|
Target Drone
A target drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle, generally remote controlled, usually used in the training of anti-aircraft crews. One of the earliest drones was the British DH.82 Queen Bee, a variant of the Tiger Moth trainer aircraft operational from 1935. Its name led to the present term "drone". In their simplest form, target drones often resemble radio-controlled model aircraft. More modern drones may use countermeasures, radar, and similar systems to mimic manned aircraft. More advanced drones are made from large, older missiles which have had their warheads removed. In the United Kingdom, obsolete Royal Air Force and Royal Navy jet and propeller-powered aircraft (such as the Fairey Firefly, Gloster Meteor and de Havilland Sea Vixen used at RAE Llanbedr between the 1950s and 1990s) have also been modified into remote-controlled drones, but such modifications are costly. With a much larger budget, the U.S. military has been more likely to convert retired aircraft or ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAF Turana
The GAF Turana was a target drone produced by the Australian Government Aircraft Factories (GAF). The name is believed to be from an Aboriginal Australian word meaning ''rainbow''. The Turana target drone was designed and built in Australia as a development of the Ikara anti-submarine weapon system. It was a target drone with remote control that was launched from the Ikara launcher for use in naval anti-aircraft target practice. Design and development The Turana had a composite metal/fibre glass structure and was powered by a Microturbo Cougar 022 Turbojet. The Turana was first flown from Woomera in August 1971. The program was cancelled in 1979 as water ingress during recovery of the drone was causing failure of the electronics. See also *List of unmanned aerial vehicles Notes References Further reading * * External linksTurana target droneHistorical Aircraft Restoration Society The Historical Aircraft Restoration Society, often referred to by its acronym, HARS, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAF Jindivik
The GAF Jindivik is a radio-controlled target drone produced by the Australian Government Aircraft Factories (GAF). The name is from an Aboriginal Australian word meaning "the hunted one". Two manually-controlled prototypes, were built as the GAF Pika (Project C) as a proof of concept to test the aerodynamics, engine and radio control systems, serialled ''A92-1/2'', 'B-1/2'. The radio-controlled Jindivik was initially designated the Project B and received serials in the A93 series. Pika is an Aboriginal Australian word meaning ''flier''. Design and development The Jindivik was developed as a result of a bilateral agreement between Australia and the UK regarding guided missile testing. While the UK provided the missiles, Australia provided test facilities, such as the Woomera Test Range. As a result of the talks, Australia gained the contract for developing a target drone to Ministry of Supply specification E.7/48. The specification called for an aircraft capable of a 15-minute s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
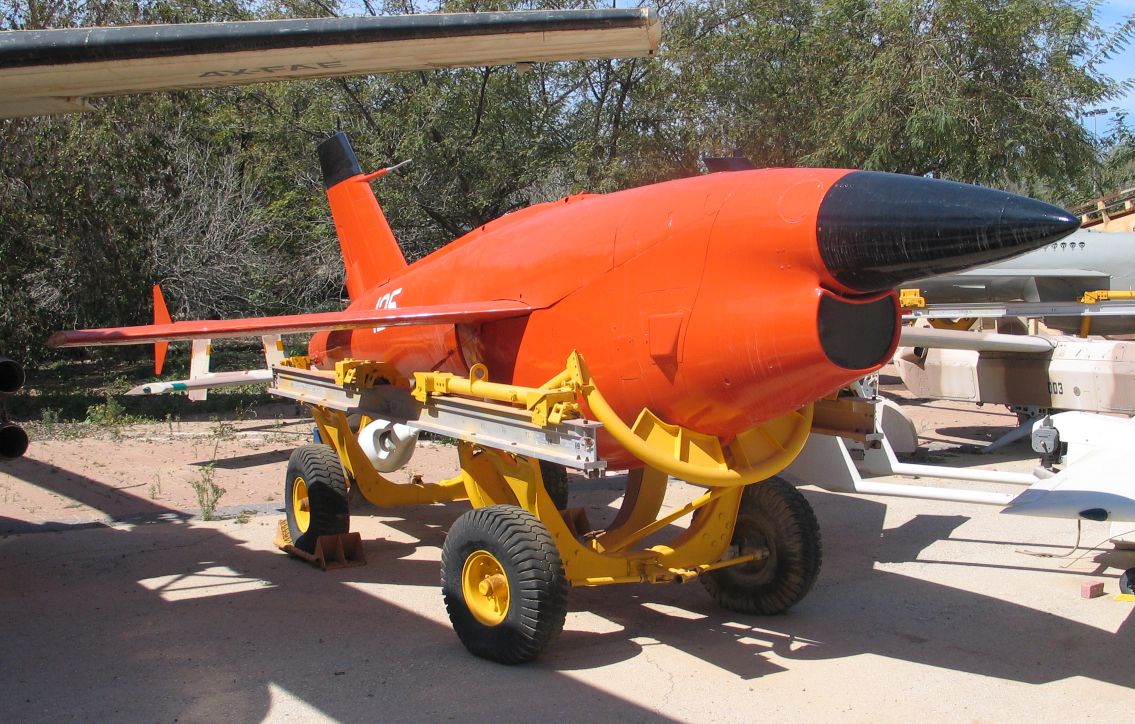
Meggitt Banshee
The BTT3 Banshee, formerly the Target Technology Banshee & Meggitt Banshee, is a British target drone developed in the 1980s for air defence systems training. Design and development The Banshee was developed by Target Technology Ltd. The company had been specialising in lightweight engines for drones and had developed its own design in 1983. Banshee is a built mostly out of composite material (Kevlar and glass-reinforced plastic) with a tailless delta wing planform. The first models used a 26 hp 342 cc Normalair-Garrett two-cylinder two-stroke driving a pusher propeller. Performance was 35-185 kt with an endurance from 1–3 hours. Flight control is by two elevons. 185kt. Later models used Norton P73 rotary engines Operational history Banshee entered service with the British Army in the mid-1980s as an aerial target for the Short Blowpipe and Javelin shoulder-launched missiles. Banshee has been deployed in over 40 Countries. It has been tested against Blowpipe, Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denel Dynamics Skua
The Denel Dynamics Skua is a turbojet-engined target drone used to simulate fast-moving attack aircraft during surface-to-air and air-to-air training exercises and weapons tests. It is manufactured by the Denel Dynamics division of the South African state-owned Denel aerospace and defence conglomerate. Airframe The Skua has a composite airframe, its wingspan is 3,57 m and length 6,00 m. Under-wing hardpoints can carry tow-targets and signature enhancement equipment up to 160 kg. An internal payload bay has a capacity of 70 kg. It is recovered by parachute and lands in an inverted position on airbags, this makes water landings possible. Performance * Maximum speed: Mach 0,86 at 10 000 m * Controllable range: 200 km (line of sight) * Altitude: from 10 m to 10 700 m * Endurance: 85 minutes at 10 000 m and Mach 0,75 System The system includes between four and eight UAVs, a launcher vehicle, a mobile ground control station (GCS) and various support equipment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRDO Ulka
Ulka (Sanskrit: meteor or firebrand) is an air-launched expendable target drone of India. Description It has been developed by DRDO's laboratory Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE). Ulka was earlier simply known as MT (Missile Target). It has been designed to be launched from subsonic or supersonic aircraft by means of an ejector release unit. It performed missions between 50 m to 13,000 m altitude at speeds ranging from 0.7 to 1.4 Mach with a rocket motor. It is able to simulate the speed and altitude characteristics of approaching, receding or crossing of a variety of aircraft using false radar signatures. It is used for defensive training of surface-to-air missile crews against anti-ship missiles and for development testing and evaluation of air defense systems. It can be air-launched by a variety of aircraft. It is the first Indian aerial vehicle to incorporate a canard configuration. It has been succeeded by Lakshya PTA Lakshya ("target" in Sanskrit) is an Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRDO Lakshya
Lakshya ("target" in Sanskrit) is an Indian remotely piloted high speed target drone system developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) of DRDO. A variant ''Lakshya-1'' is used to perform discreet aerial reconnaissance of battlefield and target acquisition. The drone remotely piloted by a ground control station provides realistic towed aerial sub-targets for live fire training. The drone is ground or ship launched from a zero length launcher and recovery is by a two-stage parachute system developed by ADE (DRDO), for land- or sea-based recovery. The drone has a crushable nose cone, which absorbs the impact of landing, minimizing damage. The flight path may be controlled or pre-programmed, based upon the type of mission. Development The requirement for a pilotless target aircraft (PTA) arose in 1976. Feasibility studies were carried out by ADE to provide for a target system that met the requirements of all 3 services of the armed forces. An Inter Services Qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRDO Fluffy
The DRDO Fluffy was a target drone designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation's Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) in Bangalore in early 1970s for use by the Indian Armed Forces. It had a maximum endurance of 5 minutes and could be launched from the maximum altitude of 30,000 feet. After the development of the reusable Aerial Target DRDO Lakshya, which was simpler and more economical to use than Fluffy, the production of the latter was discontinued. See also *DRDO Lakshya *List of unmanned aerial vehicles The following is a list of unmanned aerial vehicles developed and operated in various countries around the world. Algeria * AL fajer L-10 * Amel (UAV) Argentina * AeroDreams Chi-7 (AeroDreams) * AeroDreams Strix Reconnaissance (2006) ... Unmanned military aircraft of India Military equipment of India Fluffy {{UAV-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRDO Abhyas
DRDO Abhyas is a high-speed expendable aerial target (HEAT) being built by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the Indian Armed Forces. Development As of January 2013, the proof of concept and pre-project trials were completed. The first experimental launch without the main turbojet engine of the Abhyas was held at the Chitradurga Aeronautical Test Range on 23 June 2012 to check the launch and configuration capability. The gas turbine engine has been identified and integrated on the Abhyas airframe and its test run with the aircraft fuel system and s-airtake has been completed. The project was sanctioned with an initial DRDO funding of ₹15 crore. Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) will carry out 15 technology demonstrators (TDs) till 2015. After the acceptance of the prototypes or TDs by the Indian Armed Forces, serial production will start. The Indian Defense Services have also revealed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Queen Bee
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ''ab initio'' training, the Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers. The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was replaced by the de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civilian operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civilian applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft. It is still occasionally used as a primary training aircraft, particularly for those pilots wanting to gain expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed Queen Wasp
The Airspeed AS.30 Queen Wasp was a British pilotless target aircraft built by Airspeed Limited at Portsmouth during the Second World War. Although intended for both Royal Air Force and Royal Navy use, the aircraft never went into series production. Design and development The Queen Wasp was built to meet an Air Ministry Specification Q.32/35 for a pilotless target aircraft to replace the de Havilland Tiger Moth based de Havilland Queen Bee. Two prototypes were ordered in May 1936, one to have a wheeled landing gear for use by the Royal Air Force and the other as a floatplane for Royal Navy use for air-firing practice at sea. Powered by the Armstrong Siddeley Cheetah engine, a total of 65 aircraft were ordered, contingent on the success of the flight test programme. The aircraft was a single- engined biplane constructed of wood with sharply-tapered wings and fabric-covered control surfaces. An enclosed cabin with one seat was provided so the Queen Wasp could be flown manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |