|
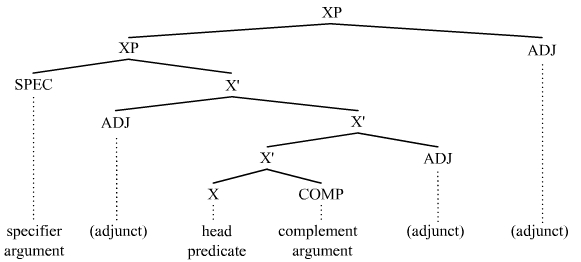
Unergative And Unaccusative Trees
An unergative verb is an intransitive verb that is characterized semantically by having a subject argument which is an ''agent'' that actively initiates the action expressed by the verb. For example, in English, ''talk'' and ''resign'' in the sentence "You talk and you resign" are unergative verbs, since they are intransitive (one does not say "you talk someone") and "you" is the initiator or is responsible for talking and resigning. But ''fall'' and ''die'' in the sentence "They fall and die" are unaccusative verbs, since usually they are not responsible for falling or dying but still the verb is intransitive, meaning it is comprehensively used without a direct object. (They cannot "fall something" or "die someone").Note: Dąbrowska (2016)pointed out that the phrase "''to die''" in English does not comply with the strict definition of an unaccusative verb, since it fails some of the distinctions from unergative verbs such as causative alternation, where an unaccusative like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intransitive Verb
In grammar, an intransitive verb is a verb, aside from an auxiliary verb, whose context does not entail a transitive object. That lack of an object distinguishes intransitive verbs from transitive verbs, which entail one or more objects. Additionally, intransitive verbs are typically considered within a class apart from modal verbs and defective verbs. Examples In the following sentences, verbs are used without a direct object: *"Rivers flow." *"I sneezed." *"My dog ran." *"Water evaporates when it's hot." *"You've grown since I last saw you!" *"I wonder how long it will be until I see you again after I move." The following sentences contain transitive verbs (they entail one or more objects): *"We watched ''a movie'' last night." *"She's making ''promises''." *"When I said that, my sister smacked ''me''." *"Santa gave ''me'' ''a present''." *"He continuously clicked ''his pen'' and it was incredibly annoying to me." Some verbs, called ambitransitive verbs, may entail o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''Complement (linguistics), complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic category, syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (grammar)
In linguistics, a grammatical agent is the thematic relation of the cause or initiator to an event. The agent is a semantic concept distinct from the subject of a sentence as well as from the topic. While the subject is determined syntactically, primarily through word order, the agent is determined through its relationship to the action expressed by the verb. For example, in the sentence "The little girl was bitten by the dog", ''girl'' is the subject, but ''dog'' is the agent. The word ''agent'' comes from the present participle , ('the one doing') of the Latin verb , to 'do' or 'make'. Theory Typically, the situation is denoted by a sentence, the action by a verb in the sentence, and the agent by a noun phrase. For example, in the sentence "Jack kicked the ball", ''Jack'' is the agent and ''the ball'' is the patient. In certain languages, the agent is declined or otherwise marked to indicate its grammatical role. Modern English does not mark the agentive grammatical role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unaccusative Verb
In linguistics, an unaccusative verb is an intransitive verb whose grammatical subject is not a semantics, semantic agent (grammar), agent. In other words, the subject does not actively initiate, or is not actively responsible for, the action expressed by the verb. An unaccusative verb's subject is semantically similar to the direct object of a transitive verb or to the subject of a verb in the passive voice. Examples in English are "the tree ''fell''"; "the window ''broke''". In those sentences, the action (falling, breaking) can be considered as something that happened to the subject, rather than being initiated by it. Semantically, the word "tree" in the sentence "the tree fell" plays a similar role to that in a transitive sentence, such as "they cut down the tree", or its passive transformation "the tree was cut down". Unaccusative verbs thus contrast with unergative verbs, such as ''run'' or ''resign'', which describe actions voluntarily initiated by the subject. They are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphosyntax
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent Meaning (linguistics), meaning. Morphemes include root (linguistics), roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root ''catch'' and the suffix ''-ing'' are both morphemes; ''catch'' may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with ''-ing'' to form the new word ''catching''. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including Grammatical number, number, Grammatical tense, tense, and Grammatical aspect, aspect. Concepts such as Productivity (linguistics), productivity are concerned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Voice
A passive voice construction is a grammatical voice construction that is found in many languages. In a clause with passive voice, the grammatical subject expresses the ''theme'' or ''patient'' of the main verb – that is, the person or thing that undergoes the action or has its state changed. This contrasts with active voice, in which the subject has the agent role. For example, in the passive sentence "The tree was pulled down", the subject (''the tree'') denotes the patient rather than the agent of the action. In contrast, the sentences "Someone pulled down the tree" and "The tree is down" are active sentences. Typically, in passive clauses, what is usually expressed by the object (or sometimes another argument) of the verb is now expressed by the subject, while what is usually expressed by the subject is either omitted or is indicated by some adjunct of the clause. Thus, turning an active sense of a verb into a passive sense is a valence-decreasing process ("detransiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impersonal Passive
The impersonal passive voice is a verb voice that decreases the valency of an intransitive verb (which has valency one) to zero. Dixon, R. M. W. & Alexandra Aikhenvald (1997). "A Typology of Argument-Determined Constructions". In Bybee, Joan, John Haiman, & Sandra A. Thompson (eds.) ''Essays on Language Function and Language Type: Dedicated to T. Givón''. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, 71–112. The impersonal passive deletes the subject of an intransitive verb. In place of the verb's subject, the construction instead may include a syntactic placeholder, also called a '' dummy''. This placeholder has neither thematic nor referential content. (A similar example is the word "there" in the English phrase "There are three books.") In some languages, the deleted argument can be reintroduced as an '' oblique argument'' or ''complement''. Test of unergative verbs In most languages that allow impersonal passives, only unergative verbs may undergo impersonal passivization. Unaccusativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dummy Subject
A dummy pronoun, also known as an expletive pronoun, is a deictic pronoun that fulfills a syntactical requirement without providing a contextually explicit meaning of its referent. As such, it is an example of exophora. A dummy pronoun is used when a particular verb argument (or preposition) is nonexistent, but when a reference to the argument (a pronoun) is nevertheless syntactically required. This is commonly the case if the verb is an impersonal verb, but it could also be that the argument is unknown, irrelevant, already understood, or otherwise taboo (as in naming taboo). For example, in the phrase " is obvious that the violence will continue", the term 'it' is a dummy pronoun, not referring to any agent. Unlike a regular pronoun of English, it cannot be replaced by any noun phrase. The term 'dummy pronoun' refers to the function of a word in a particular sentence, not a property of individual words. For example, 'it' in the example from the previous paragraph is a du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergative Verb
In general linguistics, a labile verb (or ergative / diffused / ambivalent verb) is a verb that undergoes causative alternation; that is, it can be used both transitively and intransitively, with the requirement that the direct object of its transitive use corresponds to the subject of its intransitive use, as in "I ring the bell" and "The bell rings." Labile verbs are a prominent feature of English, and also occur in many other languages. This behavior can be seen as evidence that the distribution of verb classes in that language does not depend on transitivity. In this respect, it is a phenomenon that is common to both Active languages and Ergative languages. This is because they are often not possible to distinguish between transitive and intransitive verbs in terms of word formation or morphology. They have the same morphological form or suffix regardless of whether they are transitive or intransitive, and the transitivity or intransitivity of the verb is determined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |