|
Vanguard 2
Vanguard 2 (or Vanguard 2E before launch) is an Earth-orbiting satellite launched 17 February 1959 at 15:55:02 GMT, aboard a Vanguard SLV-4 rocket as part of the United States Navy's Project Vanguard. The satellite was designed to measure cloud cover distribution over the daylight portion of its orbit, for a period of 19 days, and to provide information on the density of the atmosphere for the lifetime of its orbit (about 300 years). As the first weather satellite and one of the first orbital space missions, the launch of Vanguard 2 was an important milestone in the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Vanguard 2 remains in orbit. upright=1.3, The Vanguard 2 satellite sketch Previous satellites Before the successful 1959 launch of the satellite that became known as Vanguard 2, multiple attempted launches of satellites named "Vanguard 2" were made in 1958. All of these launches failed to reach orbit. The satellites that failed to reach orbit were: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously) or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanguard 2 Satellite Sketch
The vanguard (sometimes abbreviated to van and also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force. In naval warfare the van is the advance ship, or fleet, that will make the initial engagement with an enemy fleet. History The vanguard derives from the traditional division of a medieval army into three battles or ''wards''; the Van, the Main (or Middle), and the Rear. The term originated from the medieval French ''avant-garde'', i.e. "the advance guard". The vanguard would lead the line of march and would deploy first on the field of battle, either in front of the other wards or to the right if they deployed in line. The makeup of the vanguard of a 15th century Burgundian army is a typical example. This consisted of: *A contingent of foreriders, from whom a forward detachment of scouts was drawn; *The main body of the vanguard, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecraft (nonfunctional spacecraft and abandoned launch vehicle stages), mission-related debris, and particularly numerous in-Earth orbit, fragmentation debris from the breakup of derelict rocket bodies and spacecraft. In addition to derelict human-made objects left in orbit, space debris includes fragments from disintegration, erosion, or collisions; solidified liquids expelled from spacecraft; unburned particles from solid rocket motors; and even paint flecks. Space debris represents a risk to spacecraft. Space debris is typically a negative externality. It creates an external cost on others from the initial action to launch or use a spacecraft in near-Earth orbit, a cost that is typically not taken into account nor fully accoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
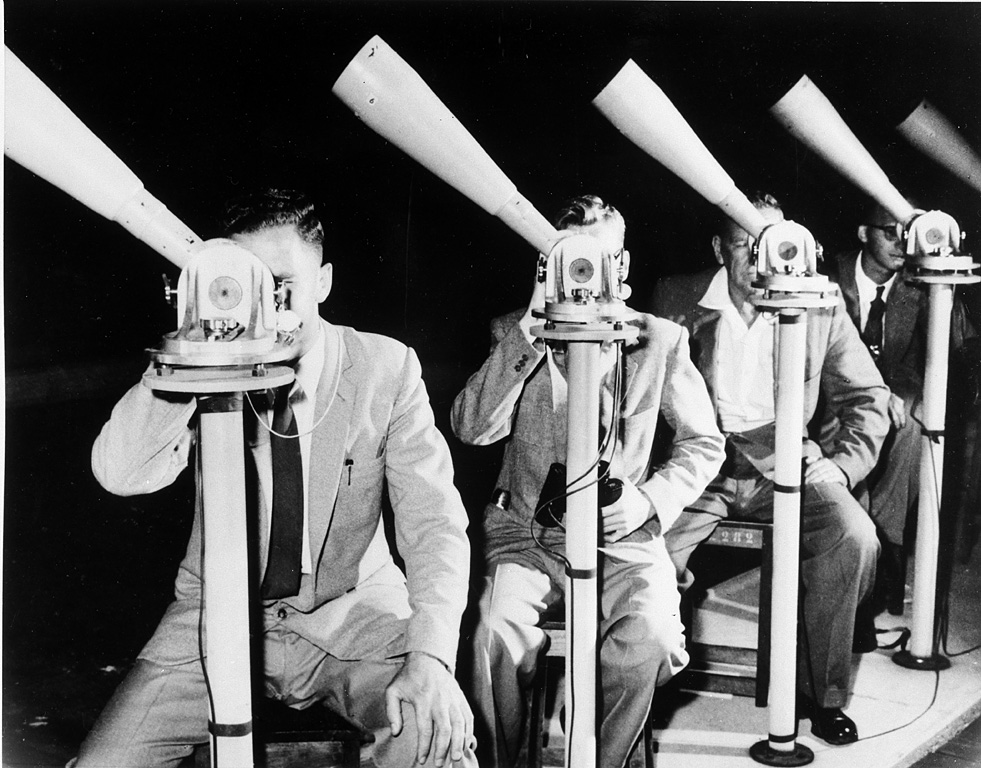
Operation Moonwatch
Operation Moonwatch (also known as ''Project Moonwatch'' and, more simply, as ''Moonwatch'') was an amateur science program formally initiated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) in 1956. The SAO organized Moonwatch as part of the International Geophysical Year (IGY) which was probably the largest single scientific undertaking in history. Its initial goal was to enlist the aid of amateur astronomers and other citizens who would help professional scientists spot the first artificial satellites. Until professionally staffed optical tracking stations came on-line in 1958, this network of amateur scientists and other interested citizens played a critical role in providing crucial information regarding the world's first satellites. Origins of Moonwatch Moonwatch's origins can be traced to two sources. In the United States, there was a thriving culture of amateur scientists including thousands of citizens who did astronomy for an avocation. During the Cold War, the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Camera
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Some notable examples are the Samuel Oschin telescope (formerly Palomar Schmidt), the UK Schmidt Telescope and the ESO Schmidt; these provided the major source of all-sky photographic imaging from 1950 until 2000, when electronic detectors took over. A recent example is the Kepler space telescope exoplanet finder. Other related designs are the Wright camera and Lurie–Houghton telescope. Invention and design The Schmidt camera was invented by Estonian-German optician Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Its optical components are an easy-to-make spherical primary mirror, and an aspherical correcting lens, known as a Schmidt corrector plate, located at the center of curvature of the primary mirror. The film or other detector is placed inside the camera, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whisk Broom Scanner
A whisk broom or spotlight sensor, also known as an across-track scanner, is a technology for obtaining satellite images with optical cameras. It is used for passive remote sensing from space. In a whisk broom sensor, a mirror scans across the satellite’s path (ground track), reflecting light into a single detector which collects data one pixel at a time. The moving parts make this type of sensor expensive and more prone to wearing out, such as in the Landsat 7. Whisk broom scanners have the effect of stopping the scan, and focusing the detector on one part of the swath width. Because the detector is only focused on a subsection of the full swath at any time, it typically has a higher resolution than a push broom design for the same size of scan swath. All sensors aboard the Landsat series of satellites used the whisk broom design until Landsat 8 Landsat 8 is an American Earth observation satellite launched on 11 February 2013. It is the eighth satellite in the Landsat p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
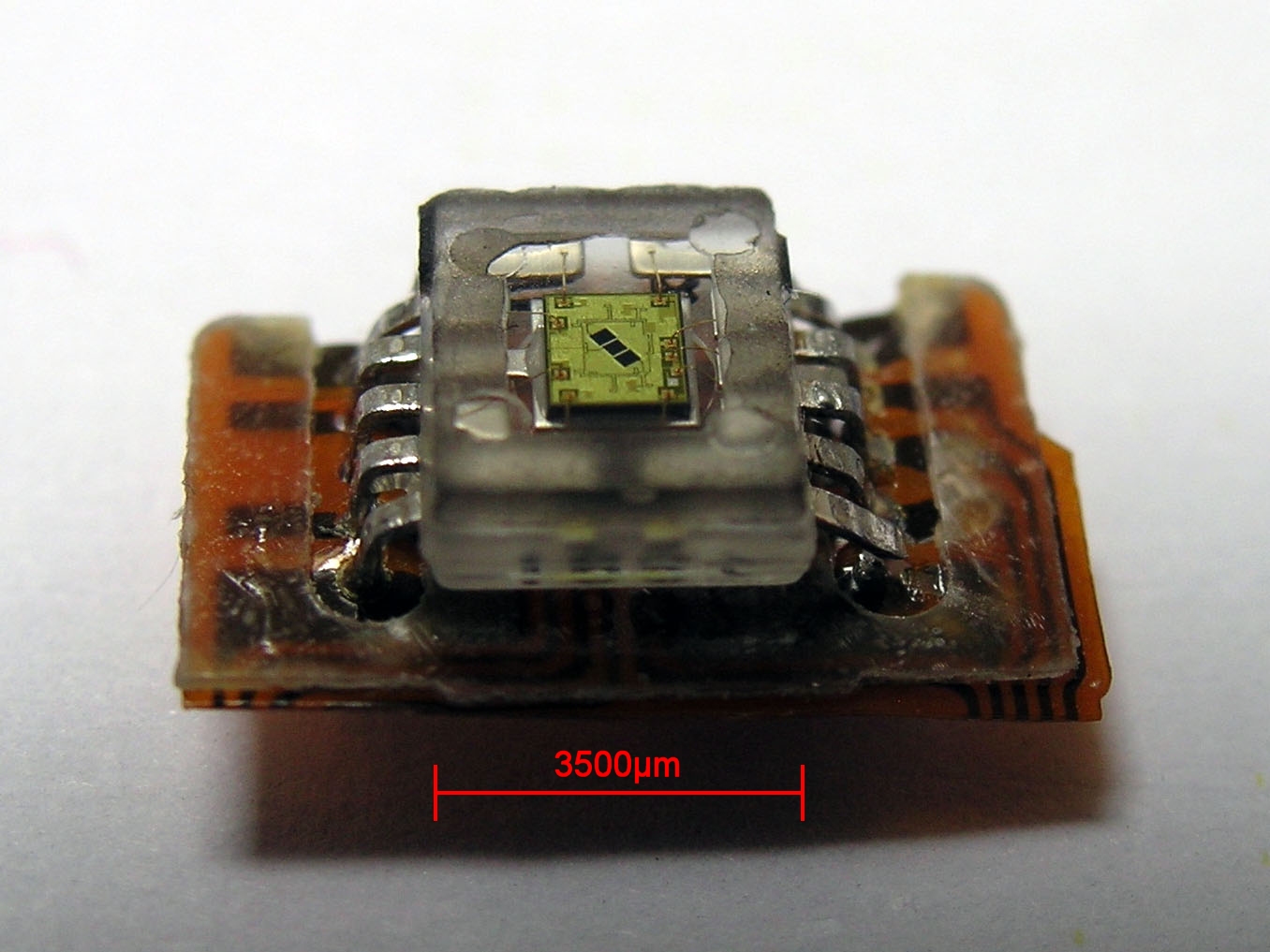
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical communication to scientific research and industrial automation. Photodetectors can be classified by their mechanism of detection, such as the photoelectric effect, photochemical reactions, or thermal effects, or by performance metrics like spectral response. Common types include photodiodes, phototransistors, and photomultiplier tubes, each suited to specific uses. Solar cells, which convert light into electricity, are also a type of photodetector. This article explores the principles behind photodetectors, their various types, applications, and recent advancements in the field. History The development of photodetectors began with the discovery of the photoelectric effect by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, later explained by Albert Einst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Battery
A mercury battery (also called mercuric oxide battery, mercury cell, button cell, or Ruben-Mallory) is a non-rechargeable electrochemical battery, a primary cell. Mercury batteries use a reaction between mercuric oxide and zinc electrodes in an alkaline electrolyte. The voltage during discharge remains practically constant at 1.35 volts, and the capacity is much greater than that of a similarly sized zinc-carbon battery. Mercury batteries were used in the shape of button cells for watches, hearing aids, cameras and calculators, and in larger forms for other applications. For a time during and after World War II, batteries made with mercury became a popular power source for portable electronic devices. Due to the content of toxic mercury and environmental concerns about its disposal, the sale of mercury batteries is now banned in many countries. Both ANSI and IEC have withdrawn their standards for mercury batteries. History The mercury oxide-zinc battery system was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', and ''metron'', 'measure'. Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry: telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Thermal Control
In spacecraft design, the function of the thermal control system (TCS) is to keep all the spacecraft's component systems within acceptable temperature ranges during all mission phases. It must cope with the external environment, which can vary in a wide range as the spacecraft is exposed to the extreme coldness found in the shadows of deep space or to the intense heat found in the unfiltered direct sunlight of outer space. A TCS must also moderate the internal heat generated by the operation of the spacecraft it serves. A TCS can eject heat passively through the simple and natural infrared radiation of the spacecraft itself, or actively through an externally mounted infrared radiation coil. Thermal control is essential to guarantee the optimal performance and success of the mission because if a component is subjected to temperatures which are too high or too low, it could be damaged or its performance could be severely affected. Thermal control is also necessary to keep specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoresistor
A photoresistor (also known as a light-dependent resistor, LDR, or photo-conductive cell) is a passive component that decreases in resistance as a result of increasing luminosity (light) on its sensitive surface, in other words, it exhibits photoconductivity. A photoresistor can be used in light-sensitive detector circuits and light-activated and dark-activated switching circuits acting as a semiconductor resistance. In the dark, a photoresistor can have a resistance as high as several megaohms (MΩ), while in the light, it can have a resistance as low as a few hundred ohms. If incident light on a photoresistor exceeds a certain frequency, photons absorbed by the semiconductor give bound electrons enough energy to jump into the conduction band. The resulting free electrons (and their hole partners) conduct electricity, thereby lowering resistance. The resistance range and sensitivity of a photoresistor can substantially differ among dissimilar devices. Moreover, unique photor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |