|
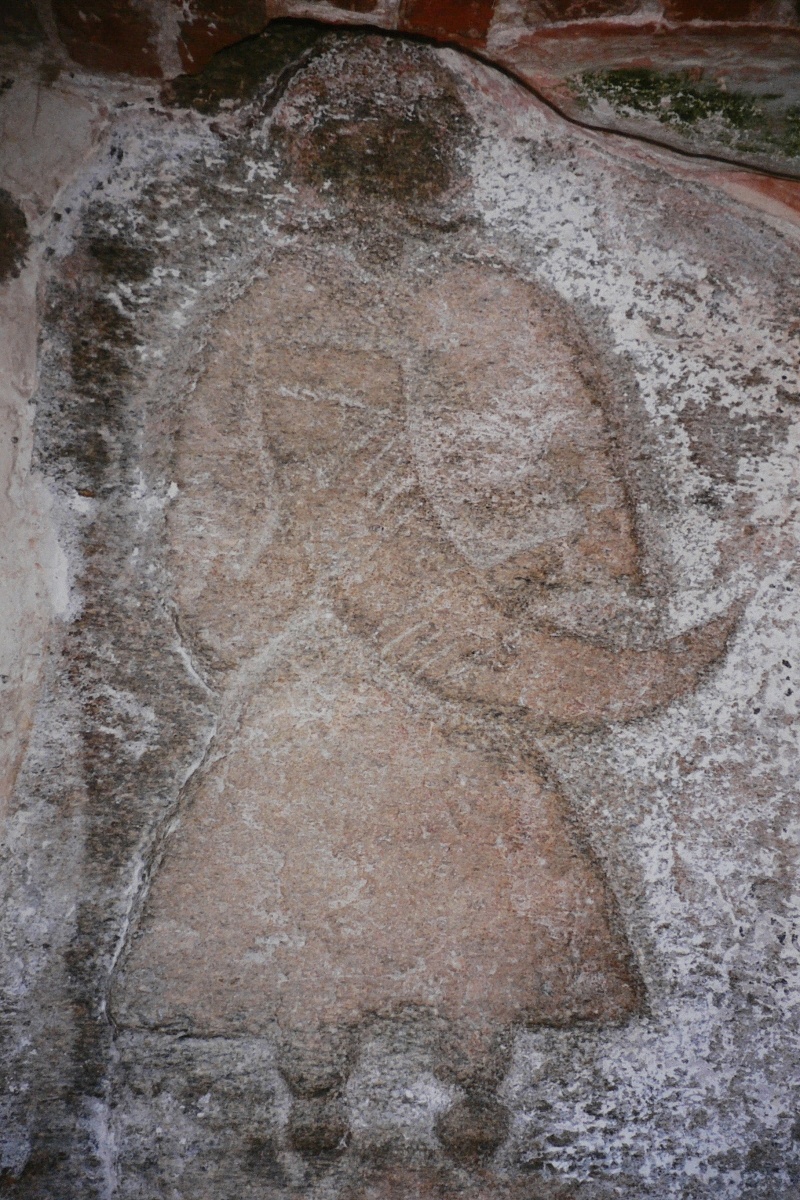
Upiór
Upiór is a demonic being from Slavic and Turkic folklore, a prototype of the vampire. It is suggested that the ''ubır'' (''upiór'') belief spread across the Eurasian steppes through the migrations of the Kipchak-Cuman people, after having its origins in the regions surrounding the Volga (İtil) River and the Pontic steppes. The modern word "vampire" derives from the Old Slavic and Turkic form "онпыр" (''onpyr''), with the addition of the sound "v" before a large nasal vowel (on), characteristic of Old Bulgarian, as evidenced by the traditional Bulgarian form "впир" (''vpir''). Other names include ''onpyr'', ''vopir'', ''vpir'', ''upir'', and ''upierz''. Etymology The exact etymology is unclear. Among the proposed Proto-Slavic forms are and . Another, less widespread theory, is that the Slavic languages have borrowed the word from a Turkic term for ''or'' 'witch, vampire, hortdan'. Czech linguist Václav Machek proposes the Slovak verb ('stick to, thrust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead humanoid creatures that often visited loved ones and caused mischief or deaths in the neighbourhoods which they inhabited while they were alive. They wore shrouds and were often described as bloated and of ruddy or dark countenance, markedly different from today's gaunt, pale vampire which dates from the early 19th century. Vampiric entities have been Vampire folklore by region, recorded in cultures around the world; the term ''vampire'' was popularized in Western Europe after reports of an 18th-century mass hysteria of a pre-existing folk belief in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Eastern Europe that in some cases resulted in corpses being staked and people being accused of vampirism. Local variants in Southeastern Europe were also known by different names, such as ''shtriga'' in Albanian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strzyga
(, plural: strzygi, masculine: strzygoń), sometimes translated as striga, (which is also the latin term for it) is usually a female demon in Slavic mythology, which stems from the mythological Strix of ancient Rome and ancient Greece. The demon is similar to a vampire, and is predominantly found in Polish and Silesian folklore. Etymology and origin According to Aleksander Brückner, the word is derived from Strix, Latin for owl and a bird-like creature which fed on human flesh and blood in Roman and Greek mythology. Hungarian ''sztriga'', the Albanian '' shtriga'' and are also cognate and related. It is unclear how the word was adapted by the Polish people, though it might have been through the Balkan peoples. The term could also sometimes mean a vampire or ''upiór''. After the 18th century, there was a distinction between and upiór; the first one was more connected to witchcraft, while the latter was more of a flying, vampiric creature. The remained a popular eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Paganism
Slavic paganism, Slavic mythology, or Slavic religion refer to the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Balkans during the 6th–7th centuries AD, bordering with the Byzantine Empire to the south, came under the sphere of influence of Eastern Christianity relatively early, beginning with the creation of writing systems for Slavic languages (first Glagolitic, and then Cyrillic script) in 855 by the brothers Saints Cyril and Methodius and the adoption of Christianity in Bulgaria in 864 and 863 in Great Moravia. The East Slavs followed with the official adoption in 988 by Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus'. The process of Christianising the West Slavs was more gradual and complicated compared to their eastern counterparts. The Moravians accepted Christianity as early as 831, the Bohemian dukes followed in 845, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and remains the liturgical language of many Christian Orthodox churches. Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with Standard language, standardizing the language and undertaking the task of translating the Gospels and necessary Eastern Orthodox worship#Liturgical books, liturgical books into it as part of the Christianization of the Slavs. It is thought to have been based primarily on the dialect of the 9th-century Sclaveni, Byzantine Slavs living in the Thessalonica (theme), Province of Thessalonica (in present-day Greece). Old Church Slavonic played an important rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
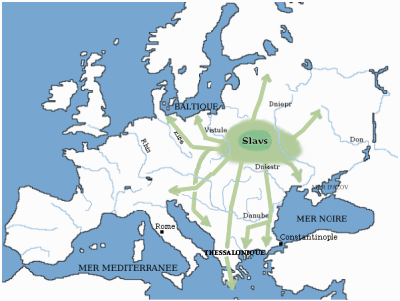
Slavic Countries
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, and West S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unclean Spirit
In English translations of the Bible, unclean spirit is a common rendering of Greek ''pneuma akatharton'' (πνεῦμα ἀκάθαρτον; plural ''pneumata akatharta'' (πνεύματα ἀκάθαρτα)), which in its single occurrence in the Septuagint translates Hebrew ' (). The Greek term appears 21 times in the New Testament in the context of demonic possession. It is also translated into English as spirit of impurity or more loosely as "evil spirit." The Latin equivalent is ''spiritus immundus''. The association of physical and spiritual cleanliness is, if not universal, widespread and continues into the 21st century: "To be virtuous is to be physically clean and free from the impurity that is sin," notes an article in ''Scientific American'' published 10 March 2009. Some scholarship seeks to differentiate between "unclean spirit" and "evil spirit" ('' pneuma ponêron'') or "demon" ('' daimonion''). The concept of ''pneuma'' In the Christian scriptures, the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Rites
''Burial Rites'' (2013) is a novel by Australian author Hannah Kent, based on a true story about the last woman to be executed in Iceland. Premise ''Burial Rites'' tells the story of Agnes Magnúsdóttir, a servant in northern Iceland who was condemned to death after the murder of two men, one of whom was her employer, and became the last woman put to death in Iceland in 1830. Background Kent was inspired to write ''Burial Rites'' during her time as an exchange student in Iceland when she was 17, where she learnt the story of Agnes Magnúsdóttir. She then made it the topic of her honours thesis and PhD at Flinders University, with additional mentoring by Geraldine Brooks. After this, Kent was awarded the Writing Australia Unpublished Manuscript Award in 2011. Publication ''Burial Rites'' was published in 2013 by Pan Macmillan in Australia, by Little, Brown in the US, and by Picador in the UK. Reviews ''Burial Rites'' was well-received by critics and other writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chigirinsky Uyezd
The Chigirin uezd (; ) was one of the subdivisions of the Kiev Governorate of the Russian Empire. It was situated in the southeastern part of the governorate. Its administrative centre was Chigirin (Chyhyryn). Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Chigirin uezd had a population of 225,915. Of these, 89.4% spoke Ukrainian, 8.6% Yiddish, 1.4% Russian, 0.3% Polish, 0.1% Belarusian and 0.1% Romani Romani may refer to: Ethnic groups * Romani people, or Roma, an ethnic group of Indo-Aryan origin ** Romani language, an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities ** Romanichal, Romani subgroup in the United Kingdom * Romanians (Romanian ... as their native language. Демоскоп Weekly - Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей References |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. He also largely influenced Ukrainian literature. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's " Three Bards" () and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama '' Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Grażyna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dracula
''Dracula'' is an 1897 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish author Bram Stoker. The narrative is Epistolary novel, related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist and opens with solicitor Jonathan Harker taking a business trip to stay at the castle of a Transylvanian nobleman, Count Dracula. Harker flees after learning that Dracula is a vampire, and the Count moves to England and plagues the seaside town of Whitby. A small group, led by Abraham Van Helsing, hunts and kills him. The novel was mostly written in the 1890s, and Stoker produced over a hundred pages of notes, drawing extensively from Folklore of Romania, folklore and History of Romania, history. Scholars have suggested various figures as the inspiration for Dracula, including the Wallachian prince Vlad the Impaler and the Countess Elizabeth Báthory, but recent scholarship suggests otherwise. He probably found the name Dracula in Whitby's public l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of the most famous classics of English literature. The primary antagonist of the novel, Count Dracula, is often ranked among the most iconic and best-known fictional figures of the entire Victorian era, and the character's popularity has led to over 700 adaptations for films, movies, plays, comics, video games, cartoons, stage performances, and other forms of media. Although he was the author of 12 mystery novels and novellas, Stoker's reputation as one of the most influential writers of Gothic horror fiction lies solely with ''Dracula''. During his life, he was better known as the personal assistant of the actor Sir Henry Irving and business manager of the West End's Lyceum Theatre, which Irving owned. Stoker was also a distant relative o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |