|
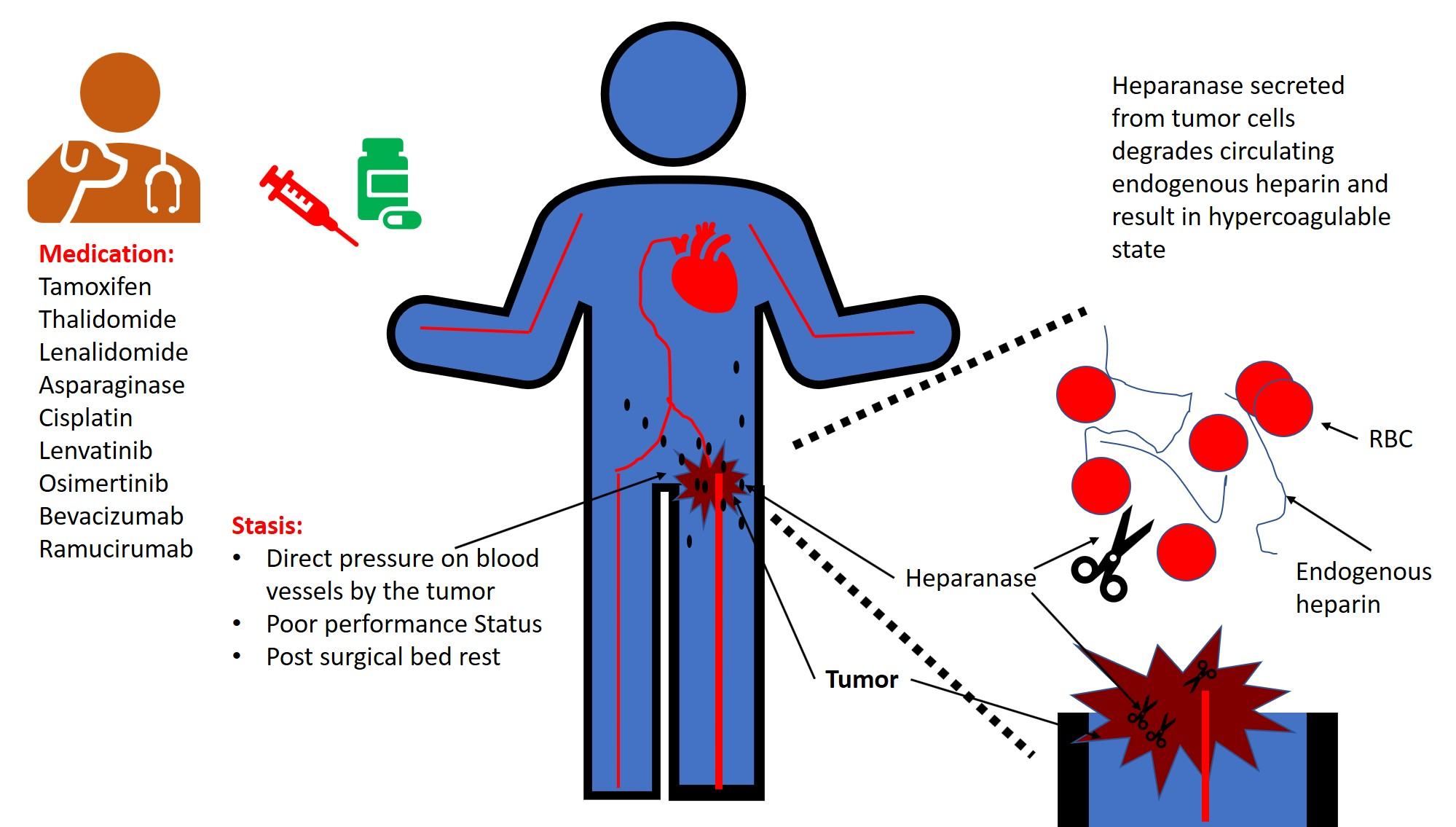
Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia (sometimes called hypercoagulability or a prothrombotic state) is an abnormality of blood coagulation that increases the risk of thrombosis (blood clots in blood vessels). Such abnormalities can be identified in 50% of people who have an episode of thrombosis (such as deep vein thrombosis in the leg) that was not provoked by other causes. A significant proportion of the population has a detectable thrombophilic abnormality, but most of these develop thrombosis only in the presence of an additional risk factor. There is no specific treatment for most thrombophilias, but recurrent episodes of thrombosis may be an indication for long-term preventive anticoagulation. The first major form of thrombophilia to be identified by medical science, antithrombin deficiency, was identified in 1965, while the most common abnormalities (including factor V Leiden) were described in the 1990s. Signs and symptoms The most common conditions associated with thrombophilia are deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrent Miscarriage
Recurrent miscarriage is three or more consecutive pregnancy losses. In contrast, infertility is the inability to conceive. In many cases the cause of RPL is unknown. After three or more losses, a thorough evaluation is recommended by American Society of Reproductive Medicine. About 1% of couples trying to have children are affected by recurrent miscarriage. Causes There are various causes for recurrent miscarriage, and some can be treated. Some couples never have a cause identified, often after extensive investigations. About 50–75% of cases of recurrent miscarriage are unexplained. Chromosomal disorders A balanced translocation or Robertsonian translocation in one of the partners leads to unviable fetuses that are miscarried. This explains why a karyogram is often performed in both partners if a woman has experienced repeated miscarriages. Aneuploidy may be a cause of a random spontaneous as well as recurrent pregnancy loss. Aneuploidy is more common with advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden (rs6025 or ''F5'' p.R506Q) is a variant (mutated form) of human factor V (one of several substances that helps blood clot), which causes an increase in blood clotting (hypercoagulability). Due to this mutation, protein C, an anticoagulant protein that normally inhibits the pro-clotting activity of factor V, is not able to bind normally to factor V, leading to a hypercoagulable state, i.e., an increased tendency for the patient to form abnormal and potentially harmful blood clots. Factor V Leiden is the most common hereditary hypercoagulability (prone to clotting) disorder amongst ethnic Europeans. It is named after the Dutch city of Leiden, where it was first identified in 1994 by Rogier Maria Bertina under the direction of (and in the laboratory of) Pieter Hendrick Reitsma. Despite the increased risk of venous thromboembolisms, people with one copy of this gene have not been found to have shorter lives than the general population. Signs and symptoms The symptoms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis may occur in veins ( venous thrombosis) or in arteries ( arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery ( ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a venous thrombus can break off as an embolus, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterial Thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis may occur in veins (venous thrombosis) or in arteries ( arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery (ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a venous thrombus can break off as an embolus, which co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's birth weight percentile. The causes of IUGR are broad and may involve maternal, fetal, or placental complications. At least 60% of the 4 million neonatal deaths that occur worldwide every year are associated with low birth weight (LBW), caused by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, and genetic abnormalities, demonstrating that under-nutrition is already a leading health problem at birth. Intrauterine growth restriction can result in a baby being small for gestational age (SGA), which is most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. At the end of pregnancy, it can result in a low birth weight. Types There are two major categories of IUGR: pseudo IUGR and true IUGR With pseud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein Thrombosis
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a vascular disease of the liver that occurs when a blood clot occurs in the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to increased pressure in the portal vein system and reduced blood supply to the liver. The mortality rate is approximately 1 in 10. An equivalent clot in the vasculature that exits the liver carrying deoxygenated blood to the right atrium via the inferior vena cava, is known as hepatic vein thrombosis or Budd-Chiari syndrome. Signs and symptoms Portal vein thrombosis causes upper abdominal pain, possibly accompanied by nausea and an enlarged liver and/or spleen; the abdomen may be filled with fluid (ascites). A persistent fever may result from the generalized inflammation. While abdominal pain may come and go if the thrombus forms suddenly, long-standing clot build-up can also develop without causing symptoms, leading to portal hypertension before it is diagnosed. Other symptoms can develop based on the cause. For example, if portal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin. Coagulation begins almost instantly after an injury to the endothelium lining a blood vessel. Exposure of blood to the subendothelial space initiates two processes: changes in platelets, and the exposure of subendothelial tissue factor to plasma factor VII, which ultimately leads to cross-linked fibrin formation. Platelets immediately form a plug at the site of injury; this is called ''primary hemostasis. Secondary hemostasis'' occurs simultaneously: additional coagulation (clotting) factors beyond factor VII ( listed below) respond in a cascade to form fibrin strands, which strengthen the platelet plug. Disorders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
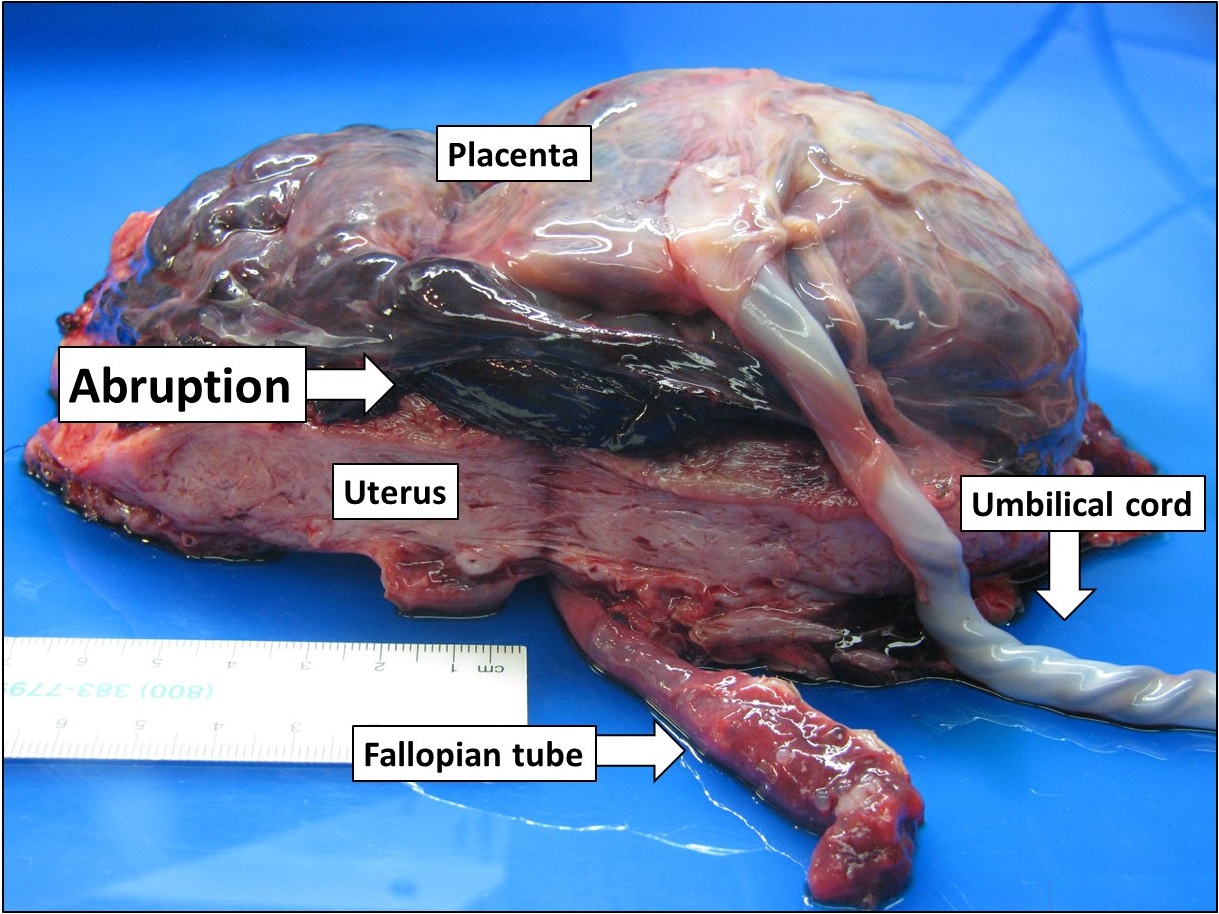
Abruptio Placentae
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth. The cause of placental abruption is not entirely clear. Risk factors include smoking, pre-eclampsia, prior abruption (most important and predictive risk factor), trauma during pregnancy, cocaine use, and previous cesarean section. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and supported by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For small abruption, bed rest may be recommended, while for more significant abruptions or those that occur near term, delivery may be recommended. If everything is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they help keep the bite area unclotted long enough for the animal to obtain some blood. As a class of medications, anticoagulants are used in therapy for thrombotic disorders. Oral anticoagulants (OACs) are taken by many people in pill or tablet form, and various intravenous anticoagulant dosage forms are used in hospitals. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as sample tubes, blood transfusion bags, heart–lung machines, and dialysis equipment. One of the first anticoagulants, warfarin, was initially approved as a rodenticide. Anticoagulants are closely related to antiplatelet drugs and thrombolytic drugs by manipulating the various pathways of blood coagulation. Specifically, antiplatelet drugs inhibit pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize (detach from the veins), travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE). About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT. The most frequent long-term DVT complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
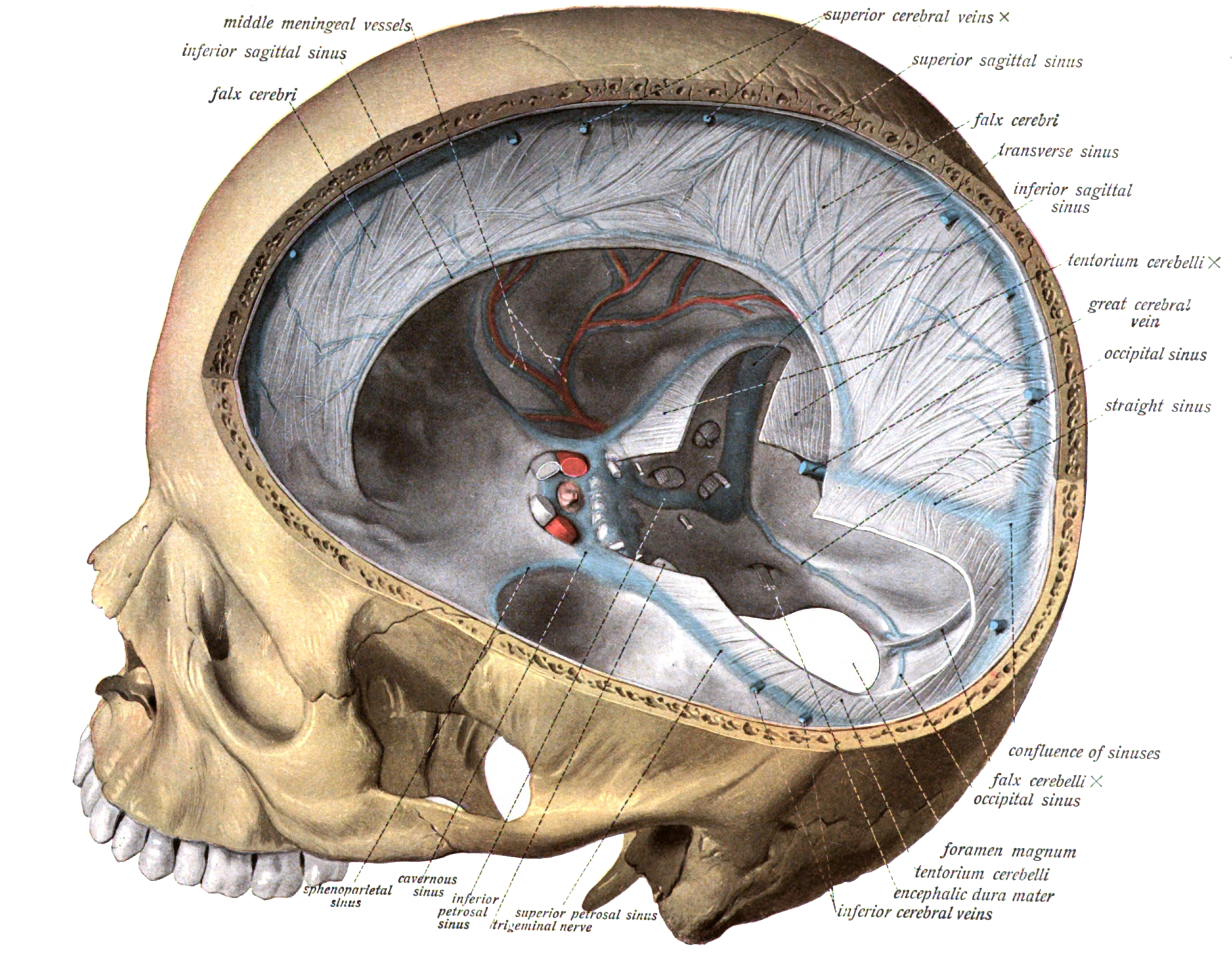
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis or cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), is the presence of a blood clot in the dural venous sinuses (which drain blood from the brain), the cerebral veins, or both. Symptoms may include severe headache, visual symptoms, any of the symptoms of stroke such as weakness of the face and limbs on one side of the body, and seizures, which occur in around 40% of patients. The diagnosis is usually by computed tomography (CT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to demonstrate obstruction of the venous sinuses. After confirmation of the diagnosis, investigations may be performed to determine the underlying cause, especially if one is not readily apparent. Treatment is typically with anticoagulants (medications that suppress blood clotting) such as low molecular weight heparin. Rarely, thrombolysis (enzymatic destruction of the blood clot) or mechanical thrombectomy is used, although evidence for this the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive. Often the cause is unknown. Causes may include pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and birth complications, problems with the placenta or umbilical cord, birth defects, infections such as malaria and syphilis, and poor health in the mother. Risk factors include a mother's age over 35, smoking, drug use, use of assisted reproductive technology, and first pregnancy. Stillbirth may be suspected when no fetal movement is felt. Confirmation is by ultrasound. Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems. Around half of stillbirths occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |