|
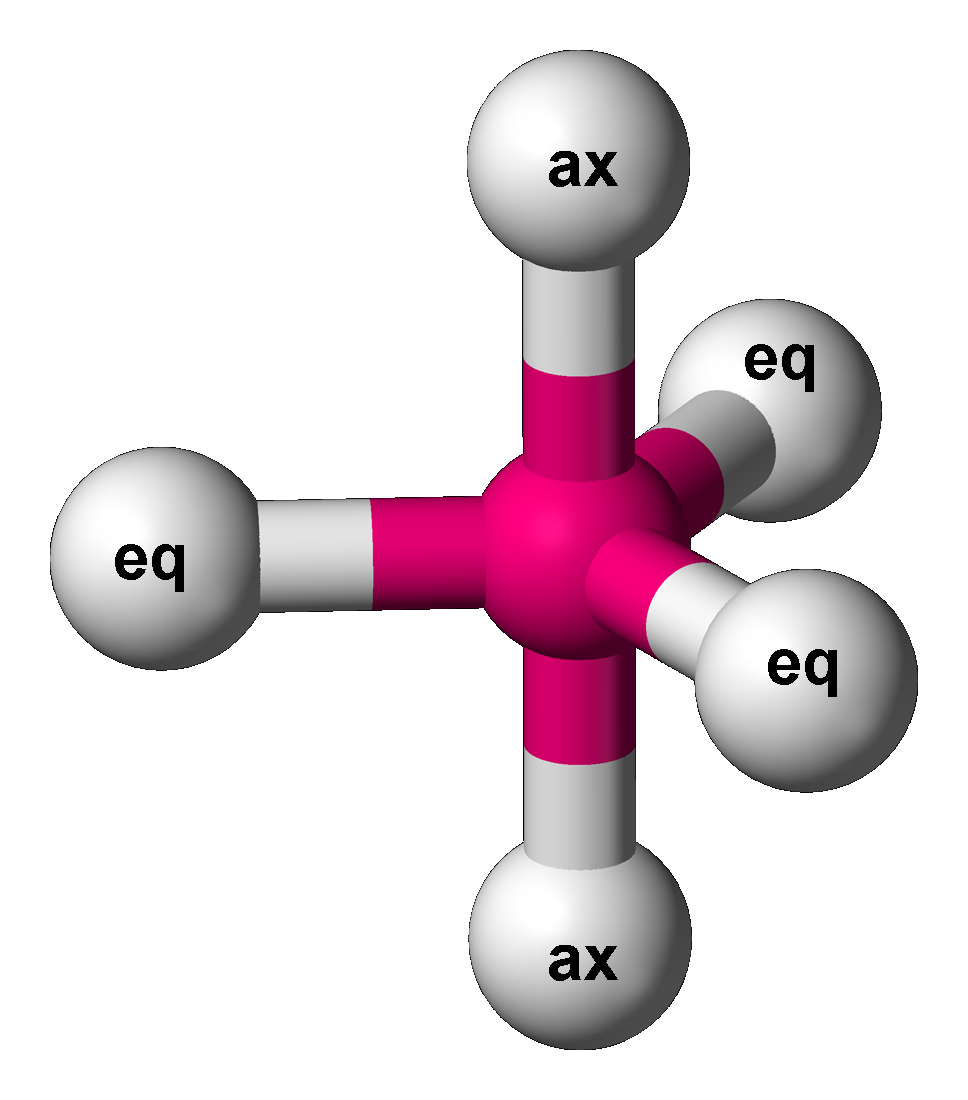
Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (), and phosphorus pentachloride () in the gas phase. Axial (or apical) and equatorial positions The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For phosphorus pentachloride as an example, the phosphorus atom shares a plane with three chlorine atoms at 120° angles to each other in ''equatorial'' positions, and two more chlorine atoms above and below the plane (''axial'' or ''apical'' positions). According to the VSEPR theory of molecular geometry, an axial position is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihedral Symmetry In Three Dimensions
In geometry, dihedral symmetry in three dimensions is one of three infinite sequences of point groups in three dimensions which have a symmetry group that as an abstract group is a dihedral group Dih''n'' (for ''n'' ≥ 2). Types There are 3 types of dihedral symmetry in three dimensions, each shown below in 3 notations: Schönflies notation, Coxeter notation, and orbifold notation. ;Chiral: *''Dn'', 'n'',2sup>+, (22''n'') of order 2''n'' – dihedral symmetry or para-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dihn''). ;Achiral: *''Dnh'', 'n'',2 (*22''n'') of order 4''n'' – prismatic symmetry or full ortho-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dihn'' × ''Z''2). *''Dnd'' (or ''Dnv''), ''n'',2+ (2*''n'') of order 4''n'' – antiprismatic symmetry or full gyro-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dih''2''n''). For a given ''n'', all three have ''n''-fold rotational symmetry about one axis (rotation by an angle of 360°/''n'' does not change the object), and 2-fold rotational symmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism and biological activity. The angles between bonds that an atom forms depend only weakly on the rest of molecule, i.e. they can be understood as approximately local and hence transferable properties. Determination The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. IR, microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the details of the vibrational and rotational absorbance detected by these techniques. X-ray crystallography, neutron diffraction and electron diffraction can give molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry Mechanism
The Berry mechanism, or Berry pseudorotation mechanism, is a type of vibration causing molecules of certain geometries to isomerize by exchanging the two axial ligands (see Figure at right) for two of the equatorial ones. It is the most widely accepted mechanism for pseudorotation and most commonly occurs in trigonal bipyramidal molecules such as PF5, though it can also occur in molecules with a square pyramidal geometry. The Berry mechanism is named after R. Stephen Berry, who first described this mechanism in 1960.RS Berry, 1960, "Correlation of rates of intramolecular tunneling processes, with application to some Group V compounds," ''J. Chem. Phys.'' 32:933-938, DOI 10.1063/1.1730820; seo accessed 28 May 2014M Cass, KK Hii & HS Rzepa, 2005, "Mechanisms that interchange axial and equatorial atoms in fluxional processes: Illustration of the Berry pseudorotation, the turnstile and the lever mechanisms via animation of transition state normal vibrational modes", ''J. Chem. Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Difluoride
Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula , and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid. It has a nauseating odour and low vapor pressure. Structure Xenon difluoride is a linear molecule with an Xe–F bond length of in the vapor stage, and 200 pm in the solid phase. The packing arrangement in solid shows that the fluorine atoms of neighbouring molecules avoid the equatorial region of each molecule. This agrees with the prediction of VSEPR theory, which predicts that there are 3 pairs of non-bonding electrons around the equatorial region of the xenon atom. At high pressures, novel, non-molecular forms of xenon difluoride can be obtained. Under a pressure of ~50 GPa, transforms into a semiconductor consisting of units linked in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, the linear molecular geometry describes the geometry around a central atom bonded to two other atoms (or ''ligands'') placed at a bond angle of 180°. Linear organic molecules, such as acetylene (), are often described by invoking sp orbital hybridization for their carbon centers. According to the VSEPR model (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model), linear geometry occurs at central atoms with two bonded atoms and zero or three lone pairs ( or ) in the AXE notation. Neutral molecules with linear geometry include beryllium fluoride () with two single bonds, carbon dioxide () with two double bonds, hydrogen cyanide () with one single and one triple bond. The most important linear molecule with more than three atoms is acetylene (), in which each of its carbon atoms is considered to be a central atom with a single bond to one hydrogen and a triple bond to the other carbon atom. Linear anions include azide () and thiocyanate (), and a linear cation is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triiodide
In chemistry, triiodide usually refers to the triiodide ion, . This anion, one of the polyhalogen ions, is composed of three iodine atoms. It is formed by combining aqueous solutions of iodide salts and iodine. Some salts of the anion have been isolated, including thallium(I) triiodide (Tl+ 3sup>−) and ammonium triiodide ( H4sup>+ 3sup>−). Triiodide is observed to be a red colour in solution. Nomenclature Other chemical compounds with "triiodide" in their name may contain three iodide centers that are not bonded to each other as the triiodide ion, but exist instead as separate iodine atoms or iodide ions. Examples include nitrogen triiodide (NI3) and phosphorus triiodide (PI3), where individual iodine atoms are covalently bonded to a central atom. As some cations have the theoretical possibility to form compounds with both triiodide and iodide ions, such as ammonium, compounds containing iodide anions in a 3:1 stoichiometric ratio should only be referred to as triiodides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine Trifluoride
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. This colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold (pressurized at room temperature). The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry, in nuclear reactor fuel processing, as a component in rocket fuels, and other industrial operations. Preparation, structure, and properties It was first reported in 1930 by Ruff and Krug who prepared it by fluorination of chlorine; this also produced ClF (chlorine monofluoride) and the mixture was separated by distillation. :3 F2 + Cl2 → 2 ClF3 The molecular geometry of ClF3 is approximately T-shaped, with one short bond (1.598 Å) and two long bonds (1.698 Å). This structure agrees with the prediction of VSEPR theory, which predicts lone pairs of electrons as occupying two equatorial positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-shaped Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, T-shaped molecular geometry describes the structures of some molecules where a central atom has three ligands. Ordinarily, three-coordinated compounds adopt trigonal planar or pyramidal geometries. Examples of T-shaped molecules are the halogen trifluorides, such as ClF3. According to VSEPR theory, T-shaped geometry results when three ligands and two lone pairs of electrons are bonded to the central atom, written in AXE notation as AX3E2. The T-shaped geometry is related to the trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry for AX5 molecules with three equatorial and two axial ligands. In an AX3E2 molecule, the two lone pairs occupy two equatorial positions, and the three ligand atoms occupy the two axial positions as well as one equatorial position. The three atoms bond at 90° angles on one side of the central atom, producing the T shape. The trifluoroxenate(II) anion, , has been investigated as a possible first example of an AX3E3 molecule, which might be expected b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Tetrafluoride
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula S F4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. Structure Sulfur in SF4 is in the formal +4 oxidation state. Of sulfur's total of six valence electrons, two form a lone pair. The structure of SF4 can therefore be anticipated using the principles of VSEPR theory: it is a see-saw shape, with S at the center. One of the three equatorial positions is occupied by a nonbonding lone pair of electrons. Consequently, the molecule has two distinct types of F ligands, two axial and two equatorial. The relevant bond distances are = 164.3 pm and = 154.2 pm. It is typical for the axial ligands in hypervalent molecules to be bonded less strongly. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seesaw Molecular Geometry
Disphenoidal or seesaw (also known as sawhorse) is a type of molecular geometry where there are four bonds to a central atom with overall C2v molecular symmetry. The name "seesaw" comes from the observation that it looks like a playground seesaw. Most commonly, four bonds to a central atom result in tetrahedral or, less commonly, square planar geometry. The seesaw geometry occurs when a molecule has a steric number of 5, with the central atom being bonded to 4 other atoms and 1 lone pair (AX4E1 in AXE notation). An atom bonded to 5 other atoms (and no lone pairs) forms a trigonal bipyramid with two axial and three equatorial positions, but in the seesaw geometry one of the atoms is replaced by a lone pair of electrons, which is always in an equatorial position. This is true because the lone pair occupies more space near the central atom (A) than does a bonding pair of electrons. An equatorial lone pair is repelled by only two bonding pairs at 90°, whereas a hypothetical ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicophilicity
Apicophilicity is the phenomenon in which electronegative substituents of trigonal bipyramidal pentacoordinate compounds prefer to occupy apical (axial) positions (Lap). The term "apicophilicity" was first proposed by Earl L. Muetterties in 1963 for the structural analysis of pentacoordinate phosphorus fluorides by 19F NMR. Since the apical bonding of a pentacoordinate typical (group 1, 2, 13-18) element compound consists of a 3-center-4-electron bond, in which the electron density is localized on two apical substituents, an arrangement in which electronegative substituents occupy apical positions is more stable. The apicophilicity of a substituent is defined as the difference in energy between two isomeric structures in which the substituent occupies an apical position and an equatorial position (Leq). Experimentally, instead of direct measurement of the energy difference, which is usually difficult to measure, the relative energy barriers for pseudorotation In chemistry, a ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |