|
Vanadium(V) Chloride
Vanadium(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl5. It is a black diamagnetic solid. The molecules adopt a bioctahedral structure similar to that of niobium(V) chloride. Preparation and reactions Vanadium(V) chloride is prepared from the vanadium pentafluoride with excess boron trichloride: :2 VF5 + 10 BCl3 → Cl5sub>2 + 10 BF2Cl It is unstable at room temperature with respect to vanadium(IV) chloride Vanadium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula V Cl4. This bright red liquid serves as a useful reagent for the preparation of other vanadium compounds. Synthesis, bonding, basic properties With one more valence electron tha ...: : Cl5sub>2 → 2 VCl4 + Cl2 In contrast, the heavier analogues NbCl5 and TaCl5 are stable and not particularly oxidizing. References {{Chlorides Vanadium(V) compounds Chlorides Metal halides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer (chemistry)
A dimer () (''di-'', "two" + ''-mer'', "parts") is an oligomer consisting of two monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak, covalent or intermolecular. Dimers also have significant implications in polymer chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and biochemistry. The term ''homodimer'' is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A) and ''heterodimer'' when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerization is often called dissociation. When two oppositely charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as ''Bjerrum pairs'', after Niels Bjerrum. Noncovalent dimers Anhydrous carboxylic acids form dimers by hydrogen bonding of the acidic hydrogen and the carbonyl oxygen. For example, acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. Excimers and exciplexes are excited structures with a short life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon ( graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
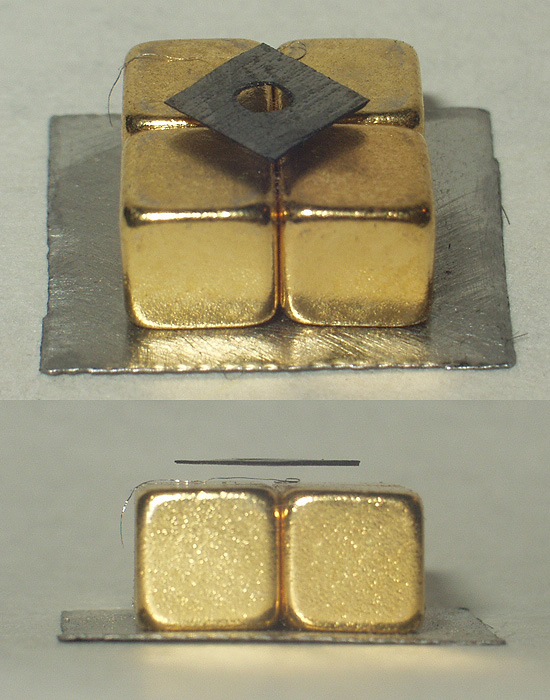
Diamagnetic
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it repels a magnetic field entirely from its interior. Diamagnetism was first discovered when Anton Brugmans observed in 1778 that bismuth was repel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioctahedral
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix ''octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Werne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium(V) Chloride
Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation. Structure and properties Niobium(V) chloride forms chloro-bridged dimers in the solid state (''see'' figure). Each niobium centre is six-coordinate, but the octahedral coordination is significantly distorted. The equatorial niobium–chlorine bond lengths are 225 pm (terminal) and 256 pm (bridging), whilst the axial niobium-chlorine bonds are 229.2 pm and are deflected inwards to form an angle of 83.7° with the equatorial plane of the molecule. The Nb–Cl–Nb angle at the bridge is 101.3°. The Nb–Nb distance is 398.8 pm, too long for any metal-metal interaction. NbBr5, TaCl5 and TaBr5 are isostructural with NbCl5, but NbI5 and TaI5 have different structures. Preparation Industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium Pentafluoride
Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances. Properties and structure The compound is exclusively a monomer in the gas phase. In the gas phase it adopts D3h symmetric trigonal bipyramidal geometry as indicated by electron diffraction. As a solid, VF5 forms a polymeric structure with fluoride-bridged octahedral vanadium centers. The formation enthalpy of VF5 is -1429.4 ± 0.8 kJ/mol. It is the only known pentahalide of vanadium. Synthesis Vanadium pentafluoride can be prepared by fluorination of vanadium metal: : 2 V + 5 F2 → 2 VF5 Alternatively, disproportionation of vanadium tetrafluoride yields equal amounts of the solid trifluoride and the volatile pentafluoride: :2 VF4 → VF3 + VF5 This conversion is conducted at 650 °C. It can also be synthesized by using elemental fluorine to fluorinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trichloride
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive toward water. Production and structure Boron reacts with halogens to give the corresponding trihalides. Boron trichloride is, however, produced industrially by direct chlorination of boron oxide and carbon at 501 °C. :B2O3 + 3 C + 3 Cl2 → 2 BCl3 + 3 CO The carbothermic reaction is analogous to the Kroll process for the conversion of titanium dioxide to titanium tetrachloride. In the laboratory BF3 reacted with AlCl3 gives BCl3 via halogen exchange. BCl3 is a trigonal planar molecule like the other boron trihalides, and has a bond length of 175pm. A degree of π-bonding has been proposed to explain the short B− Cl distance although there is some debate as to its extent. It does not dimerize, although NMR studies of mixtures of boron trihalides shows the presence of mixed halides. The absence of dimerisation contrasts with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(IV) Chloride
Vanadium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula V Cl4. This bright red liquid serves as a useful reagent for the preparation of other vanadium compounds. Synthesis, bonding, basic properties With one more valence electron than diamagnetic TiCl4, VCl4 is a paramagnetic liquid. It is one of only a few paramagnetic compounds that is liquid at room temperature. VCl4 is prepared by chlorination of vanadium metal. VCl5 does not form in this reaction; Cl2 lacks the oxidizing power to attack VCl4. VCl5 can however be prepared indirectly from VF5 at −78 °C. In contrast, the heavier analogues NbCl5 and TaCl5 are stable and not particularly oxidizing. VF5 can be prepared directly by fluorination of vanadium metal, reflecting the increased oxidizing power of F2 vs Cl2. Indicative of its oxidizing power, VCl4 releases Cl2 at its boiling point (standard pressure) to afford VCl3. Reactions Consistent with its high oxidizing power, VCl4 reacts with HBr at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium(V) Chloride
Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation. Structure and properties Niobium(V) chloride forms chloro-bridged dimers in the solid state (''see'' figure). Each niobium centre is six-coordinate, but the octahedral coordination is significantly distorted. The equatorial niobium–chlorine bond lengths are 225 pm (terminal) and 256 pm (bridging), whilst the axial niobium-chlorine bonds are 229.2 pm and are deflected inwards to form an angle of 83.7° with the equatorial plane of the molecule. The Nb–Cl–Nb angle at the bridge is 101.3°. The Nb–Nb distance is 398.8 pm, too long for any metal-metal interaction. NbBr5, TaCl5 and TaBr5 are isostructural with NbCl5, but NbI5 and TaI5 have different structures. Preparation Industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantalum(V) Chloride
Tantalum(V) chloride, also known as tantalum pentachloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula TaCl5. It takes the form of a white powder and is commonly used as a starting material in tantalum chemistry. It readily hydrolyzes to form tantalum(V) oxychloride (TaOCl3) and eventually tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5); this requires that it be synthesised and manipulated under anhydrous conditions, using air-free techniques. Structure TaCl5 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group ''C''2/''m''. The ten chlorine atoms define a pair of octahedra that share a common edge. The tantalum atoms occupy the centres of the octahedra and are joined by two chlorine bridging ligands. The dimeric structure is retained in non-complexing solvents and to a large extent in the molten state. In the vapour state, however, TaCl5 is monomeric. This monomer adopts a trigonal bipyramidal structure, like that of PCl5. Physical Properties The solubility of tantalum pentachloride increases slightly fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(V) Compounds
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spanish scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 in Mexico by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio's lead mineral was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorides
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word ''chloride'' may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane (see IUPAC books) is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion. Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |