|
Ti-sapphire Laser
Ti:sapphire lasers (also known as Ti:Al2O3 lasers, titanium-sapphire lasers, or Ti:sapphs) are tunable lasers which emit red and infrared, near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses. Lasers based on Ti:sapphire were first constructed and invented in June 1982 by Peter Moulton at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory. Titanium-sapphire refers to the lasing medium, a crystal of sapphire (Al2O3) that is doped with titanium, Ti3+ ions. A Ti:sapphire laser is usually Laser pumping, pumped with another laser with a wavelength of 514 to 532 nm, for which argon-ion lasers (514.5 nm) and Second harmonic generation, frequency-doubled Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, and Neodymium-doped yttrium orthovanadate, Nd:YVO lasers (527-532 nm) are used. They are capable of laser operation from 670 nm to nm wavelength. Ti:sapphire lasers operate most efficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Sapphire Oscillator
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Variables
Conjugate variables are pairs of variables mathematically defined in such a way that they become Fourier transform duals, or more generally are related through Pontryagin duality. The duality relations lead naturally to an uncertainty relation—in physics called the Heisenberg uncertainty principle—between them. In mathematical terms, conjugate variables are part of a symplectic basis, and the uncertainty relation corresponds to the symplectic form. Also, conjugate variables are related by Noether's theorem, which states that if the laws of physics are invariant with respect to a change in one of the conjugate variables, then the other conjugate variable will not change with time (i.e. it will be conserved). Examples There are many types of conjugate variables, depending on the type of work a certain system is doing (or is being subjected to). Examples of canonically conjugate variables include the following: * Time and frequency: the longer a musical note is sustained, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femtosecond Laser Spark
A femtosecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10 or of a second; that is, one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth, of a second. For context, a femtosecond is to a second as a second is to about 31.71 million years; a ray of light travels approximately 0.3 μm (micrometers) in 1 femtosecond, a distance comparable to the diameter of a virus.Compared with overview in: Page 3 The word ''femtosecond'' is formed by the SI prefix ''femto'' and the SI unit ''second''. Its symbol is fs. A femtosecond is equal to 1000 attoseconds, or 1/1000 picosecond. Because the next higher SI unit is 1000 times larger, times of 10−14 and 10−13 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of femtoseconds. * Typical time steps for molecular dynamics simulations are on the order of 1 fs. * The periods of the waves of visible light have a duration of about 2 femtoseconds. = = 2.0 \times 10^~ The precise duration depends on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinuum
In optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam, for example using a microstructured optical fiber. The result is a smooth spectral continuum (see figure 1 for a typical example). There is no consensus on how much broadening constitutes a supercontinuum; however researchers have published work claiming as little as 60 nm of broadening as a supercontinuum. There is also no agreement on the spectral flatness required to define the bandwidth of the source, with authors using anything from 5 dB to 40 dB or more. In addition the term supercontinuum itself did not gain widespread acceptance until this century, with many authors using alternative phrases to describe their continua during the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s. During the last decade, the development of supercontinua sources has emerged as a research field. This is largely due to ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filament Propagation
In nonlinear optics, filament propagation is propagation of a beam of light through a medium without diffraction. This is possible because the Kerr effect causes an index of refraction change in the medium, resulting in self-focusing of the beam. Filamentary damage tracks in glass caused by laser pulses were first observed by Michael Hercher in 1964. Filament propagation of laser pulses in the atmosphere was observed in 1994 by Gérard Mourou and his team at University of Michigan. The balance between the self-focusing refraction and self-attenuating diffraction by ionization and rarefaction of a laser beam of terawatt intensities, created by chirped pulse amplification, in the atmosphere creates "filaments" which act as waveguides for the beam thus preventing divergence. Competing theories, that the observed filament was actually an illusion created by an axiconic (bessel) or moving focus instead of a "waveguided" concentration of the optical energy, were put to rest by workers at L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
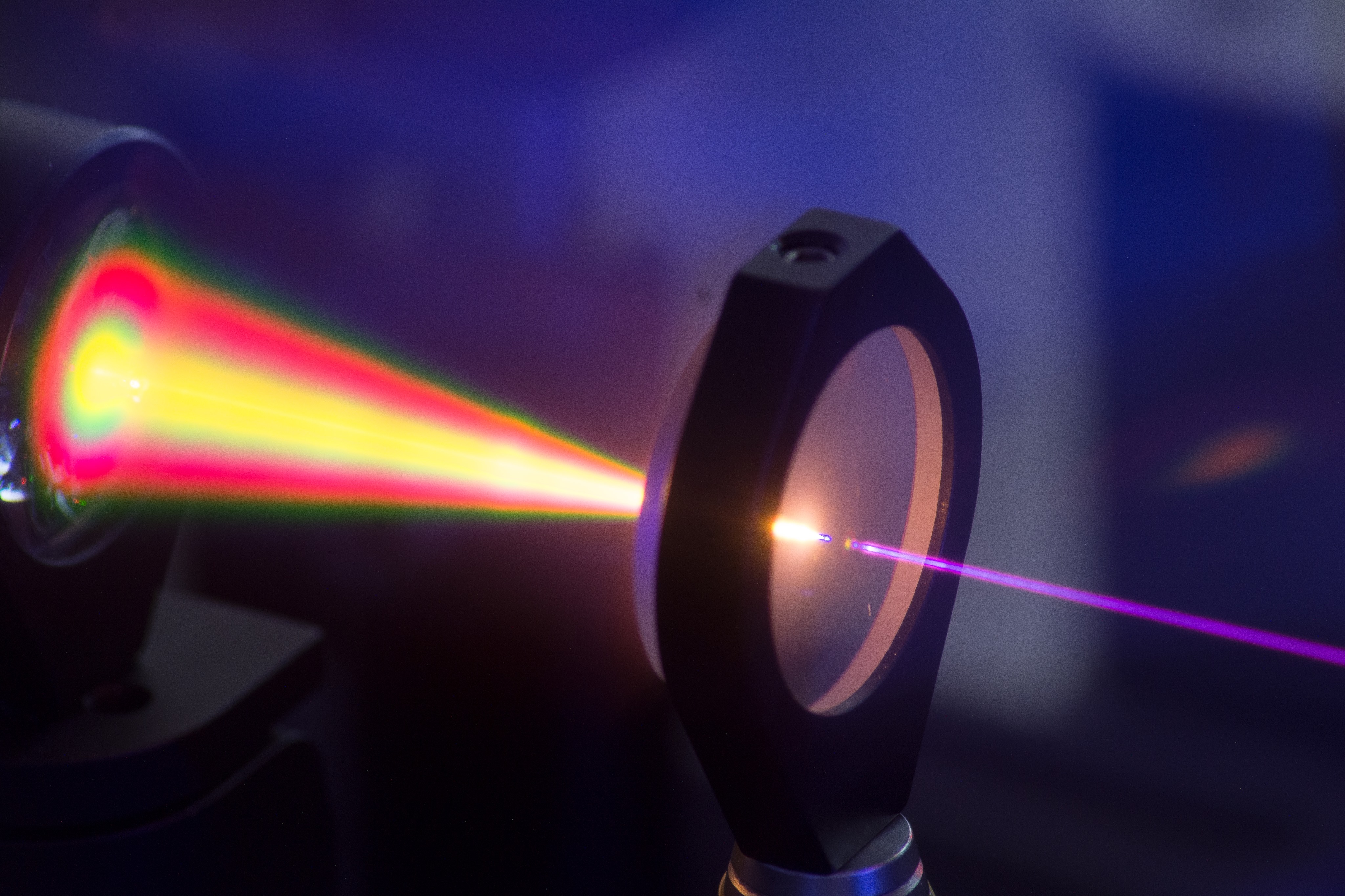
ODIN Ti-Sapphire Laser In Operation
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was also known in Old English as ', in Old Saxon as , in Old Dutch as ''Wuodan'', in Old Frisian as ''Wêda'', and in Old High German as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *''Wōðanaz'', meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'. Odin appears as a prominent god throughout the recorded history of Northern Europe, from the Roman occupation of regions of Germania (from BCE) through movement of peoples during the Migration Period (4th to 6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th to 11th centuries CE). In the modern period, the rural folklore of Germanic E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases (''up-chirp'') or decreases (''down-chirp'') with time. In some sources, the term ''chirp'' is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly applied to sonar, radar, and laser systems, and to other applications, such as in spread-spectrum communications (see chirp spread spectrum). This signal type is biologically inspired and occurs as a phenomenon due to dispersion (a non-linear dependence between frequency and the propagation speed of the wave components). It is usually compensated for by using a matched filter, which can be part of the propagation channel. Depending on the specific performance measure, however, there are better techniques both for radar and communication. Since it was used in radar and space, it has been adopted also for communication standards. For automotive radar applications, it is usually called linear frequency modulated waveform (LFMW). In spread-spectrum usage, surface acoustic wave (SA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Construction
A laser is constructed from three principal parts: *An energy source (usually referred to as the '' pump'' or ''pump source''), *A ''gain medium'' or ''laser medium'', and *Two or more mirrors that form an ''optical resonator''. Pump source The ''pump source'' is the part that provides energy to the laser system. Examples of pump sources include electrical discharges, flashlamps, arc lamps, light from another laser, chemical reactions and even explosive devices. The type of pump source used principally depends on the ''gain medium'', and this also determines how the energy is transmitted to the medium. A helium–neon (HeNe) laser uses an electrical discharge in the helium-neon gas mixture, a Nd:YAG laser uses either light focused from a xenon flash lamp or diode lasers, and excimer lasers use a chemical reaction. Gain medium / Laser medium The ''gain medium'' is the major determining factor of the wavelength of operation, and other properties, of the laser. ''Gain media'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |