|
UNIVAC 1105
The UNIVAC 1105 was a follow-on computer to the UNIVAC 1103A introduced by UNIVAC, Sperry Rand in September 1958. The UNIVAC 1105 used 21 types of vacuum tubes, 11 types of diodes, 10 types of transistors, and three core types. The UNIVAC 1105 had either 8,192 or 12,288 words of 36-bit magnetic core memory, in two or three banks of 4,096 words each. Magnetic drum memory provided either 16,384 or 32,768 words, in one or two drums with 16,384 words each. Sixteen to twenty-four UNISERVO, UNISERVO II tape drives were connected, with a maximum capacity (not counting block overhead) of 1,200,000 words per tape. Major differences from the UNIVAC_1103#1103A, 1103A were in the addition of a buffered Input/Output system consisting of two 120-word buffers which allowed for overlapping of magnetic tape reading with writing at the same time. fixed-point arithmetic, Fixed-point numbers had a one-bit sign and a 35-bit value, with negative values represented in ones' complement format. floating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Factor
In electrical engineering, the power factor of an AC power system is defined as the ratio of the ''real power'' absorbed by the electrical load, load to the ''apparent power'' flowing in the circuit. Real power is the average of the instantaneous product of voltage and current and represents the capacity of the electricity for performing work. Apparent power is the product of root mean square (RMS) current and voltage. Due to energy stored in the load and returned to the source, or due to a non-linear load that distorts the wave shape of the current drawn from the source, the apparent power may be greater than the real power, so more current flows in the circuit than would be required to transfer real power alone. A power factor magnitude of less than one indicates the voltage and current are not in phase, reducing the average Product (mathematics), product of the two. A negative power factor occurs when the device (normally the load) generates real power, which then flows back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube Computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transistors. Some later computers on the list had both vacuum tubes and transistors. This list of vacuum-tube computers is sorted by date put into service: See also * List of transistorized computers * History of computing hardware The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology. The first aids to computation were purely mec ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Vacuum Tube Computers Vacuum tube computers Computers, list of vacuum tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC Mainframe Computers
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company and successor organizations. The BINAC, built by the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation, was the first general-purpose computer for commercial use, but it was not a success. The last UNIVAC-badged computer was produced in 1986. History and structure J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly built the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) at the University of Pennsylvania's Moore School of Electrical Engineering between 1943 and 1946. A 1946 patent rights dispute with the university led Eckert and Mauchly to depart the Moore School to form the Electronic Control Company, later renamed Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation (EMCC), based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. That company first built a computer called BINAC (BINary Automa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Vacuum Tube Computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transistors. Some later computers on the list had both vacuum tubes and transistors. This list of vacuum-tube computers is sorted by date put into service: See also * List of transistorized computers * History of computing hardware The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology. The first aids to computation were purely mec ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Vacuum Tube Computers Vacuum tube computers Computers, list of vacuum tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing Hardware
The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology. The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. In later stages, computing devices began representing numbers in continuous forms, such as by distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a specific voltage level. Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor technology, followed by the invention of integrated circuit chips, led to revolutionary breakthroughs. Transistor-based computers and, later, integrated circuit-based computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of UNIVAC Products
This is a list of UNIVAC products. It ends in 1986, the year that Sperry Corporation merged with Burroughs Corporation to form Unisys as a result of a hostile takeover bid launched by Burrough's CEO W. Michael Blumenthal. The Remington Rand years (1950 to 1955) Calculating devices * UNIVAC 40 * UNIVAC 60 * UNIVAC 120 Computer systems *UNIVAC I *UNIVAC 1101 * UNIVAC 1102 * UNIVAC 1103 * UNIVAC 1104 Peripherals Storage * UNISERVO tape drive Display and print * UNIVAC High speed printer 600 line/min printer Offline tape handling units * UNIPRINTER 10 char/s printer with tape drive * UNITYPER keyboard with tape drive *UNIVAC Tape to Card converter card punch with tape drive * UNIVAC Card to Tape converter card reader with tape drive * UNIVAC Paper Tape to Tape converter paper tape reader with tape drive The Sperry Rand years (1955 to 1978) Calculating devices * UNIVAC 1004 * UNIVAC 1005 Computer systems Embedded systems *AN/USQ-17 – the Naval Tactical Data Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC 1100/2200 Series
The UNIVAC 1100/2200 series is a series of compatible 36-bit computer systems, beginning with the UNIVAC 1107 in 1962, initially made by Sperry Rand. The series continues to be supported today by Unisys Corporation as the ClearPath Dorado Series. The solid-state 1107 model number was in the same sequence as the earlier vacuum-tube computers, but the early computers were not compatible with their solid-state successors. Architecture Data formats * Fixed-point, either integer or fraction **Whole word – 36-bit (ones' complement) **Half word – two 18-bit fields per word (unsigned or ones' complement) **Third word – three 12-bit fields per word (ones' complement) **Quarter word – four 9-bit fields per word (unsigned) **Sixth word – six 6-bit fields per word (unsigned) * Floating point **Single precision – 36 bits: sign bit, 8-bit characteristic, 27-bit mantissa **Double precision – 72 bits: sign bit, 11-bit characteristic, 60-bit mantissa *Alphanumeric ** FIELDATA � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News And Observer
''The News & Observer'' is an American regional daily newspaper that serves the greater Triangle area based in Raleigh, North Carolina. The paper is the largest in circulation in the state (second is the '' Charlotte Observer''). The paper has been awarded three Pulitzer Prizes, the most recent of which was in 1996 for a series on the health and environmental impact of North Carolina's booming hog industry. The paper was one of the first in the world to launch an online version of the publication, Nando.net in 1994. Ownership On May 17, 1995 the News & Observer Publishing Company was sold to McClatchy Newspapers of Sacramento, California, for $373 million, ending 101 years of Daniels family ownership. In the mid-1990s, flexo machines were installed, allowing the paper to print thirty-two pages in color, which was the largest capacity of any newspaper within the United States at the time. The McClatchy Company currently operates a total of twenty-nine daily newspapers in fourte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
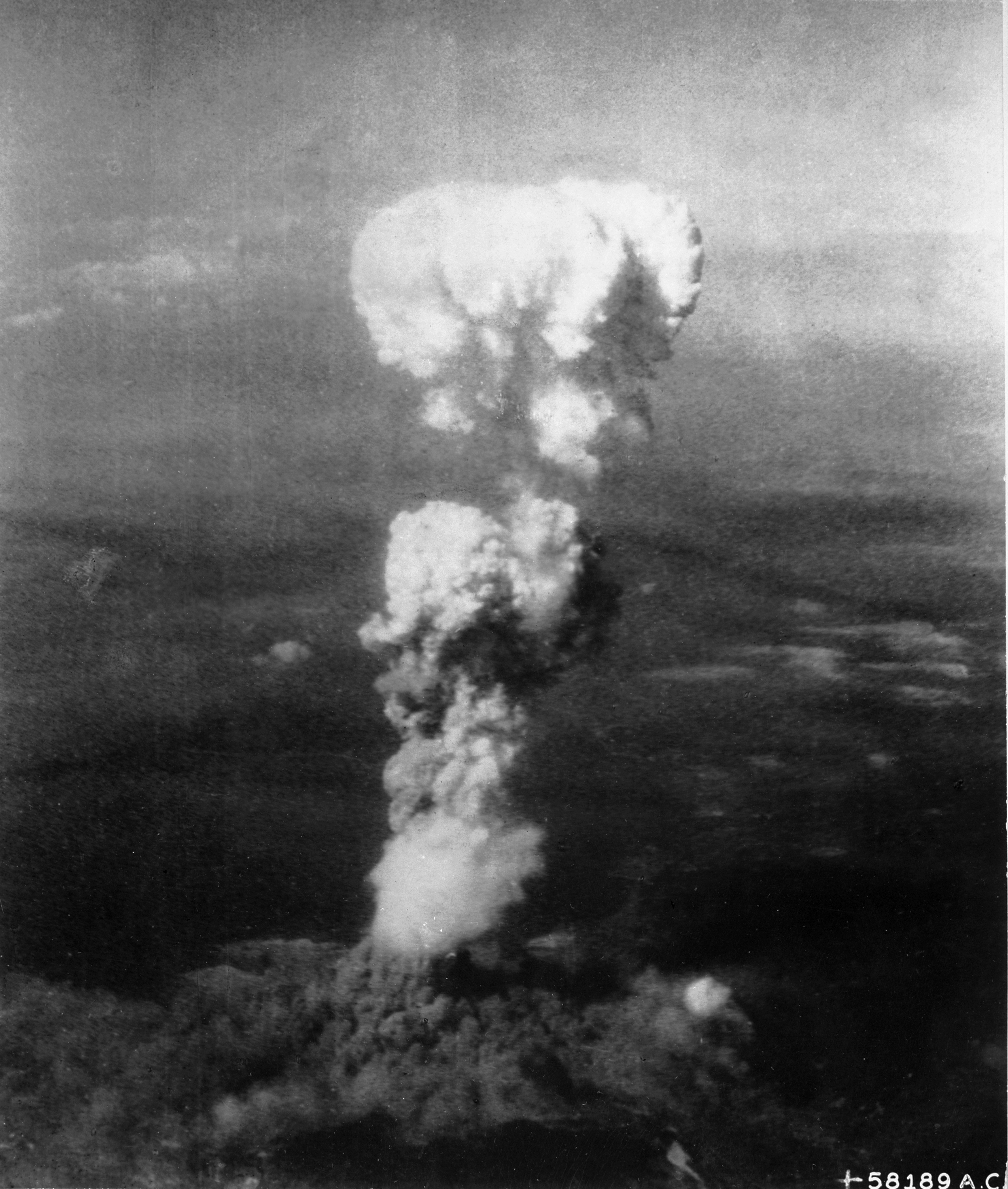
Nuclear Warfare
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological warfare, radiological result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the Nuclear fallout, fallout released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter", nuclear famine, and societal collapse. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including human extinction. To date, the only use of nuclear weapons in armed conflict occurred in 1945 with the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. On August 6, 1945, a uranium Nuclear weapon design, gun-type device (code name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
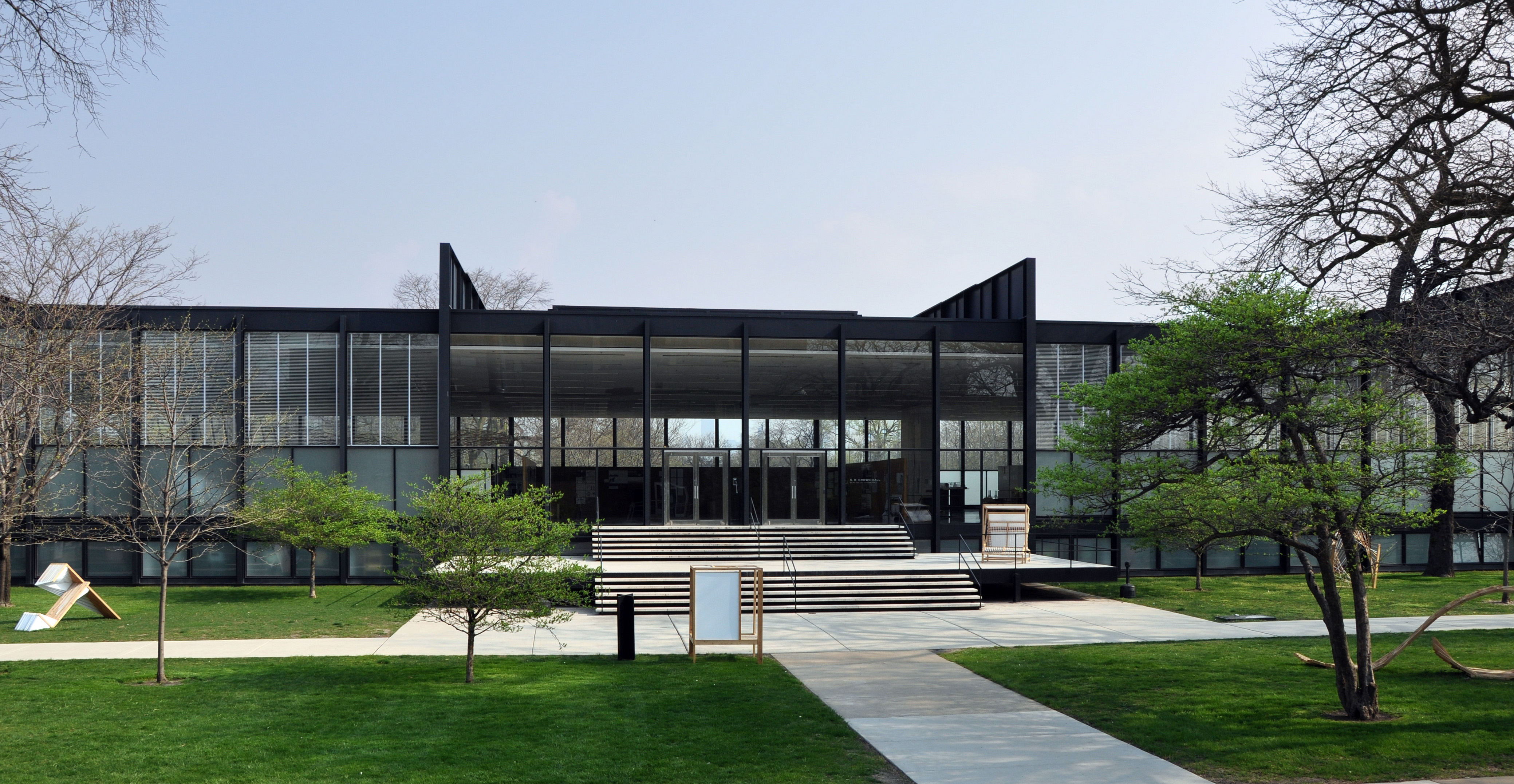
Armour Institute Of Technology
The Illinois Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Illinois Tech and IIT, is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Tracing its history to 1890, the present name was adopted upon the merger of the Armour Institute and Lewis Institute in 1940. The university has programs in architecture, business, communications, design, engineering, industrial technology, information technology, law, psychology, and science. It is classified Classified may refer to: General *Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive *Classified advertising or "classifieds" Music *Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper * The Classified, a 1980s American ro ... among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". The university's historic roots are in several 19th-century engineering and professional education institutions in the United States. In the mid 20th century, it became closely associated with trends in moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce and its Director of the United States Census Bureau, director is appointed by the president of the United States. Currently, Ron S. Jarmin is the acting director of the U.S. Census Bureau. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the United States census, U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives to the U.S. state, states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses in making informed decisions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |