|
VERITAS (spacecraft)
VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy) is an upcoming mission from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to map the surface of the planet Venus in high resolution. The combination of topography, near-infrared spectroscopy, and radar image data will provide knowledge of Venus's tectonic and impact history, gravity, geochemistry, the timing and mechanisms of Volcanism on Venus, volcanic resurfacing, and the mantle processes responsible for them. On 4 November 2022, NASA announced the postponement of the mission launch from 2027 to 2031, citing institutional problems at JPL delaying the launch of Psyche (spacecraft), Psyche. The mission's Principal Investigator Suzanne Smrekar has counterproposed a November 2029 launch date, which she argued would require only modest "bridge" funding and compared to the 2031 option would offer lower overall cost and fewer conflicts with DAVINCI and EnVision; this position obtained endorsement by a Congressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the Sublimation (phase transition), sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds and fog. Being a component of Earth's hydrosphere and hydrologic cycle, it is particularly abundant in Earth's atmosphere, where it acts as a greenhouse gas and warming feedback, contributing more to total greenhouse effect than non-condensable gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Use of water vapor, as steam, has been important for cooking, and as a major component in energy prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (, abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. The DLR acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.348 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sites, as well as offices in Brussels, Paris and Washington, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
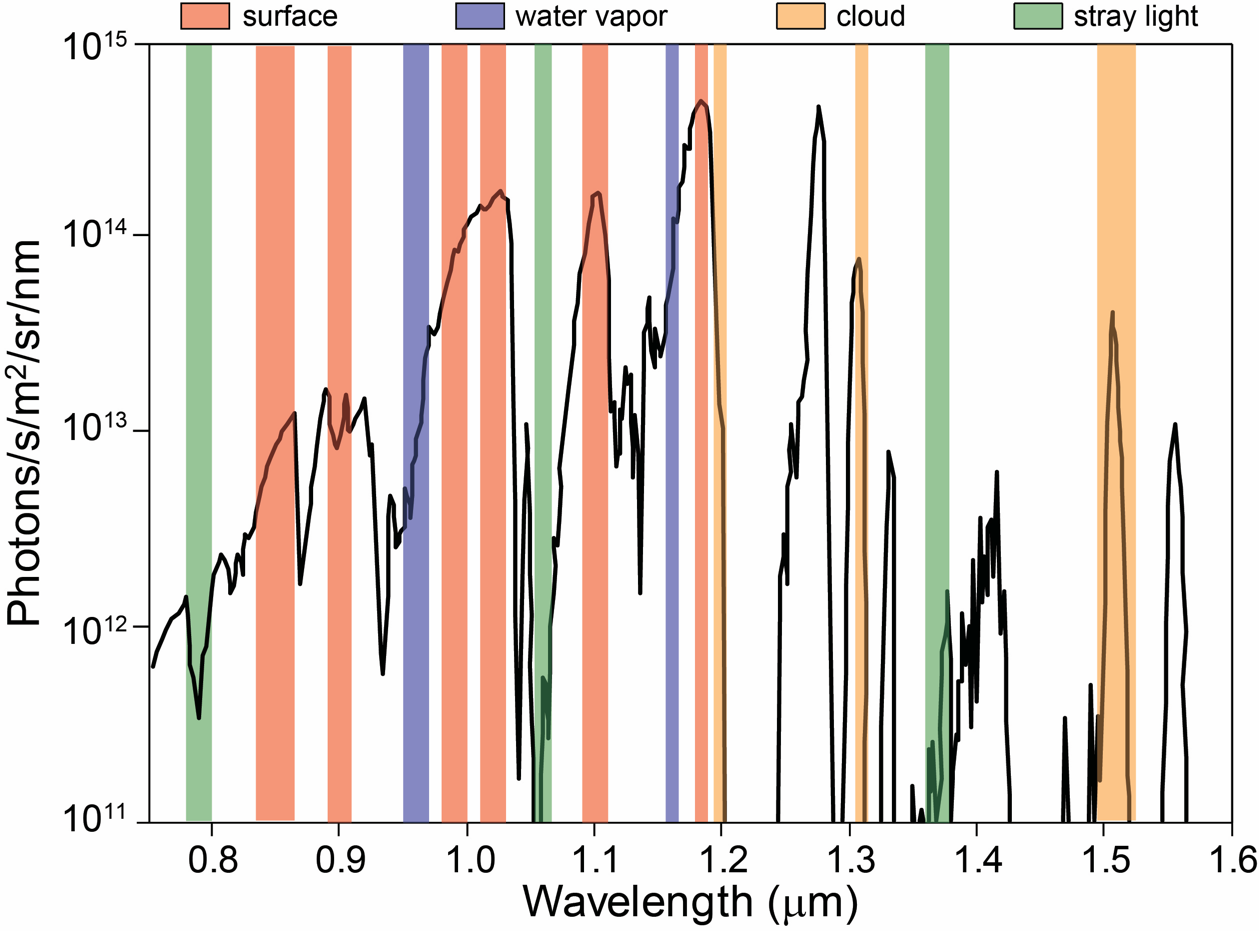
Atmospheric Window
An atmospheric window is a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can pass through the atmosphere of Earth The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather .... The Optical window, optical, Infrared window, infrared and Radio window, radio windows comprise the three main atmospheric windows. The windows provide direct channels for Earth's surface to receive electromagnetic energy from the Sun, and for thermal radiation from the surface to leave to space. Atmospheric windows are useful for Observational astronomy, astronomy, remote sensing, telecommunications and other science and technology applications. In the study of the greenhouse effect, the term ''atmospheric window'' may be limited to mean the ''infrared window'', which is the primary escape route for a fraction of the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Emissivity Mapper
The Venus Emissivity Mapper (VEM) is a spectrometer for mapping the surface composition of Venus through a distinct number of atmospheric spectral windows. It will be one of the two payloads onboard the ''VERITAS'' mission, and will also be the VenSpec-M channel of the ''EnVision'' mission's spectrometer suite. Overview While Earth and Venus are similar in many aspects, they evolved very differently and currently have distinct surface and atmospheric environments. Where Earth's surface has liquid water and supports life, Venus experiences a mean surface temperature of over 400 °C, and a carbon dioxide rich atmosphere with a surface pressure of about 92 times that of Earth at sea-level. Little is known about Venus' surface composition. The dense atmosphere and its cloud layers are mostly opaque to visible and infrared radiation, making remote sensing a challenge. As light travels through the atmosphere, it is attenuated by absorption and scattering, and it is blurred by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Instrument
A scientific instrument is a device or tool used for scientific purposes, including the study of both natural phenomena and theoretical research. History Historically, the definition of a scientific instrument has varied, based on usage, laws, and historical time period. Before the mid-nineteenth century such tools were referred to as "natural philosophical" or "philosophical" apparatus and instruments, and older tools from antiquity to the Middle Ages (such as the astrolabe and pendulum clock) defy a more modern definition of "a tool developed to investigate nature qualitatively or quantitatively." Scientific instruments were made by mathematical practitioner, instrument makers living near a center of learning or research, such as a university or research laboratory. Instrument makers designed, constructed, and refined instruments for purposes, but if demand was sufficient, an instrument would go into production as a commercial product. In a description of the use of the eudiomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Venus
The geology of Venus is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Venus. Within the Solar System, it is the one nearest to Earth and most like it in terms of mass, but has no magnetic field or recognizable plate tectonic system. Much of the ground surface is exposed volcanic bedrock, some with thin and patchy layers of soil covering, in marked contrast with Earth, the Moon, and Mars. Some impact craters are present, but Venus is similar to Earth in that there are fewer craters than on the other rocky planets that are largely covered by them. This is due in part to the thickness of the Venusian atmosphere disrupting small impactors before they strike the ground, but the paucity of large craters may be due to volcanic re-surfacing, possibly of a catastrophic nature. Volcanism appears to be the dominant agent of geological change on Venus. Some of the volcanic landforms appear to be unique to the planet. There are shield and composite volcanoes simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically relief, even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form ( DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Field
In physics, a gravitational field or gravitational acceleration field is a vector field used to explain the influences that a body extends into the space around itself. A gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, such as the '' gravitational force field'' exerted on another massive body. It has dimension of acceleration (L/T2) and it is measured in units of newtons per kilogram (N/kg) or, equivalently, in meters per second squared (m/s2). In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses. Following Isaac Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace attempted to model gravity as some kind of radiation field or fluid, and since the 19th century, explanations for gravity in classical mechanics have usually been taught in terms of a field model, rather than a point attraction. It results from the spatial gradient of the gravitational potential field. In general relativity, rather than two particles attracting each other, the particles distort spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multispectral Image
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range (i.e. infrared and ultraviolet). It can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis. Multispectral imaging measures light in a small number (typically 3 to 15) of spectral bands. ''Hyperspectral imaging'' is a special case of spectral imaging where often hundreds of conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |