|
Tretes
Tretes is a mountain tourist area in East Java, Indonesia. This area is located 60 km south of Surabaya, the capital city of East Java, and its administrative is part of Prigen, Pasuruan Regency. Tretes area is located on the slopes mountain of Arjuno-Welirang. The area is a popular area for tourism. This area is located at an altitude of 600–900 meters above sea level. Etymology The word of Tretes comes from the water dripping sounds like "tes" "tes". This can be seen by the presence of a source of water dripping in the cracks of the stone walls in the Dong Biru area (located near the area of ''Kakek Bodo'' tourist attractions and from the direction of Surabaya located on the right side of the main road). History Since a long time ago the Tretes was known as one of the main rest areas in Java because of its natural scenic and cool air. Tretes was once known as the rest area of the Dutch colonial people. In this area, there are many Dutch heritage buildings. Usually in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prigen
Prigen ( jv, Prigèn or called "Tretes") is a district in the Pasuruan Regency of East Java, Indonesia. Prigen is located on the slope of the Arjuno volcano. Taman Safari II is located in Prigen. The 13th century Candi Jawi (originally known as Jajawa) temple is located on the eastern slope of Mount Welirang outside Candi Wates village in the Prigen district. It is a syncretic Hindu-Buddhist Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ... temple ( candi) References {{coord, 7.6833, S, 112.6167, E, source:wikidata, display=title Pasuruan Regency Districts of East Java ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Java
East Java ( id, Jawa Timur) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost hemisphere of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern and southern coasts, respectively, while the narrow Bali Strait to the east separates Java from Bali by around . Located in eastern Java (island), Java, the province also includes the island of Madura Island, Madura (which is connected to Java by the longest bridge in Indonesia, the Suramadu Bridge), as well as the Kangean Islands, Kangean islands and other smaller island groups located further east (in the northern Bali Sea) and Masalembu Islands, Masalembu archipelagos in the north. Its capital is Surabaya, the Largest cities in Indonesia, second largest city in Indonesia, a major industrial center and also a major business center. Banyuwangi is the largest regency in East Java and the largest on the island of Java. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Village (Indonesia)
In Indonesia, a tourist village (''desa wisata'') is a village officially designated as one that welcomes tourism. In the Special Region of Yogyakarta (which includes the Sleman Regency), the concept was embraced around 2000 with dozens of villages being dubbed as tourist villages.(3 January 2004)Sleman, home of a tourist villages ''The Jakarta Post'' According to a 2009 report in ''The Jakarta Post'' there were 48 tourist villages listed in Yogyakarta, though only ten were actually operating as such, including: Kebonagung, Manding, Krebet, Kasongan (Bantul), Trumpon, Turgo, Ketingan, Brayut, Gamplong (Sleman) and Bobung (Gunungkidul). The designation as a "tourist village" may not mean that the village is actually developed for tourism, but that it is believed the potential for tourism exists. Nearby Mount Merapi Mount Merapi, ''Gunung Merapi'' (literally Fire Mountain in Indonesian and Javanese), is an active stratovolcano located on the border between the province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuno-Welirang
Mount Arjuno-Welirang is a stratovolcano in the province of East Java on Java, Indonesia. Mount Arjuno-Welirang lies about 50 kilometers (31 mi) south of Surabaya, and 20 kilometers (12 mi) north of Malang. It is a twin volcano, with the 'twins' being Arjuno and Welirang. There is at least one other stratovolcano in the area, and there are around 10 pyroclastic cones nearby. They are located in a 6 km line between Arjuno and Welirang. The Arjuno-Welirang volcanic complex itself lies in the older two volcanoes, Mount Ringgit to the east and Mount Linting to the south. The summit lacks vegetation. Fumarolic areas with sulfur deposits are found in several locations on Welirang. The name ''Arjuno'' is Javanese rendition of Arjuna, a hero in Mahabharata epic, while ''Welirang'' is Javanese word for ''sulfur''. A 1950 eruption had a VEI=2. There was an explosive eruption. Another eruption occurred two years later in 1952. This eruption had a VEI=0. A 300 hectares at slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a refrigerator and other kitchen facilities, upholstered chairs, a flat screen television, and en-suite bathrooms. Small, lower-priced hotels may offer only the most basic guest services and facilities. Larger, higher-priced hotels may provide additional guest facilities such as a swimming pool, business centre (with computers, printers, and other office equipment), childcare, conference and event facilities, tennis or basketball courts, gymnasium, restaurants, day spa, and social function services. Hotel rooms are usually numbered (or named in some smaller hotels and B&Bs) to allow guests to identify their room. Some boutique, high-end hotels have custom decorated rooms. Some hotels offer meals as part of a room and board arrangement. In Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity, sometimes transferred to the Church for reuse as a monastery. Then they gradually re-evolved through the Middle Ages into elegant upper-class country homes. In the Early Modern period, any comfortable detached house with a garden near a city or town was likely to be described as a villa; most survivals have now been engulfed by suburbia. In modern parlance, "villa" can refer to various types and sizes of residences, ranging from the suburban semi-detached double villa to, in some countries, especially around the Mediterranean, residences of above average size in the countryside. Roman Roman villas included: * the ''villa urbana'', a suburban or country seat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Monsoon Climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ''Am''. Tropical monsoon climates have monthly mean temperatures above in every month of the year and a dry season. The tropical monsoon climate is the intermediate climate between the wet Af (or tropical rainforest climate) and the drier Aw (or tropical savanna climate). A tropical monsoon climate's driest month has on average less than 60 mm, but more than 100-\left(\frac\right). This is in direct contrast to a tropical savanna climate, whose driest month has less than 60 mm of precipitation and also less than 100-\left(\frac\right) of average monthly precipitation. In essence, a tropical monsoon climate tends to either have more rainfall than a tropical savanna climate or have less pronounced dry seasons. A tropical monsoon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metres Above Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''. The combination of unit of measurement and the physical quantity (height) is called "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, while in United States customary and imperial units it would be called " feet above mean sea level". Mean sea levels are affected by climate change and other factors and change over time. For this and other reasons, recorded measurements of elevation above sea level at a reference time in history might differ from the actual elevation of a given location over sea level at a given moment. Uses Metres above sea level is the standard measurement of the elevation or altitude of: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Flying objects su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
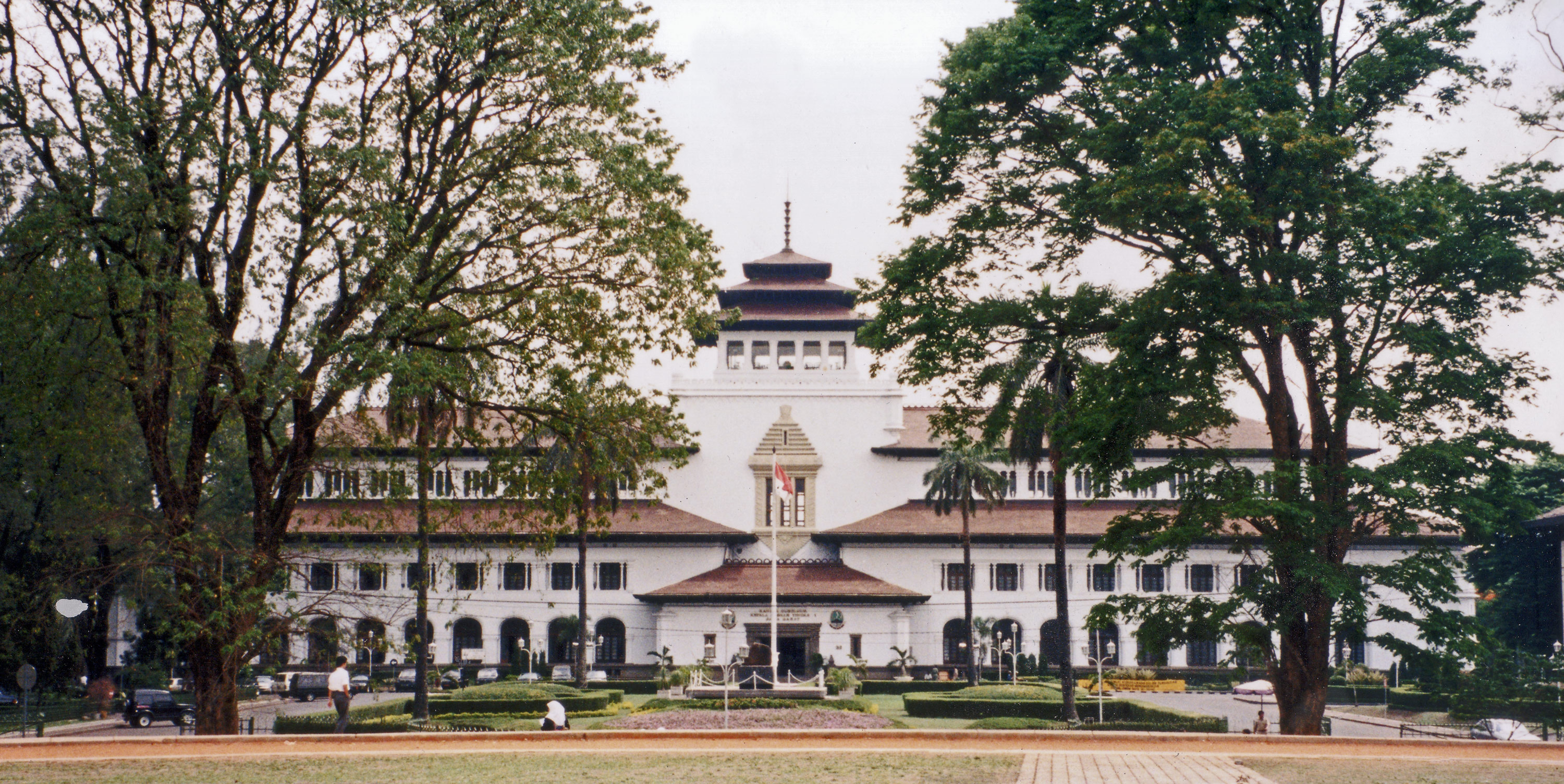
Colonial Architecture Of Indonesia
The colonial architecture of Indonesia refers to the buildings that were created across Indonesia during the Dutch colonial period, during that time, this region was known as the Dutch East Indies. These types of colonial era structures are more prevalent in Java and Sumatra, as those islands were considered more economically significant during the Dutch imperial period. As a result of this, there is a large number of well preserved colonial era buildings that are still densely concentrated within Indonesian cities in Java and Sumatra to this day. In the rest of the archipelago, there is also a sizeable amount of old Dutch East India Company (VOC) era forts and warehouses that were built during the Dutch colonial period of Indonesia, particularly around the Maluku Islands and Sulawesi, though these tend to be more scattered about and in less dense concentrations compared to those found on Java and Sumatra. The three styles of colonial architecture in Indonesia are: * Old Indies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
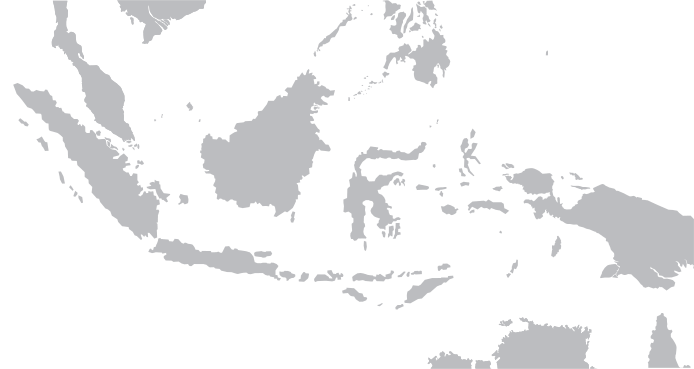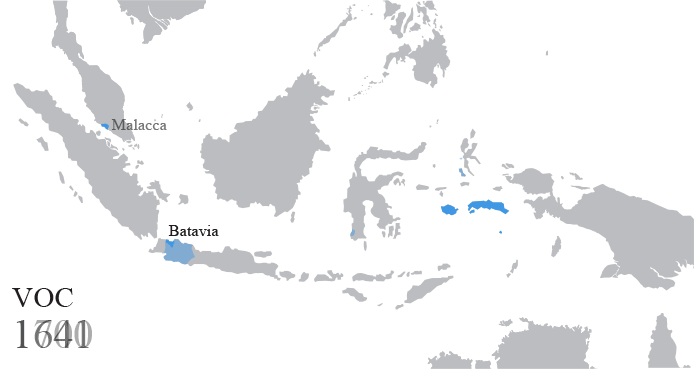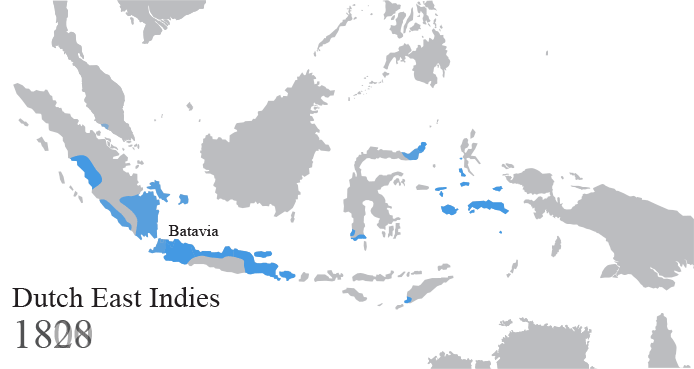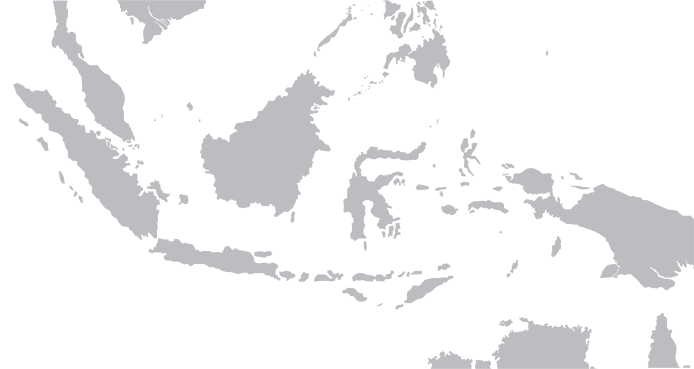
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |