|
Tamshiyacu Tahuayo Regional Conservation Area
Tamshiyacu Tahuayo Regional Conservation Area (ACRCTT; Spanish: Área de Conservación Regional Comunal Tamshiyacu Tahuayo) is a protected area located south east of Iquitos, extending over the Peruvian department of Loreto, provinces of Maynas ( district of Fernando Lores), Ramón Castilla ( district of Yavarí) and Requena (district of Sapuena and district of Yaquerana). It was established by the Peruvian Ministry of Environment (MINAM; Spanish: Ministerio del Ambiente) on May 15, 2009. The reserve is managed and funded by the Regional Government of Loreto. Tamshiyacu Tahuayo Regional Conservation Area spans an area of 4,200.8 km2 (420,080.25 ha; 1'038,040.9 acre; 1,621.94 sq miles) comprising floodable and upland forest of the Peruvian Amazon. It is known for its abundant wildlife. It has high levels of biodiversity. Hundreds of species of mammals, primates, birds, fish and reptiles have been documented, including several that are endemic as well as either endange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maynas Province
Maynas is one of the eight provinces in the Loreto Region in northeastern Peru. Its capital, Iquitos, is also Loreto's regional capital and the largest city in the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest. History A decree signed on 26 April 1822 signed by the Marquis of Torre Tagle, transformed what once was the General Command of Maynas into the Quijos Department, allowing it to also choose deputies. In 1925, Maynas was integrated into the Department of La Oroya. In 1822, Joaquín Mosquera travelled on behalf of Colombia to request the restitution of the province. On July 25, 1824, the Congress of Gran Colombia issued a law of territorial division intending to include the Canton of Quijos in the Pichincha Province of the Department of Quito, according to the limits it had at the time of creation as the Viceroyalty of New Granada. It also intended to incorporate the Provinces of Jaén, Matamoros and Maynas into the Department of Azuay. The Peruvian refusal to give up the territor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedrela Odorata
''Cedrela odorata'' is a commercially important species of tree in the chinaberry family, Meliaceae, commonly known as Spanish cedar or Cuban cedar; it is also known as cedro in Spanish. Classification The genus ''Cedrela'' has undergone two major systematic revisions since 1960. The most recent revision reduced the number of species in the genus to seven (Styles, 1981). The common cedro, ''Cedrela odorata'' L., embraces 28 other synonyms, including ''C. mexicana'' M. J. Roem. The taxon "''C. angustifolia''," a very vigorous type now in demand because of its apparent resistance to the shootborer, was left in an indeterminate status due to insufficient herbarium material. The result is that ''C. odorata'' as now constituted is a species showing a high degree of population variation. Distribution and habitat Cedro is a tree of the New World tropics, appearing in forests of moist and seasonally dry subtropical or tropical life zones (24) from latitude 26°N on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iquitos Várzea
The Iquitos várzea (NT0128) is an ecoregion of flooded forest along rivers in Brazil, Peru and Bolivia in the west of the Amazon biome. The forest is seasonally flooded up to by whitewater rivers carrying nutrient-rich sediment from the Andes. The meandering rivers often shift course, creating a complex landscape of oxbow lakes, marshes, levees and bars, with grasslands, shrubs and forests in different stages of succession. During the extended flood periods fish enter the forest in search of fruit. The várzea is accessible by the navigable rivers that run through it, and has suffered from extensive deforestation to extract timber and create pasture for livestock. Location The Iquitos várzea has an area of in northwest Brazil, northeast Peru and northern Bolivia. The várzea, or flooded forest, is found along seasonally flooded basins of tributaries of the upper Amazon River, and of the Amazon itself. To the west the Iquitos várzea extends to the highest places where várz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Várzea Forest
A várzea forest is a seasonal floodplain forest inundated by whitewater rivers that occurs in the Amazon biome. Until the late 1970s, the definition was less clear and várzea was often used for all periodically flooded Amazonian forests. Although sometimes described as consisting only of forest, várzea also contains more open, seasonally flooded habitats such as grasslands, including floating meadows. Description Along the Amazon River and many of its tributaries, high annual rainfall that occurs mostly within a rainy season results in extensive seasonal flooding of areas from stream and river discharge. The result is a rise in water level, with nutrient rich waters. The Iquitos várzea ecoregion covers the margins of the upper Amazon and its tributaries. Further down are the Purus várzea in the middle Amazon, the Monte Alegre várzea and Gurupa várzea on the lower Amazon and the Marajó várzea at the mouth of the Amazon. The Marajó várzea is affected by both freshwate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations.Hughes, F.M.R. (ed.). 2003. The Flooded Forest: Guidance for policy makers and river managers in Europe on the restoration of floodplain forests. FLOBAR2, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK. 96 p. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodic inu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxbow Lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called '' resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are called billabongs. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether or not it is cut off from the main stream. Geology An oxbow lake forms when a meandering river erodes through the neck of one of its meanders. This takes place because meanders tend to grow and become more curved over time. The river then follows a shorter course that bypasses the meander. The entrances to the abandoned meander eventually silt up, forming an oxbow lake. Because oxbow lakes are stillwater lakes, with no current flowing through them, the entire lake gradually silts up, becoming a bog or swamp and then evaporating completely. When a river reaches a low-lying plain, often in its final course to the sea or a lake, it meanders w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranitomeya Uakarii
''Ranitomeya'' is a genus of dart poison frogs found in Panama and South America south to Peru and Brazil, possibly into Bolivia. Taxonomy In 2006 Grant ''et al.'' revised the systematics of poison dart frogs and placed many species formerly classified in the genera ''Dendrobates'', '' Minyobates'' and ''Phyllobates'' in ''Ranitomeya''. In 2011 Brown and colleagues, following other scientists who assumed the existence of two distinct clades in ''Ranitomeya'', erected the genus ''Andinobates'' for 12 species of ''Ranitomeya''. ''Ranitomeya'' and ''Andinobates'' frogs can be distinguished from those in genera such as ''Dendrobates'' in that they are generally smaller, have more than two colors, and seem to glitter if viewed from certain angles. ''Ranitomeya'' is widespread in the Amazon basin, whereas ''Andinobates'' species are found only in the northern Andes down to Central America. Description Adults measure no more than in snout–vent length and are typically brightly colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
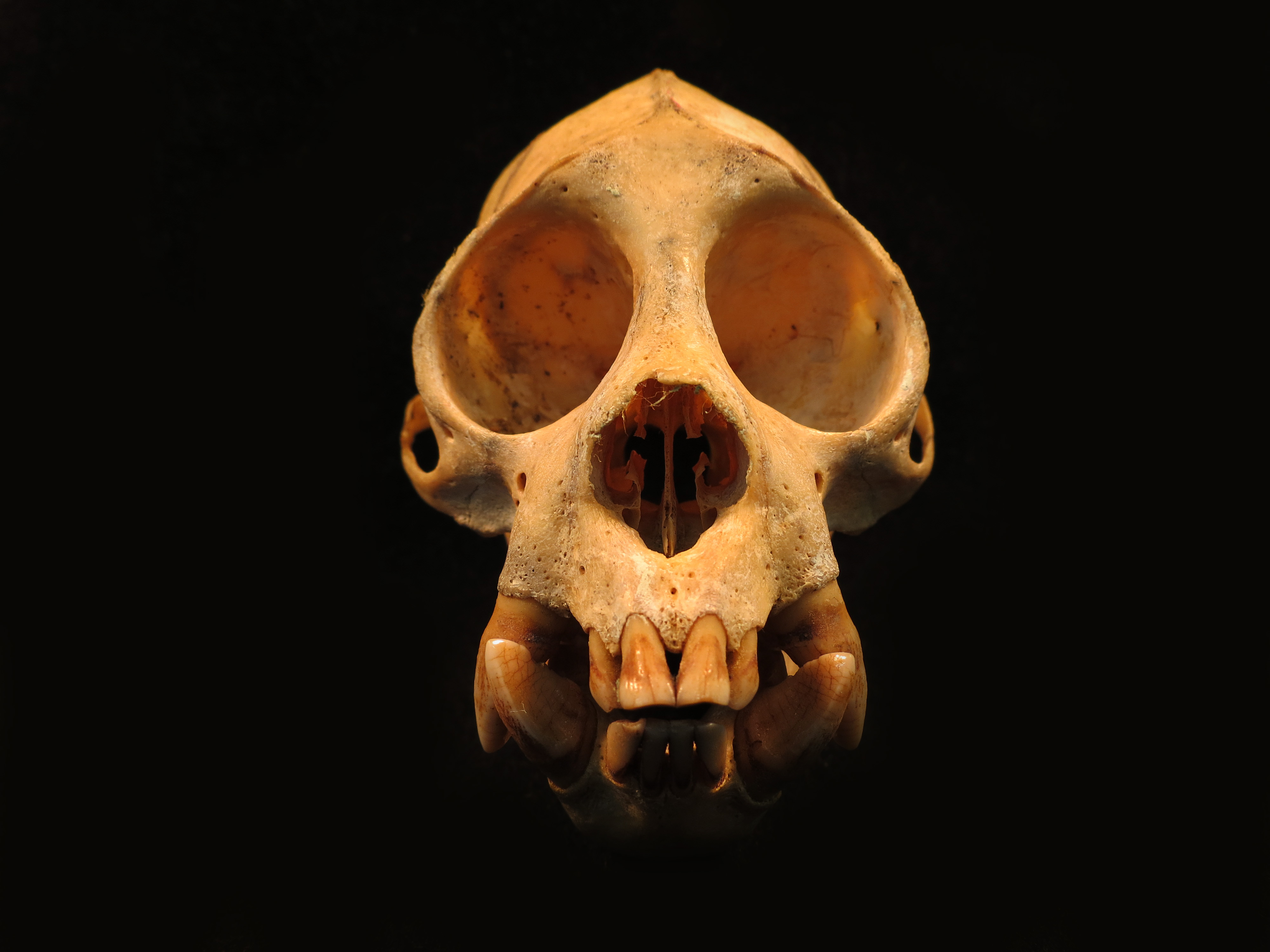
Cacajao Calvus Ucayalii
The bald uakari (''Cacajao calvus'') or bald-headed uakari is a small New World monkey characterized by a very short tail; bright, crimson face; a bald head; and long coat. The bald uakari is restricted to várzea forests and other wooded habitats near water in the western Amazon of Brazil and Peru. Taxonomy There are four recognized subspecies of the bald uakari, each of which is considered vulnerable to extinction: * White bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus calvus'' * Ucayali bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus ucayalii'' * Red bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus rubicundus'' * Novae's bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus novaesi'' Description The bald uakari weighs between 2.75 and 3.45 kg (6.1 and 7.6 lb), with head and body lengths average 45.6 cm (18.0 in) (male) and 44.0 cm (17.3 in) (female). In general, the bald uakari has a long, shaggy coat ranging from white in color to red and its head is bald. The tail is bob-like and rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)