|
University Of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public university, public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by French theologian John Calvin as a Theology, theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th century, when it became a center for the Enlightenment, enlightenment scholarship. Today, it is the third largest university in Switzerland by number of students. In 1873, it dropped its religious affiliations and became officially secular. In 2009, the University of Geneva celebrated the 450th anniversary of its founding. Almost 40% of the students come from over 150 foreign countries. The university holds and actively pursues teaching, Research university, research, and community service as its primary objectives. The University of Geneva is a member of the League of European Research Universities, 4EU+ Alliance, Coimbra Group, International Forum of Public Universities, and European University A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Canton of Geneva, Republic and Canton of Geneva, and a centre for international diplomacy. Geneva hosts the highest number of International organization, international organizations in the world, and has been referred to as the world's most compact metropolis and the "Peace Capital". Geneva is a global city, an international financial centre, and a worldwide centre for diplomacy hosting the highest number of international organizations in the world, including the headquarters of many agencies of the United Nations and the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC and International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, IFRC of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. In the aftermath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a European intellectual and philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained through rationalism and empiricism, the Enlightenment was concerned with a wide range of social and political ideals such as natural law, liberty, and progress, toleration and fraternity, constitutional government, and the formal separation of church and state. The Enlightenment was preceded by and overlapped the Scientific Revolution, which included the work of Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei, Francis Bacon, Pierre Gassendi, Christiaan Huygens and Isaac Newton, among others, as well as the philosophy of Descartes, Hobbes, Spinoza, Leibniz, and John Locke. The dating of the period of the beginning of the Enlightenment can be attributed to the publication of René Descartes' ''Discourse on the Method'' in 1637, with his method of systematically disbelieving everything ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophie Kanza
Sophie Lihau-Kanza or Zala Lusibu N'Kanza (8 February 1940 – 2 April 1999) was a Congolese politician and sociologist. She was the first woman of her country to receive a secondary education, the first to graduate from a university, and the first to hold a government office in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, serving as Minister of Social Affairs from 31 October 1966 to 6 December 1970. In her later life she held positions within the United Nations. Early life and education Sophie Kanza was born on 8 February 1940 in Léopoldville, Belgian Congo, the sixth of seven children to Élisabeth Mansangaza and Daniel Kanza. She received much of her primary and secondary education in Brazzaville, French Congo. At the time of the Belgian Congo's independence in 1960, Kanza was the only woman in the country who had been enrolled in secondary education. She eventually graduated from ''Lycée du Sacré Cœur'' (Sacred Heart High School) in June 1961. In 1964, she became the first Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
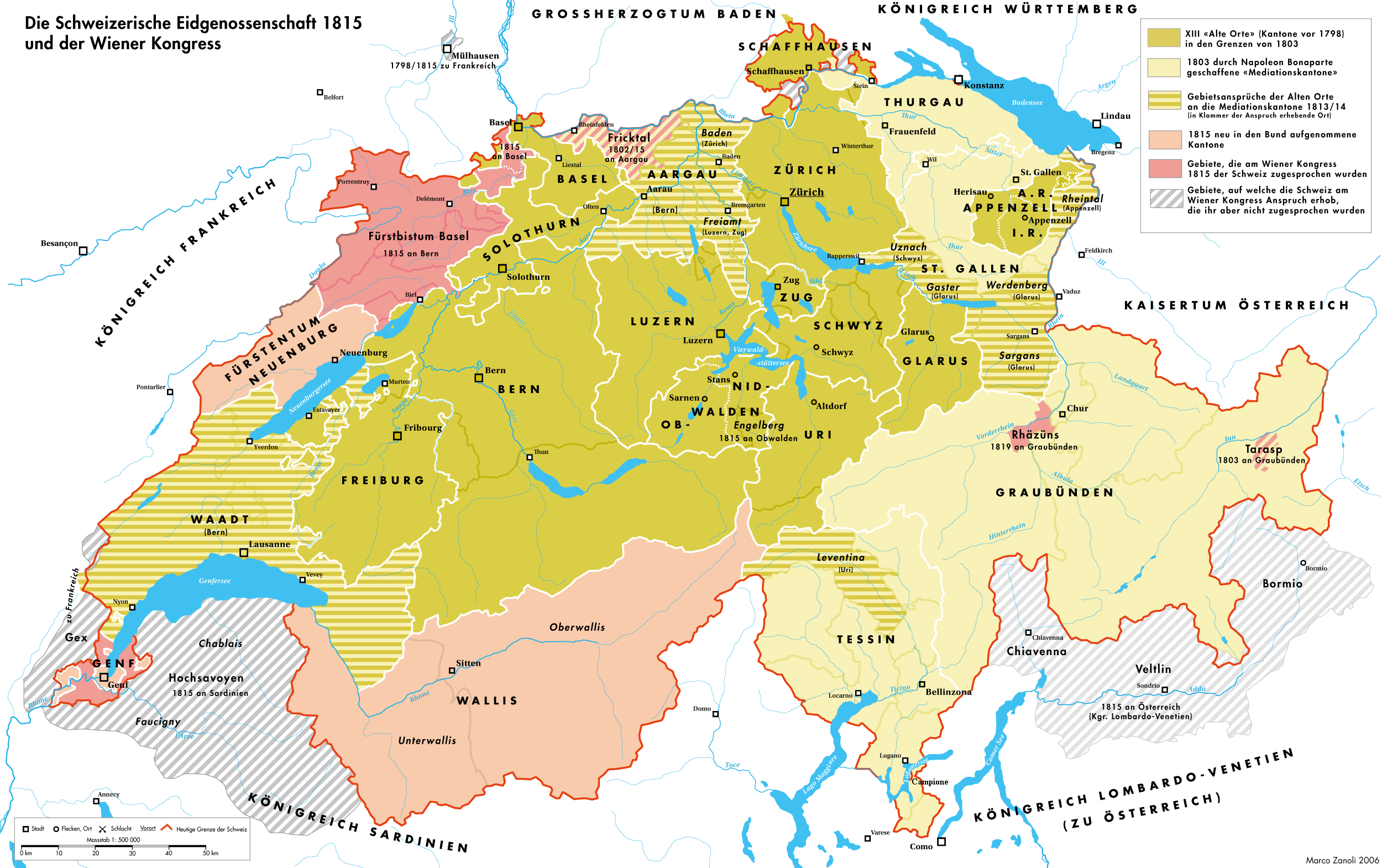
Restoration And Regeneration In Switzerland
The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the ''Ancien Régime'' (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" ''Ancien Régime'' was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847. Restoration When Napoleon's fall appeared imminent, the Act of Mediation was suspended in late December 1813, and lengthy discussions about future constitutions were initiated in all cantons of Switzer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faculty (division)
A faculty is a division within a university or college comprising one subject area or a group of related subject areas, possibly also delimited by level (e.g. undergraduate). In North America, academic divisions are sometimes titled colleges, schools, or departments, with universities occasionally using a mixture of terminology, e.g., Harvard University has a Faculty of Arts and Sciences and a Law School. History The medieval University of Bologna, which served as a model for most of the later medieval universities in Europe, had four faculties: students began at the Faculty of Arts, graduates from which could then continue at the higher Faculties of Theology, Law, and Medicine. The privilege to establish these four faculties was usually part of medieval universities' charters, but not every university could do so in practice. The ''Faculty of Arts'' took its name from the seven liberal arts: the triviumThe three of the humanities (grammar, rhetoric, dialectics) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to a student upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions often offer degrees at various levels, usually divided into undergraduate and postgraduate degrees. The most common undergraduate degree is the bachelor's degree, although some educational systems offer lower-level undergraduate degrees such as associate degree, associate and foundation degree, foundation degrees. Common postgraduate degrees include engineer's degrees, master's degrees and doctorates. In the UK and countries whose educational systems are based on the British system, honours degrees are divided into classes: first, second (broken into upper second, or 2.1, and lower second, or 2.2) and third class. History Emergence of the doctor's and master's degrees and the licentiate The doctorate (Latin: ''doceo'', "I teach") first appeared in Middle Ages, medieval Europe as a license to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léman (department)
Léman () was a department of the French First Republic and French First Empire. Its name came from the French name of Lake Geneva, ''Lac Léman''. It was formed in 1798, when the Republic of Geneva was annexed by the French Republic. Léman also included districts that were previously part of the departments of Mont-Blanc (northern Savoy) and Ain (the Pays de Gex). Its territory corresponded with the present Swiss canton of Geneva and parts of the present French departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie. The Chef-lieu of the department was Geneva. The department was subdivided into the following three arrondissements and cantons: * Genève: Carouge, Chêne-Thônex, Collonge, Frangy, Genève (3 cantons), Gex, Reignier and Saint-Julien. * Bonneville: Bonneville, Chamonix, Cluses, Megève, La Roche, Sallanches, Samoëns, Taninges and Viuz-en-Sallaz. * Thonon: Douvaine, Évian, Saint-Jean-d'Aulps and Thonon. After the final defeat of Napoleon in 1815, the former Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Law
A law school (also known as a law centre/center, college of law, or faculty of law) is an institution, professional school, or department of a college or university specializing in legal education, usually involved as part of a process for becoming a judge, lawyer, or other legal professional within a given jurisdiction. Depending on the country, legal system, or desired qualifications, the coursework is undertaken at undergraduate, graduate, or both levels. Law degrees Argentina In Argentina, lawyers-to-be need to obtain an undergraduate degree in law in order to practice the profession, as opposed to the US system in which a law degree is not obtained until successfully completing a postgraduate program. In spite of that, it is customary to call Argentine lawyers 'doctors,' although the vast majority of them do not hold a Juris Doctor degree. The reason lies in that the career was originally called 'Doctorate in Laws' (''Doctorado en Leyes''), which was an undergraduate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva, is one of the Cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons of the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of forty-five Municipality, municipalities, and the seat of the government and parliament is in the Geneva, city of Geneva. Geneva is the French-speaking westernmost canton of Switzerland. It lies at the western end of Lake Geneva and on both sides of the Rhone, its main river. Within the country, the canton borders Vaud to the east, the only adjacent canton. However, most of Geneva's border is with France, specifically the region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. As is the case in several other Swiss cantons (Ticino, canton of Neuchâtel, Neuchâtel, and canton of Jura, Jura), Geneva is referred to as a republic within the Swiss Confederation. One of the most populated cantons, Geneva is considered one of the most cosmopolitan regions of the country. As a center of the Calvinism, Calvinist Protestant Reformation, Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magistrates
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a ''magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judicial and executive powers. In other parts of the world, such as China, magistrate is a word applied to a person responsible for administration over a particular geographic area. Today, in some jurisdictions, a magistrate is a judicial officer who hears cases in a lower court, and typically deals with more minor or preliminary matters. In other jurisdictions (e.g., England and Wales), magistrates are typically trained volunteers appointed to deal with criminal and civil matters in their local areas. Original meaning In ancient Rome, the word ''magistratus'' referred to one of the highest offices of state. Analogous offices in the local authorities, such as ''municipium'', were subordinate only to the legislature of which they generally were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Dictionary Of Switzerland
The ''Historical Dictionary of Switzerland'' (Dictionnaire historique de la Suisse; DHS) is an encyclopedia on the history of Switzerland. It aims to present the history of Switzerland in the form of an encyclopaedia, published both on paper and on the internet, in three of the country's national languages: German, French and Italian. When it was completed at the end of 2014, the paper version contained around 36,000 articles divided into thirteen volumes. At the same time, a reduced edition of the dictionary has been published in Romansh language, Romansh under the title ''Lexicon istoric retic'' (LIR), and constitutes the first specialist dictionary in the Rhaeto-Romance languages, Rhaeto-Romance, Switzerland. The encyclopedia is published by a Foundation (charity), foundation under the patronage of the Swiss Academies of Arts and Sciences, Swiss Academy of Humanities and Social Sciences (SAGW/ASSH) and the Swiss Historical Society (SGG-SHH) and is financed by national resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Geneva
The history of Geneva dates from before the Roman occupation in the second century BC. Now the principal French-speaking city of Switzerland, Geneva was an independent city state from the Middle Ages until the end of the 18th century. John Calvin was the Protestant leader of the city in the 16th century. Antiquity and Early Middle Ages Geneva first appears in history as an Allobrogian border town, fortified against the Celtic Helvetii tribe, which the Roman Republic took in 121 BC. In 58 BC, Caesar, Roman governor of Gaul, destroyed the Rhône bridge at Geneva and built a 19-mile earthwork from Lake Geneva to the Jura Mountains in order to block the migration of the Helvetii, who "attempted, sometimes by day, more often by night, to break through, either by joining boats together and making a number of rafts (''ratis''), or by fording the Rhône where the depth of the stream was least" (De Bello Gallico, I, 8). Then he helped establish Geneva as a Roman city (vicus and then ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |