|
Undecaprenyl-diphosphatase
In enzymology, an undecaprenyl-diphosphatase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :undecaprenyl diphosphate + H2O \rightleftharpoons undecaprenyl phosphate + phosphate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are undecaprenyl diphosphate and H2O, whereas its two products are undecaprenyl phosphate and phosphate. The enzymatic activity is enhanced by divalent cations, particularly Ca2+. In many bacteria, this enzyme is a membrane protein that participates in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. The enzyme has been implicated in conferring resistance to the antibiotic bacitracin. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on acid anhydrides in phosphorus-containing anhydrides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is undecaprenyl-diphosphate phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include Undecaprenyl-pyrophosphate phosphatase (Uppp), UPP phosphatase, BacA, C55-isoprenyl diphosphatase, C55-isoprenyl pyrophosphatas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-Acetylmuramic acid, ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is an oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Peptidoglycan hydrolysis and synthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), Parasitic disease, parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from Antibiotic misuse, antibiotic overuse, both in medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undecaprenol Kinase
In enzymology, an undecaprenol kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + undecaprenol \rightleftharpoons ADP + undecaprenyl phosphate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and undecaprenol, whereas its two products are ADP and undecaprenyl phosphate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:undecaprenol phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include isoprenoid alcohol kinase, isoprenoid alcohol phosphokinase, C55-isoprenoid alcohol phosphokinase, isoprenoid alcohol kinase (phosphorylating), C55-isoprenoid alcohol kinase, C55-isoprenyl alcohol phosphokinase, and polyisoprenol kinase. This enzyme participates in peptidoglycan Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond: :\ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce This typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases. Esterases cleave ester bonds in lipids and phosphatases cleave phosphate groups off molecules. An example of crucial esterase is acetylcholine esterase, which assists in transforming the neuron impulse into the acetate group after the hydrolase breaks the acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. Acetic acid is an important metabolite in the body and a critical intermediate for other reactions such as glycolysis. Lipases hydrolyze glycerides. Glycosidases cleave sugar molecules off carbohydrates and peptidases hydrolyze peptide bonds. Nucleosidases hydrolyze the bonds of nucleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacitracin
Bacitracin is a polypeptide antibiotic. It is a mixture of related cyclic peptides produced by '' Bacillus licheniformis'' bacteria, that was first isolated from the variety "Tracy I" ( ATCC 10716) in 1945. These peptides disrupt Gram-positive bacteria by interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis. Bacitracin is primarily used as a topical preparation, as it can cause kidney damage when used internally. It is generally safe when used topically, but in rare cases may cause hypersensitivity, allergic or anaphylactic reactions, especially in people allergic to neomycin. In 2022, it was the 323rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 100,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Bacitracin is used in human medicine as a polypeptide antibiotic and is "approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in chickens and turkeys," though use in animals contributes to antibiotic resistance. As bacitracin zinc salt, in combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
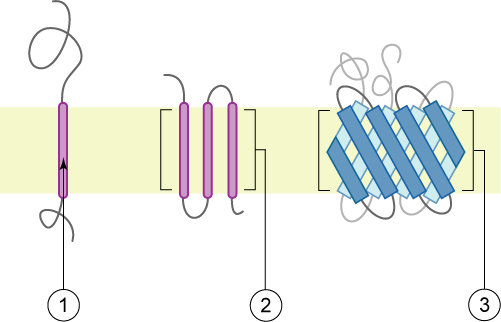
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |