|
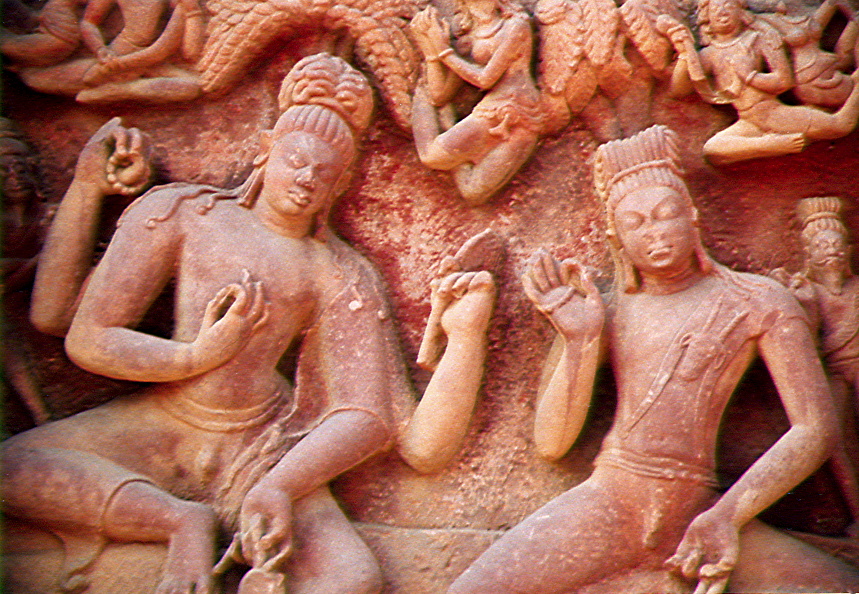
Vasishtha
Vasishtha (, ) is one of the oldest and revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis (seven great Rishis). Vasishtha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the ''Rigveda''. Vasishtha and his family are mentioned in Rigvedic verse 10.167.4, other Rigvedic mandalas and in many Vedic texts. His ideas have been influential and he was called the first sage of the Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy by Adi Shankara. The '' Yoga Vasishtha'', ''Vasishtha Samhita'', as well as some versions of the '' Agni Purana'' and ''Vishnu Purana'' are attributed to him. He is the subject of many stories, such as him being in possession of the divine cow Kamadhenu and Nandini her child, who could grant anything to their owners. He is famous in Hindu stories for his legendary conflicts with sage Vishvamitra. In the Ramayana, he was the family priest of the Raghu dynasty and teacher of Rama and his brothers. Etymology Vasishtha is also spelled as ' and is Sanskrit for "most ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arundhati (Hinduism)
Arundhati () is the wife of the sage Vasishtha, one of the seven sages (Saptarshi) of Hinduism. Etymology The name in Sanskrit literally means 'washed by the rays of sun', from 'sun rays', and , 'washed'. Legend Arundhati's birth and life are mentioned in various Hindu scriptures. The birth of Arundhati is found in the Shiva Purana and Bhagavata Purana. The instruction by Brahma to Arundhati is described in the Uttara Kanda of the Ramcharitmanas. The rivalry between Vishvamitra and Vasishtha which leads to the death of her hundred sons is described in the Balakanda of Valmiki's Ramayana. The Mahabharata and several Brahmana works describe her sons, including Shakti, and grandson Parashara. Arundhati's meetings with Sita and Rama are mentioned in the Ramayana, Ramcharitmanas and Vinaya Patrika.Rambhadracharya 1994, pp. ''iiiâvi''. Her role in pleading Shiva to marry Parvati is described in the sixth canto of Kumarasambhava of Kalidasa.Kale, pp. 197-199 As per the Bhag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamadhenu
Kamadhenu (, , ), also known as Surabhi (, or , ), is a divine bovine-goddess described in Hinduism as the mother of all cows. She is a miraculous cow of plenty who provides her owner whatever they desire and is often portrayed as the mother of other cattle. In iconography, she is generally depicted as a white cow with a female head and breasts, the wings of a bird, and the tail of a peafowl or as a white cow containing various deities within her body. Kamadhenu is not worshipped independently as a goddess. Rather, she is honored by the Hindu veneration of cows, who are regarded as her earthly embodiments. Hindu scriptures provide diverse accounts of the birth of Kamadhenu. While some narrate that she emerged from the churning of the cosmic ocean, others describe her as the daughter of the creator god Daksha, and as the wife of the sage Kashyapa. Still other scriptures narrate that Kamadhenu was in the possession of either Jamadagni or Vashista (both ancient sages), and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varuna
Varuna (; , ) is a Hindu god. He is one of the earliest deities in pantheon, whose role underwent a significant transformation from the Vedic to the Puranic periods. In the early Vedic era, Varuna is seen as the god-sovereign, ruling the sky and embodying divine authority. He is also mentioned as the king of asuras, who gained the status of a deva, serving as the chief of the Adityas, a group of celestial deities. He maintains truth and ''áđta'', the cosmic and moral order, and was invoked as an omniscient ethical judge, with the stars symbolizing his watchful eyes or spies. Frequently paired with Mitra, Varuna represents the magical and speculative aspects of sovereignty, overseeing the relationship between gods and humans. The transition from the Vedic to later periods saw Varuna's domain begin to shift from the firmament to waters. He became associated with celestial waters, marking the initial phase of his transformation. By the time of the '' Itihasa-Purana'', Varuna ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Vasistha
''Vasishta Yoga Samhita'' (, IAST: '; also known as ''MokáđĢopÄya'' or ''MokáđĢopÄyaÅÄstra'', and as ''Maha-Ramayana'', ''Arsha Ramayana'', ''VasiáđĢáđha Ramayana'', ''Yogavasistha-Ramayana'' and ''Jnanavasistha'', is a historically popular and influential syncretic philosophical text of Hinduism, dated to the 11thâ14th century CE. According to Mainkar, writing in 1977, the text started as an Upanishad, which developed into the ''Laghu Vasistha'', incorporating Buddhist ideas, and then, between 1150 and 1250, the ''Yoga Vasistha'', incorporating Shaivite Trika ideas. According to Slaje, writing in the 2000s, the ''MokáđĢopÄya'' was written in Kashmir in the 10th century. According to Hanneder and Slaje, the ''MokáđĢopÄya'' was later (11th to the 14th century) modified, showing influences from the Saivite Trika school, resulting in the ''YogavÄsiáđĢáđha'', which became an orthodox text in Advaita Vedanta. The text is attributed to Maharishi Valmiki, but the real author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urvashi
Urvashi (, ) is the most prominent apsara mentioned in the Hindu scriptures like the ''Vedas'', the epics ''Ramayana'' and ''Mahabharata'', as well as the ''Puranas''. She is regarded as the most beautiful of all the apsaras, and an expert dancer. Urvashi has been featured in many mythological events. She emerged out of the thigh of sage Narayana and occupies a special place in the court of Indra, the king of the gods and ruler of svarga. She is famous for her marriage with Pururavas, the first king of the legendary ''Chandravamsha'', whom she later abandoned. She also plays a significant part in the birth of Vashishtha and Agastya, two of the most revered sages in Hinduism. Urvashi's story has been an inspiration for various arts, performances and literature. The poet Kalidasa (fl. 4th -5th century CE) has adapted Urvashi and Pururavas as the main characters in his play Vikramorvashiyam. Etymology The Sanskrit name ''"UrvaÅÄŦ"'' is derived from roots''uru'' and ''aÅ''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
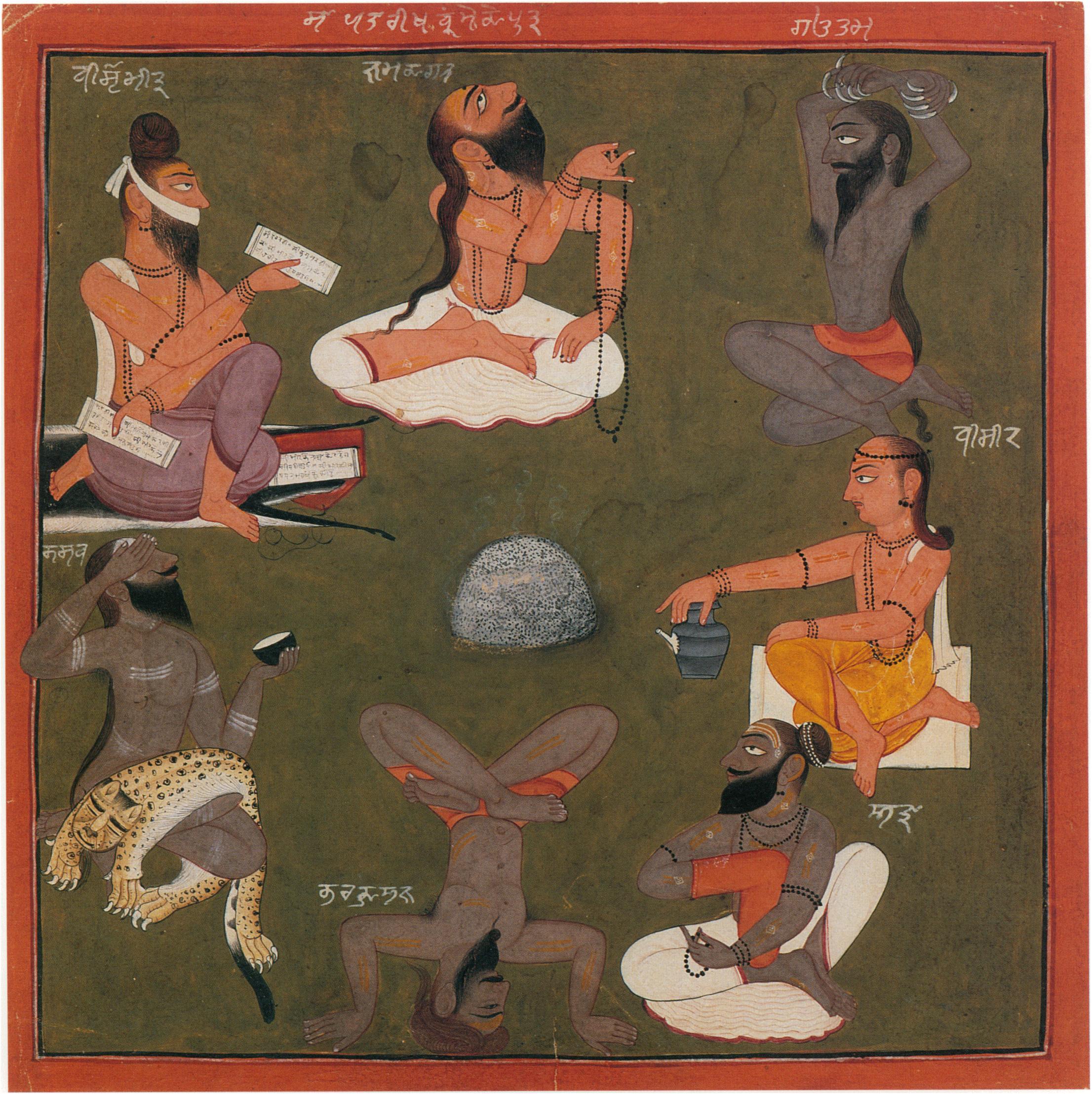
Saptarishi
The Saptarshi ( ) are the seven seers of ancient India who are extolled in the Vedas, and other Hindu literature such as the Skanda Purana. The Vedic Samhitas never enumerate these rishis by name, although later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do, so these constellations are easily recognizable. Hindu sacred text An early prototype of the "Saptarishi" concept may stem from the six families associated with the six "Family Books" in the Rigveda Samhita (Mandalas 2â7 in ascending order: GáđtsamÄda, ViÅvÄmitra, VÄmadeva, Atri, Bharadvaja, VasiáđĢáđha). While not a "Family Book", Mandala 8 is mostly attributed to Kaáđva, who could be considered the 7th prototypical Saptarishi. The earliest formal list of the seven rishis is given by Jaiminiya Brahmana 2.218â221: Agastya, Atri, Bhardwaja, Gautama, Jamadagni, Vashistha, and Vishvamitra followed by Brihadaranyaka Upanisad 2.2.6 with a slightly different list: Atri, Bharadvaja, Gautama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:āĪāĪāĨ, āĪāĪāĨ, "praise" and wikt:āĪĩāĨāĪĶ, āĪĩāĨāĪĶ, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sÅŦktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''Åruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Shakala Shakha, Åakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. Most scholars believe that the sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted with precision since the 2nd millennium BCE, through Indian mathematics#Styles of memorisation, methods of memorisation of exceptional complexity, rigour and fidelity, though the dates are not confirmed and remain contentious till concrete evidence surfaces. Philolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saptarshi
The Saptarshi ( ) are the seven seers of ancient India who are extolled in the Vedas, and other Hindu literature such as the Skanda Purana. The Vedic Samhitas never enumerate these rishis by name, although later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do, so these constellations are easily recognizable. Hindu sacred text An early prototype of the "Saptarishi" concept may stem from the six families associated with the six "Family Books" in the Rigveda Samhita (Mandalas 2â7 in ascending order: GáđtsamÄda, ViÅvÄmitra, VÄmadeva, Atri, Bharadvaja, VasiáđĢáđha). While not a "Family Book", Mandala 8 is mostly attributed to Kaáđva, who could be considered the 7th prototypical Saptarishi. The earliest formal list of the seven rishis is given by Jaiminiya Brahmana 2.218â221: Agastya, Atri, Bhardwaja, Gautama, Jamadagni, Vashistha, and Vishvamitra followed by Brihadaranyaka Upanisad 2.2.6 with a slightly different list: Atri, Bharadvaja, Gautama, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudas
''For other uses, see Suda (other) and Souda (other) SudÄs Paijavana was an Indo-Aryan tribal king of the Bharatas, during the main or middle Rigvedic period (c. 14th century BCE). He led his tribe to victory in the Battle of the Ten Kings near the ParuáđĢáđÄŦ (modern Ravi River) in Punjab, defeating an alliance of the powerful Puru tribe with other tribes, for which he was eulogized by his purohita Vashistha in a hymn of the Rigveda. His victory established the ascendency of the BhÄrata clan, allowing them to move eastwards and settle in Kurukshetra, paving the way for the emergence of the Kuru "super-tribe" or tribal union, which dominated northern India in the subsequent period. Family SudÄs' ancestors include Pijavana, DivodÄsa Atithigva, and Devavant, although scholars disagree regarding the order of these ancestors chronologically. According to Witzel, DivodÄsa was the father of SudÄs, but he includes Pijavana on the grid of Bharata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purohita
Purohita (), in the Hindu context, means '' chaplain'' or ''family priest'' within the Vedic priesthood. In Thailand and Cambodia, it refers to the royal chaplains. A ''tÄŦrthapurohit'' is a priest/ritual performer (''purohit'') at a sacred site (''tÄŦrtha''). Etymology The word ''purohita'' derives from the Sanskrit, ''puras'' meaning "front", and ''hita'', "placed". The word is also used synonymously with the word '' pandit'', which also means "priest". '' Tirtha purohita'' means the ''purohita'' who sit at the fords of the holy rivers or holy tanks and who have maintained the records of the forefathers of the Hindu family for thousands of years. ''Purohita'' can refer to a house priest. Another less-formal name for teerth purohits is ''panda'', which is derived from the word ''pandit'' (from the Sanskrit ''paáđáļita'', meaning "learned man"). Education In India, literate men from the Brahmin varna who desire to become ''purohitas'' receive special training both in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryÄda'' ''puruáđĢottama''), Rama is the male protagonist of the Hindu epic '' Ramayana''. His birth is celebrated every year on Rama Navami, which falls on the ninth day of the bright half ( Shukla Paksha) of the lunar cycle of Chaitra (MarchâApril), the first month in the Hindu calendar. According to the ''Ramayana'', Rama was born to Dasaratha and his first wife Kausalya in Ayodhya, the capital of the Kingdom of Kosala. His siblings included Lakshmana, Bharata, and Shatrughna. He married Sita. Born in a royal family, Rama's life is described in the Hindu texts as one challenged by unexpected changes, such as an exile into impoverished and difficult circumstances, and challenges of ethical questions and moral dilemmas. The most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Åakti MaharáđĢi
In Hinduism, Shakti was a rishi (sage) and son of Vashistha and Arundhati. He was the father of Parashara, mentioned in the epic ''Mahabharata''. There is a legend found in ''Mahabharata'' about Shakti. Once King Kalmashapada, going hunting, killed many animals. Tired and being hungry and thirsty, he was proceeding through the woods. On the way, Shakti came on the same path, from the opposite direction. The King ordered him to get out of his way. The Rishi addressed the King sweetly and said "O king, this is my way". In accordance with duty and tradition, a king should always make way for Brahmins. The king persisted in acting like a Rakshasa (demon). The Rishi cursed the king thus: "O worst of the worst kings, since thou persecutest an ascetic, like a Rakshasa, thou shalt from this day, became a Rakshasa subsisting on human flesh! Henceforth, O worst of kings! thou shalt wander over the earth, affecting human form!". He was the grandfather of Vyasa, author of the Indian epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |