|
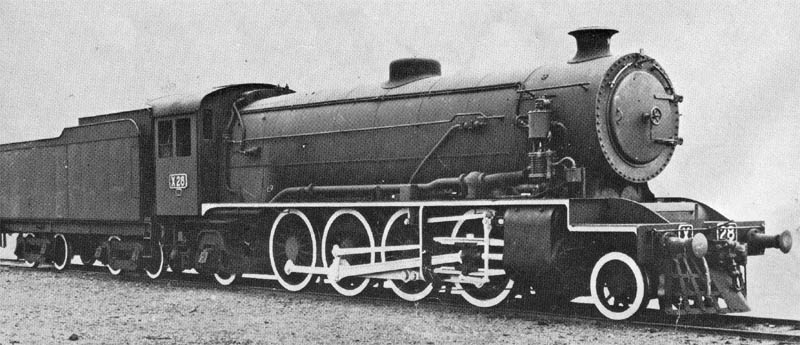
USRA Light Mikado
The USRA Light Mikado was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard light freight locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 2-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′D1′ in UIC classification. A total of 625 locomotives were built under the auspices of the USRA,Drury p.409 with a further 641 copies built after the end of the USRA's control. The first, for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, was completed in July 1918 and given #4500. The locomotives were considered well designed and modern, and were popular and successful. Large numbers remained in service until replaced by diesel locomotives. It was also called the McAdoo Mikado after William Gibbs McAdoo, head of the USRA. With later copies, over 50 railroads used the type, including the following: Copies: Preservation Nine USRA Light Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USRA Standard
The USRA standard locomotives and railroad cars were designed by the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized rail system of the United States during World War I. 1,856 steam locomotives and over 100,000 railroad cars were built to these designs during the USRA's tenure. The locomotive designs in particular were the nearest the American railroads and locomotive builders ever got to standard locomotive types, and after the USRA was dissolved in 1920 many of the designs were duplicated in number, 3,251 copies being constructed overall. The last steam locomotive built for a Class I railroad in the United States, an 0-8-0 built by the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1953, was a USRA design. A total of 97 railroads used USRA or USRA-derived locomotives. Steam locomotive types The USRA developed designs for 0-6-0 and 0-8-0 switchers, 2-6-6-2 and 2-8-8-2 Mallet locomotives, and both light and heavy versions of the 2-8-2, 2-10-2, 4-6-2, and 4-8-2 types. The light versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. At times it was also referred to on some railroads in the United States of America as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore And Ohio 4500
Baltimore and Ohio 4500 is a 2-8-2 "USRA Light Mikado" steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in July 1918 for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) as a member of the Q-3 class. The locomotive hauled freight for the B&O until retirement in August 1957 and was donated for display at the B&O Railroad Museum in Baltimore, Maryland. It is the sole surviving Baltimore and Ohio Mikado type steam locomotive. History The locomotive was the very first USRA locomotive built and it was constructed in just twenty days. It was also finished on July 4, 1918, and it was decked out with American Flags for the occasion. While it has mostly remained as built mechanically, it received some of B&O's distinctive cosmetic changes throughout its service life, but the locomotive retains the original tender and trailing truck. During its service life, the locomotive was in freight service primarily on the Ohio and St. Louis divisions of the railroad. The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Trunk Western 4070
Grand Trunk Western No. 4070 is a class "S-3-a" 2-8-2 type USRA Light Mikado steam locomotive originally built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in December 1918 for the Grand Trunk as No. 474, later re-numbered by Grand Trunk Western Railroad, after the GT was absorbed into Canadian National as GTW No. 3734. In the late 1950s the locomotive was given a larger tender, from an S-3-c, and re-numbered 4070. The locomotive has pulled passenger excursions in Illinois, Indiana, Ohio and Pennsylvania over the years. History Revenue service Grand Trunk Western 4070 was built in December 1918 by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in Schenectady, New York and assigned to Grand Trunk, which numbered it originally as 474. Sometime in the 1930s a Coffin feedwater heater was installed, and with other improvements, the number was changed by the GTW to 3734. This steam locomotive's road career consisted of pulling freight and passenger services in Michigan. After falling into a tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Trunk Western Railroad
The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants. Early history Grand Trunk Western grew out of a collection of 19th century Michigan rail lines which included: *Bay City Terminal Railway *Chicago, Detroit and Canada Grand Trunk Junction Railroad *Chicago and Grand Trunk Railway * Chicago, Kalamazoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian National Class S 2-8-2
Canadian National Railway (CN) Class S locomotives were a Class of 2-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′D1′ in UIC classification. These locomotives were designed for 16° operating curvature. The first examples of this very successful class were built for the Grand Trunk Railway in 1913. Major purchases of the class continued through 1924. Sub-classes S-3 and S-4 employed higher pressure boilers with smaller diameter cylinders to achieve similar tractive effort with higher efficiency. The class remained in freight service until the final replacement of steam with diesel-electric locomotives. 53 were renumbered between 4045 and 4097 in 1956. Sub-classes Preservation Number 3239 was preserved by the Canadian Railway Historical Association. Number 3254 by W.F. Barron of Ashland, Pennsylvania. No. 3254 first operated in excursion service at the Gettysburg Railroad in Gettysburg and Mount Holly Springs from 1985 until being put into storage again in 1986, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States. CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia across approximately of track. In the late 20th century, CN gained extensive capacity in the United States by taking over such railroads as the Illinois Central. CN is a public company with 22,600 employees, and it has a market cap of approximately CA$90 billion. CN was government-owned, having been a Canadian Crown corporation from its founding in 1919 until being privatized in 1995. , Bill Gates is the largest single shareholder of CN stock, owning a 14.2% interest through Cascade Investment and his own Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a railway system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the American states of Connecticut, Maine, Michigan, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont. The railway was operated from headquarters in Montreal, Quebec, with corporate headquarters in London, United Kingdom (4 Warwick House Street). It cost an estimated $160 million to build. The Grand Trunk, its subsidiaries, and the Canadian Government Railways were precursors of today's Canadian National Railway. GTR's main line ran from Portland, Maine to Montreal, and then from Montreal to Sarnia, Ontario, where it joined its western subsidiary. The GTR had four important subsidiaries during its lifetime: * Grand Trunk Eastern which operated in Quebec, Vermont, New Hampshire and Maine. * Central Vermont Railway which operated in Quebec, Vermont, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. * Grand Trunk Pacific Railway which operated in Northwestern Onta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Rock Island And Pacific Railroad
The Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad (CRI&P RW, sometimes called ''Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railway'') was an American Class I railroad. It was also known as the Rock Island Line, or, in its final years, The Rock. At the end of 1970, it operated 7,183 miles of road on 10,669 miles of track; that year it reported 20,557 million ton-miles of revenue freight and 118 million passenger miles. (Those totals may or may not include the former Burlington-Rock Island Railroad.) The song "Rock Island Line", a spiritual from the late 1920s first recorded in 1934, was inspired by the railway. History Incorporation Its predecessor, the Rock Island and La Salle Railroad Company, was incorporated in Illinois on February 27, 1847, and an amended charter was approved on February 7, 1851, as the Chicago and Rock Island Railroad. Construction began in Chicago on October 1, 1851, and the first train was operated on October 10, 1852, between Chicago and Joliet. Construction co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Indianapolis And Louisville Railroad
The Monon Railroad , also known as the Chicago, Indianapolis, and Louisville Railway from 1897 to 1971, was an American railroad that operated almost entirely within the state of Indiana. The Monon was merged into the Louisville and Nashville Railroad in 1971, and much of the former Monon right of way is owned today by CSX Transportation.Historic Marker in Monon, erected by the Monon Historical Society, 1982 In 1970, it operated of road on of track; that year it reported 1320 million ton-miles of revenue freight and zero passenger-miles. (It also showed zero miles of double track, the longest such Class I railroad in the country.) Timeline *1847: The New Albany and Salem Railroad (NA&S) is organized with James Brooks as president. *1854: The NA&S trackage stretches from the Ohio River (at New Albany) to Lake Michigan (at Michigan City). *1859: The overextended and struggling NA&S is renamed the Louisville, New Albany and Chicago Railroad (LNA&C). *April 30, 1865: The LNA&C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Great Western Railway
The Chicago Great Western Railway was a Class I railroad that linked Chicago, Minneapolis, Omaha, and Kansas City. It was founded by Alpheus Beede Stickney in 1885 as a regional line between St. Paul and the Iowa state line called the Minnesota and Northwestern Railroad. Through mergers and new construction, the railroad, named Chicago Great Western after 1892, quickly became a multi-state carrier. One of the last Class I railroads to be built, it competed against several other more well-established railroads in the same territory, and developed a corporate culture of innovation and efficiency to survive. Nicknamed the Corn Belt Route because of its operating area in the midwestern United States, the railroad was sometimes called the Lucky Strike Road, due to the similarity in design between the herald of the CGW and the logo used for Lucky Strike cigarettes. In 1968 it merged with the Chicago and North Western Railway (CNW), which abandoned most of the CGW's trackage. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
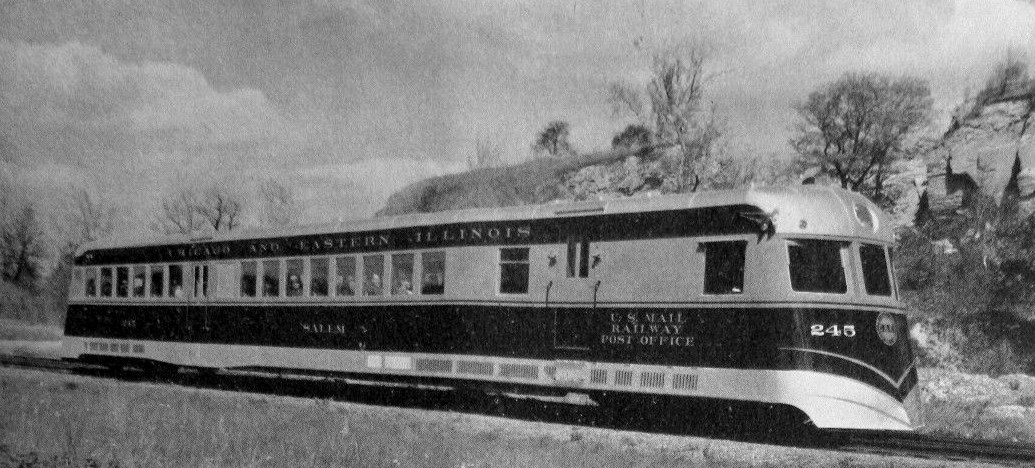
Chicago And Eastern Illinois Railroad
The Chicago and Eastern Illinois Railroad was a Class I railroad that linked Chicago to southern Illinois, St. Louis, and Evansville. Founded in 1877, it grew aggressively and stayed relatively strong throughout the Great Depression and two World Wars before finally being purchased by the Missouri Pacific Railroad (MP or MoPac) and the Louisville and Nashville Railroad (L&N). Missouri Pacific merged with the C&EI corporate entity in 1976, and was later acquired itself by the Union Pacific Railroad. History The Chicago and Eastern Illinois Railroad was organized in 1877 as a consolidation of three others: the Chicago, Danville and Vincennes Railroad (Chicago-Danville, November 1871), the Evansville, Terre Haute and Chicago Railroad (Danville-Terre Haute, October 1871) and the Evansville and Terre Haute Railroad (Terre Haute-Evansville, November 1854). Intended to merge or purchase railroads that had built lines between the southern suburbs of Chicago and Terre Haute, Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |