pierre Vernier, is a visual aid to take an accurate measurement reading between two graduation markings on a linear scale by using mechanical interpolation, thereby increasing resolution and reducing measurement uncertainty by using vernier acuity to reduce human estimation error. It may be found on many types of instrument measuring linear or angular quantities, but in particular on a vernier caliper which measures internal or external diameter of hollow cylinders. The vernier is a subsidiary scale replacing a single measured-value pointer, and has for instance ten divisions equal in distance to nine divisions on the main scale. The interpolated reading is obtained by observing which of the vernier scale graduations is coincident with a graduation on the main scale, which is easier to perceive than visual estimation between two points. Such an arrangement can go to a higher resolution by using a higher scale ratio, known as the vernier constant. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflective grating has ridges or ''rulings'' on its surface while a transmissive grating has transmissive or hollow slits on its surface. Such a gratin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital camera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |