|
Ulger
Ulger (''Ulgerius''; died 1149) was the Bishop of Angers from 1125. Like his predecessor, Rainald de Martigné (died 1123), he consolidated the Gregorian reform in his diocese. Ulger was a student of Marbod and the latter's successor as archdeacon. Ulger composed a eulogy for his teacher, crediting him with bringing genius (''ingenium'') and art (''studium'') to Anjou. He also compares his master to Cicero, Virgil and Homer: "Cicero gives way to him, Virgil as well and Homer: there I may say he has defeated them equally". Shortly after becoming bishop, Ulger entered into a dispute with Glanfeuil Abbey, whose abbot, Drogo, rejected the authority of the bishop over his monastery and even had a papal bull forged to support his claim. As bishop, Ulger established several new parish churches, began renovation to Angers Cathedral and constructed a hospice at Saint-Maimboeuf. In the 1140s, Ulger also got involved in a dispute with Fontevraud Abbey, which became an international scand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulger (cropped)
Ulger (''Ulgerius''; died 1149) was the Bishop of Angers from 1125. Like his predecessor, Rainald de Martigné (died 1123), he consolidated the Gregorian reform in his diocese. Ulger was a student of Marbod and the latter's successor as archdeacon. Ulger composed a eulogy for his teacher, crediting him with bringing genius (''ingenium'') and art (''studium'') to Anjou. He also compares his master to Cicero, Virgil and Homer: "Cicero gives way to him, Virgil as well and Homer: there I may say he has defeated them equally". Shortly after becoming bishop, Ulger entered into a dispute with Glanfeuil Abbey, whose abbot, Drogo, rejected the authority of the bishop over his monastery and even had a papal bull forged to support his claim. As bishop, Ulger established several new parish churches, began renovation to Angers Cathedral and constructed a hospice at Saint-Maimboeuf. In the 1140s, Ulger also got involved in a dispute with Fontevraud Abbey, which became an international scand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
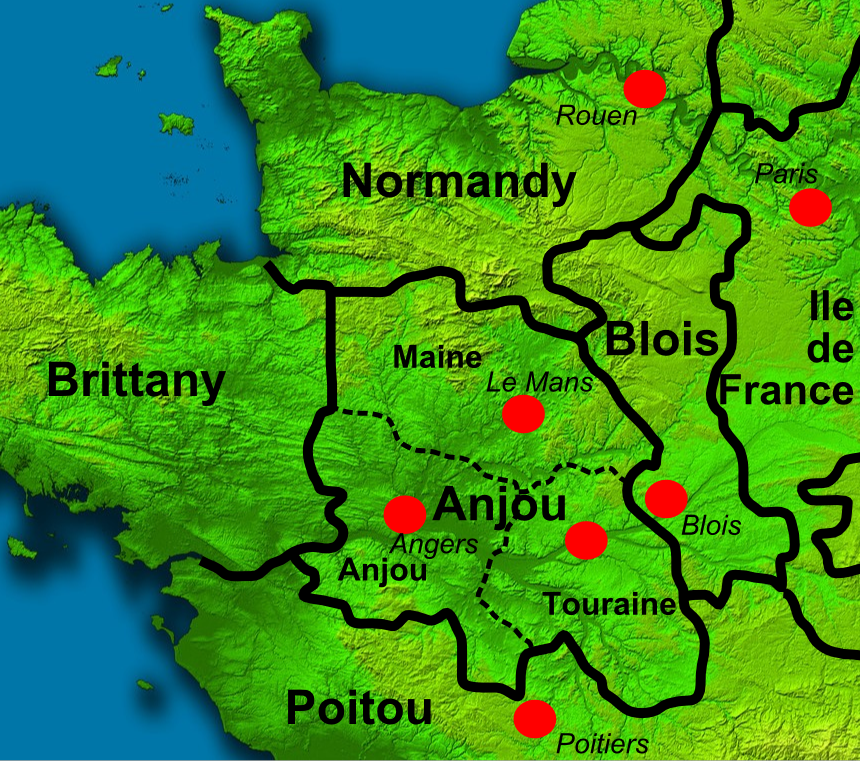
Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count Of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Handsome, the Fair (french: link=no, le Bel) or Plantagenet, was the count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also Duke of Normandy by conquest from 1144. His marriage to Empress Matilda, daughter of King Henry I of England, led to the centuries-long reign of the Plantagenet dynasty in England. The name "Plantagenet" was taken from Geoffrey's epithet. Geoffrey's ancestral domain of Anjou gave rise to the name Angevin, and what modern historians name as the Angevin Empire in the 12th century. Early life Geoffrey was the elder son of Fulk V of Anjou and Ermengarde of Maine. Geoffrey received his nickname from the yellow sprig of broom blossom (''genêt'' is the French name for the ''planta genista'', or broom shrub) he wore in his hat. The chronicler John of Marmoutier described Geoffrey as handsome, red haired, jovial, and a great warrior. King Henry I of England, having heard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1149 Deaths
Year 1149 ( MCXLIX) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Manuel I (Komnenos) recovers Corfu with the help of the Venetians, who defeat the Sicilian fleet. During the three-month siege, Byzantine admiral Stephen Kontostephanos is killed by a stone thrown by a catapult. Manuel prepares an offensive against the Normans, King Roger II sends a fleet (some 40 ships) under George of Antioch to pillage the suburbs of Constantinople. Levant * Spring – Nur al-Din, Seljuk ruler (''atabeg'') of Aleppo, invades the Principality of Antioch and defeats the Crusaders under Raymond of Poitiers at Baghras. He moves southward to besiege the fortress of Inab, one of the few strongholds of the Crusaders east of the Orontes River. Raymond with a small army (supported by the Assassin allies under Ali ibn Wafa) hurries to its rescue. Nur al-Din, misinformed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall. The Second Crusade was announced by Pope Eugene III, and was the first of the crusades to be led by European kings, namely Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany, with help from a number of other European nobles. The armies of the two kings marched separately across Europe. After crossing Byzantine territory into Anatolia, both armies were separately defeated by the Seljuk Turks. The main Western Christian source, Odo of Deuil, and Syriac Christian sources claim that the Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos secretly hindered the crusaders' progress, particularly in Anatolia, where he is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Edessa
The siege of Edessa (Arabic, ''fatḥ al-Ruhāʾ'', ) took place from November 28 to December 24, 1144, resulting in the fall of the capital of the crusader County of Edessa to Zengi, the atabeg of Mosul and Aleppo. This event was the catalyst for the Second Crusade. Background The County of Edessa was the first of the crusader states to be established during and after the First Crusade. It dates from 1098 when Baldwin of Boulogne left the main army of the First Crusade and founded his own principality. Edessa was the most northerly, the weakest, and the least populated; as such, it was subject to frequent attacks from the surrounding Muslim states ruled by the Ortoqids, Danishmends, and Seljuk Turks. Count Baldwin II and future count Joscelin of Courtenay were taken captive after their defeat at the Battle of Harran in 1104. Joscelin was captured a second time in 1122, and although Edessa recovered somewhat after the Battle of Azaz in 1125, Joscelin was killed in ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross , colors_label = Attire , march = , mascot = Two knights riding a single horse , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = The Crusades, including: , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , commander1 = Hugues de Payens , commander1_label = First Grand Master , commander2 = Jacques de Molay , commander2_label = Last Grand Master , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Pascal II
Pope Paschal II ( la, Paschalis II; 1050 1055 – 21 January 1118), born Ranierius, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 August 1099 to his death in 1118. A monk of the Abbey of Cluny, he was created the cardinal-priest of San Clemente by Pope Gregory VII (1073–85) in 1073. He was consecrated as pope in succession to Pope Urban II (1088–99) on 19 August 1099. His reign of almost twenty years was exceptionally long for a medieval pope. Early career Ranierius was born in Bleda, near Forlì, Romagna. He became a monk at Cluny at an early age. Papacy During the long struggle of the papacy with the Holy Roman emperors over investiture, Paschal II zealously carried on the Hildebrandine policy in favor of papal privilege, but with only partial success. Henry V, son of Emperor Henry IV, took advantage of his father's excommunication to rebel, even to the point of seeking out Paschal II for absolution for associating with his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Lateran Council
The Second Council of the Lateran was the tenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church. It was convened by Pope Innocent II in April 1139 and attended by close to a thousand clerics. Its immediate task was to neutralise the after-effects of the schism which had arisen after the death of Pope Honorius II in 1130 and the papal election that year that established Pietro Pierleoni as the antipope Anacletus II. Tenth Ecumenical Council After the death of Honorius II, Petrus Leonis, under the name of Anacletus II, was elected as Pope by a majority of the cardinals and with the support of the people of Rome on the same day as a minority elected Innocent II. In 1135, Innocent II held a council at Pisa, which confirmed his authority and condemned Anacletus. Anacletus's death in 1138 helped largely to solve the tension between rival factions. Nevertheless, Innocent decided to call the Tenth Ecumenical Council. The Council assembled at the Lateran Palace and nearly a thousan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legitimate son of King Henry I, who drowned in the sinking of the '' White Ship'' in 1120. Henry sought to be succeeded by his daughter, known as Empress Matilda, but was only partially successful in convincing the nobility to support her. On Henry's death in 1135, his nephew Stephen of Blois seized the throne, with the help of Stephen's brother Henry of Blois, who was the bishop of Winchester. Stephen's early reign saw fierce fighting with disloyal English barons, rebellious Welsh leaders, and Scottish invaders. Following a major rebellion in the south-west of England, Matilda invaded in 1139 with the help of her half-brother Robert of Gloucester. In the initial years of civil war, neither side was able to achieve a decisive advantage; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as a child when she married the future Holy Roman Emperor Henry V. She travelled with her husband to Italy in 1116, was controversially crowned in St Peter's Basilica, and acted as the imperial regent in Italy. Matilda and Henry V had no children, and when he died in 1125, the imperial crown was claimed by his rival Lothair of Supplinburg. Matilda's younger and only full brother, William Adelin, died in the '' White Ship'' disaster of 1120, leaving Matilda's father and realm facing a potential succession crisis. On Emperor Henry V's death, Matilda was recalled to Normandy by her father, who arranged for her to marry Geoffrey of Anjou to form an alliance to protect his southern borders. Henry I had no further legitimate children and nominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans. From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman conquest of England, the dukes of Normandy were usually also kings of England, the only exceptions being Dukes Robert Curthose (1087–1106), Geoffrey Plantagenet (1144–1150) and Henry II (1150-1152), who became king of England in 1152. In 1202, Philip II of France declared Normandy forfeit to him and seized it by force of arms in 1204. It remained disputed territory until the Treaty of Paris of 1259, when the English sovereign ceded his claim except for the Channel Islands; i.e., the Bailiwicks of Guernsey and Jersey, and their dependencies (including Sark). In the Kingdom of France, the duchy was occasionally set apart as an appanage to be ruled by a member of the royal family. After 1469, however, it was permanently united to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angevin Kings Of England
The Angevins (; "from Anjou") were a royal house of French origin that ruled England in the 12th and early 13th centuries; its monarchs were Henry II, Richard I and John. In the 10 years from 1144, two successive counts of Anjou in France, Geoffrey and his son, the future Henry II, won control of a vast assemblage of lands in western Europe that would last for 80 years and would retrospectively be referred to as the Angevin Empire. As a political entity this was structurally different from the preceding Norman and subsequent Plantagenet realms. Geoffrey became Duke of Normandy in 1144 and died in 1151. In 1152, his heir, Henry, added Aquitaine by virtue of his marriage to Eleanor of Aquitaine. Henry also inherited the claim of his mother, Empress Matilda, the daughter of King Henry I, to the English throne, to which he succeeded in 1154 following the death of King Stephen. Henry was succeeded by his third son, Richard, whose reputation for martial prowess won him the epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |