|
Upended Sugarloaf
The Upended Sugarloaf (in German: ''Der umgestülpte Zuckerhut'') is a half-timbered house in the city of Hildesheim in the federal state of Lower Saxony in Germany. History and architecture The Upended Sugarloaf is a historic building in Saint Andrew's Place (''Andreasplatz'') in the center of Hildesheim, opposite Saint Andrew's Church. Originally, it was built in the Middle Ages between 1500 and 1510, but the exact year and the architect's name remain unknown. The shape of the building is very unusual, looking similar to an upended sugarloaf. The ground floor is 17 m² in space, the first floor is larger and the second floor covers 29 m². Destruction In the Second World War, the ''Upended Sugarloaf'' was slightly damaged during an air raid on 22 February 1945. On 22 March 1945, however, the building was completely destroyed by incendiary bombs. After the war, the ''Upended Sugarloaf'' was not immediately rebuilt. The space which had been occupied by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In 2010
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Hildesheim
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
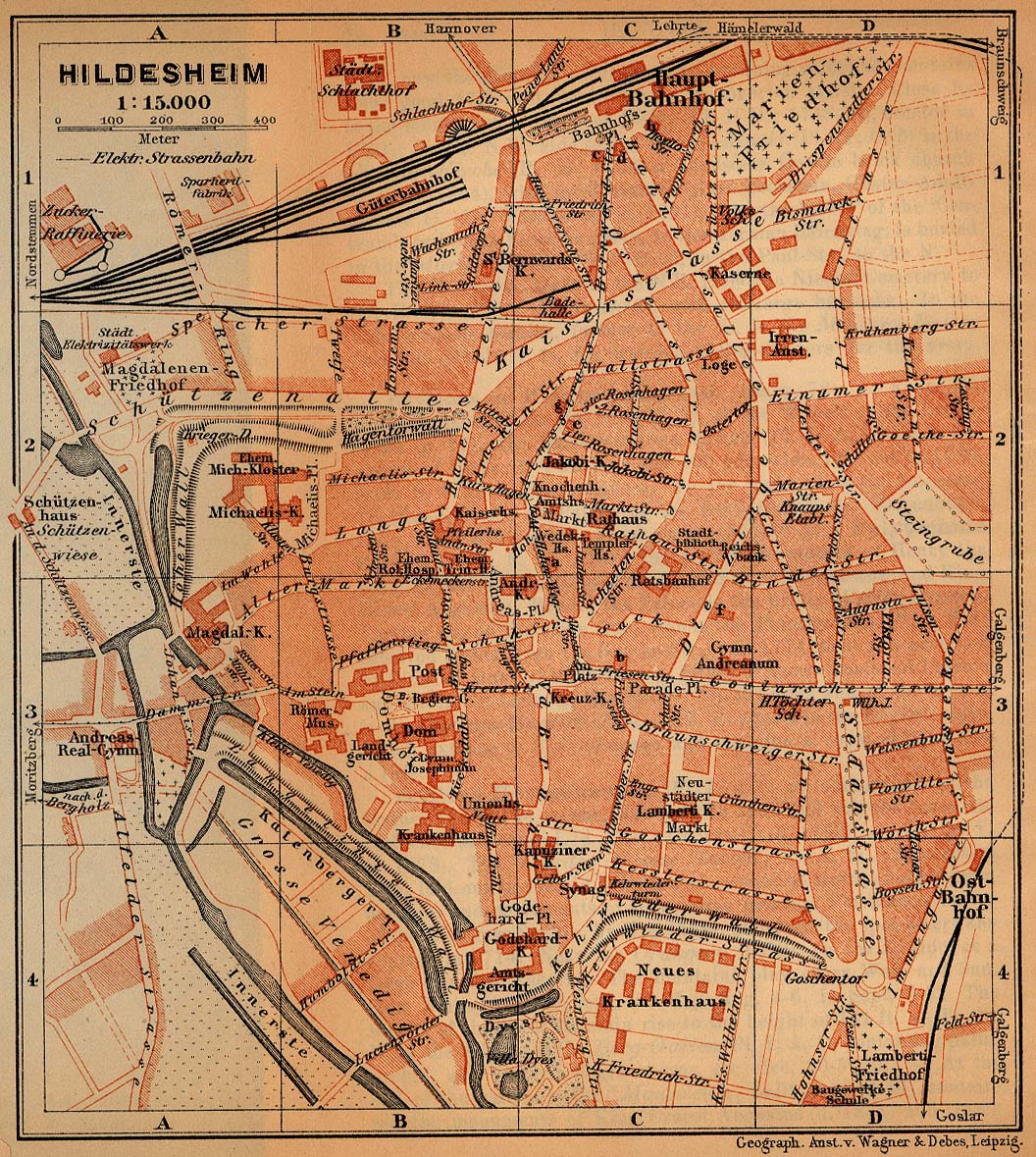
Historic Market Place, Hildesheim
The Historic Market Place is a historical structure in the city of Hildesheim in Lower Saxony, Germany History Hildesheim, one of the oldest cities in the North of Germany, was founded in 815 as a bishopric close to a ford of the river Innerste. The settlement very quickly developed into a town which was awarded market rights by King Otto III in 983. Originally the market was held in a street called Old Market (''Alter Markt'') which still exists today. The first market place was laid out around the church St. Andreas. When the city grew further, a bigger market place became necessary. The present market place of Hildesheim was laid out at the beginning of the 13th century when the city had about 5,000 inhabitants. When Hildesheim obtained city rights in 1249, it was one of the biggest cities in Northern Germany. Construction of the present City Hall started in 1268. Several impressive half-timbered houses were built in the Market Place as well. The Butchers' Guild Hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Hildesheim In World War II
The German city of Hildesheim, c. 30 kilometres south of Hanover, was the target of eight Allied air raids in 1944 and 1945 and suffered considerable bomb damage. Hildesheim during World War II In 1939 Hildesheim had about 72,000 inhabitants. For most of the war Hildesheim was regarded as a minor target by British Bomber Command mainly because the military potential of the industry in and around Hildesheim was underestimated and classified as 'minor plants in major industries, or major plants in minor industries'. However, a branch of the Vereinigte Deutsche Metallwerke (United German Metalworks) named VDM-Halbzeugwerke in the town produced aircraft parts for constant speed propellers, landing gear and aircraft engines, others were producing fuzes and tank parts (Senking-Factory), torpedoes (Ahlborn AG) and rubber products such as lifejackets and inflatable dinghies (Wetzell Gummiwerke). In the Hildesheim forest southwest of the city a subsidiary of Robert Bosch GmbH wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |