|
Transposition (chess)
In chess, a transposition is a sequence of moves that results in a position which may also be reached by another, more common sequence of moves. Transpositions are particularly common in the opening, where a given position may be reached by different sequences of moves. Players sometimes use transpositions deliberately, to avoid variations they dislike, lure opponents into unfamiliar or uncomfortable territory or simply to worry opponents. See review at In chess the verb "transpose" means to shift the game onto a different opening track from which it started. Transposition tables are an essential part of a computer chess program. Transpositions exist in other abstract strategy games such as shogi, Go, tic-tac-toe and Hex. Examples Positions reached by different routes For instance, the first position can be obtained from the Queen's Gambit: :1. d4 d5 :2. c4 e6 :3. Nc3 Nf6 But this position can also be reached from the English Opening: :1. c4 e6 :2. Nc3 Nf6 :3. d4 d5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Indian Defence
The King's Indian Defence is a common chess opening. It is defined by the following moves: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 g6 Black intends to follow up with 3...Bg7 and 4...d6 (the Grünfeld Defence arises when Black plays 3...d5 instead, and is considered a separate opening). White's major third move options are 3.Nc3, 3.Nf3 or 3.g3, with both the King's Indian and Grünfeld playable against these moves. The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' classifies the King's Indian Defence under the codes E60 through E99. The King's Indian is a hypermodern opening, where Black deliberately allows White control of the with its pawns, with the view to subsequently challenge it. In the most critical lines of the King's Indian, White erects an imposing pawn centre with Nc3 followed by e4. Black stakes out its own claim to the centre with the Benoni-style ...c5, or ...e5. If White resolves the central pawn tension with d5, then Black follows with either ...b5 and queenside play, or ...f5 and an ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benoni Defense
The Benoni Defense is a chess opening characterized by an early reply of ...c5 against White's opening move 1.d4. Most commonly, it is reached by the sequence: :1. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4, d4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...Nf6, Nf6 :2. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...Nf6/2. c4, c4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...Nf6/2. c4/2...c5, c5 :3. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...Nf6/2. c4/2...c5/3. d5, d5 Black can then Sacrifice (chess), sacrifice a pawn with 3...b5 (the Benko Gambit), otherwise 3...e6 is the most common move. (3...d6 or 3...g6 are also seen, typically Transposition (chess), transposing to main lines.) The Old Benoni Defense is characterized by :1. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4, d4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...c5, c5 This will usually transpose into a main line after 2.d5, but Black has other options such as an early ...f5. Etymology ''Benoni (given name), Benoni'' (or "Ben-Oni") is an ancient Hebrew name, still occasionally used, meaning "son of my sorrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Defense
The English Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. d4 e6 :2. c4 b6 Description White often gains a broad with 3.e4, which Black puts pressure on with moves like ...Bb7, ...Bb4, and sometimes even ...Qh4 and/or ...f5. It was developed by the Leicester player P. N. Wallis, and was taken up by several leading English players in the 1970s, such as Tony Miles, Jon Speelman and Raymond Keene. It flouts several traditional opening principles, as Black often bishops before knights and brings out the queen early. It is a somewhat unusual opening, but has been seen in high-level grandmaster play, usually as a surprise weapon, for example when Viktor Korchnoi used it to defeat Lev Polugaevsky in their world championship semifinals match at Évian 1977 (see below). Example games *Lev Polugaevsky vs. Viktor Korchnoi, Évian 1977 1.d4 e6 2.c4 b6 3.e4 Bb7 4.Qc2 Qh4 5.Nd2 Bb4 6.Bd3 f5 7.Nf3 Bxd2+ 8.Kf1 Qh5 9.Bxd2 Nf6 10.exf5 Bxf3 11.gxf3 Nc6 12.Bc3 0-0 13.Re1 Qh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Defense
The Dutch Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. d4 f5 Black's 1...f5 stakes a claim to the e4-square and envisions an attack in the middlegame on White's ; however, it also weakens Black's kingside to an extent (especially the e8–h5 diagonal). Like its 1.e4 counterpart, the Sicilian Defence, the Dutch is an aggressive and unbalancing opening, resulting in the lowest percentage of draws among the most common replies to 1.d4. Historically, White has tried many methods to exploit the kingside weaknesses, such as the Staunton Gambit (2.e4) and Korchnoi Attack (2.h3 and 3.g4). The Dutch has never been a main line against 1.d4 and is rarely seen today in high-level competition, although a number of top players, including Alexander Alekhine, Bent Larsen, Paul Morphy, Miguel Najdorf, and Hikaru Nakamura have used it with success. Its most notable use may have been in 1951, when both world champion Mikhail Botvinnik and his challenger, David Bronstein, played i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Benoni Defense
The Modern Benoni is a chess opening that begins with the moves 1. d4 Nf6 2. c4 c5 3. d5 e6. It is classified under the ECO codes A60–A79. After the initial moves, Black proceeds to capture on d5, creating a majority of black pawns on the queenside. To support their advance, the king's bishop is usually fianchettoed on g7. These two features differentiate Black's setup from the other Benoni defences and the King's Indian Defence, although transpositions between these openings are common. Frank Marshall invented the Modern Benoni in 1927, but his experiments with the opening went largely ignored for over 20 years. In the 1950s the system was revitalized by players in the Soviet Union, chief among them Mikhail Tal. Its subsequent adoption by players of a similarly aggressive and uncompromising style such as Bobby Fischer and Garry Kasparov established the opening's reputation as one of Black's most dynamic responses to 1.d4. The Modern Benoni suffered a serious theoret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Indian Defense
The Queen's Indian Defense (QID) is a chess opening defined by the moves: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 e6 :3. Nf3 b6 The opening is a solid defense to the Queen's Pawn Game. 3...b6 increases Black's control over the central light squares e4 and d5 by preparing to fianchetto the , with the opening deriving its name from this maneuver. As in the other Indian defenses, Black attempts to control the with pieces in hypermodern style, instead of occupying it with pawns in classical style. By playing 3.Nf3, White sidesteps the Nimzo-Indian Defense that arises after 3.Nc3 Bb4. The Queen's Indian is regarded as the sister opening of the Nimzo-Indian, since both openings aim to impede White's efforts to gain full control of the center by playing e2–e4. Together, they are a well-respected response to 1.d4. Main line: 4.g3 4. g3 (''ECO'' E15–E19) has long been White's most popular line against the Queen's Indian. It contests the by preparing to fianchetto the light-squared bishop. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimzo-Indian Defense
The Nimzo-Indian Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 e6 :3. Nc3 Bb4 Other move orders, such as 1.c4 e6 2.Nc3 Nf6 3.d4 Bb4, are also feasible. In the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'', the Nimzo-Indian is classified as E20–E59. This hypermodern opening was developed by Aron Nimzowitsch who introduced it to master-level chess in the early 20th century. Unlike most Indian openings, the Nimzo-Indian does not involve an immediate fianchetto, although Black often follows up with ...b6 and ...Bb7. By pinning White's knight, Black prevents the threatened 4.e4 and seeks to inflict doubled pawns on White. White will attempt to create a and develop their pieces to prepare for an assault on the Black position. Black's delay in committing to a pawn structure makes the Nimzo-Indian (sometimes colloquially referred to as the "Nimzo") a very flexible defence to 1.d4. It can also transpose into lines of the Queen's Gambit or Queen's Indian Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Opening
The Catalan Opening is a chess opening where White plays d4 and c4 and fianchettoes the white bishop on g2. A common opening sequence is 1.d4 Nf6 2.c4 e6 3.g3, although various other openings can transpose into the Catalan. The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' lists codes E01–E09 for lines with 1.d4 Nf6 2.c4 e6 3.g3 d5 4.Bg2; other lines are part of E00. In the Catalan, White adopts a combination of the Queen's Gambit and Réti Opening. White combines the space-gaining moves d4 and c4 with g3, preparing to fianchetto the king's bishop. This places pressure mainly on the queenside while hoping to keep the white king safe in the long-term. The c4-pawn can become vulnerable, however, and White might have to sacrifice a pawn. Black has two main approaches to play against the Catalan: in the Open Catalan Black plays ...dxc4 and can either try to hold on to the pawn with ...b5 or give it back for extra time to free their game. In the Closed Catalan, Black does not capture on c4; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
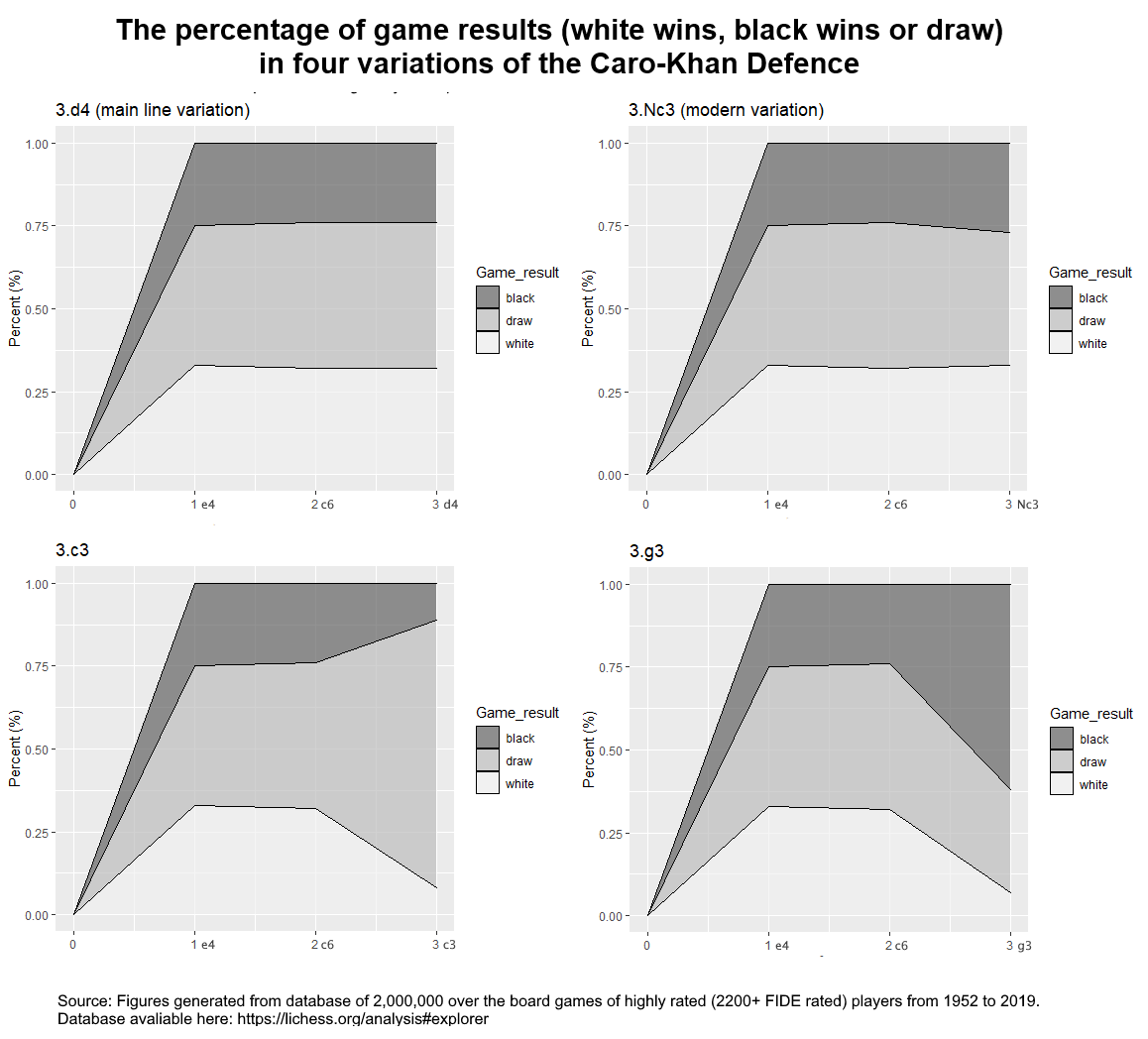
Caro–Kann Defence
The Caro–Kann Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 c6 The Caro–Kann is a common defence against the King's Pawn Opening. It is classified as a Semi-Open Game, like the Sicilian Defence and French Defence, although it is thought to be more solid and less dynamic than either of those openings. It often leads to good endgames for Black, who has the better pawn structure. It allows Black to circumvent enormous bodies of theory in 1.e4 openings such as the Ruy Lopez and the Sicilian Defence. Unlike its sister opening, the French Defence, the Caro–Kann does not hinder the development of Black's light-squared bishop. However, it comes at the cost of a tempo because Black has to play 1...c6 before pushing the pawn to c5, whereas Black can push c7–c5 in one move in the French Defence. White can combat the Caro–Kann in several different ways, often gaining a space advantage; additionally, Black has less mobility and can lag in development. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolani
In chess, an isolated pawn is a pawn that has no friendly pawn on an adjacent . Isolated pawns are usually a weakness because they cannot be protected by other pawns. The square in front of the pawn may become a good outpost or otherwise a good square for the opponent to anchor pieces. Isolated pawns most often become weaker in the endgame, as there are fewer pieces available to protect the pawn. Isolated pawns can, however, provide improved development and associated opportunities for that offset or even outweigh their weaknesses. The files adjacent to the isolated pawn are either open or half-open, providing two lanes of attack for the rooks and the queen. The absence of pawns adjacent to the isolated pawn may also mobilize the player's knights and bishops. An isolated pawn on the d-file is called an isolated queen pawn or simply an isolani. In addition to the open or half-open c- and e-files, the isolated queen pawn can provide a good outpost on the c- and e-file squares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolani
In chess, an isolated pawn is a pawn that has no friendly pawn on an adjacent . Isolated pawns are usually a weakness because they cannot be protected by other pawns. The square in front of the pawn may become a good outpost or otherwise a good square for the opponent to anchor pieces. Isolated pawns most often become weaker in the endgame, as there are fewer pieces available to protect the pawn. Isolated pawns can, however, provide improved development and associated opportunities for that offset or even outweigh their weaknesses. The files adjacent to the isolated pawn are either open or half-open, providing two lanes of attack for the rooks and the queen. The absence of pawns adjacent to the isolated pawn may also mobilize the player's knights and bishops. An isolated pawn on the d-file is called an isolated queen pawn or simply an isolani. In addition to the open or half-open c- and e-files, the isolated queen pawn can provide a good outpost on the c- and e-file squares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)