|
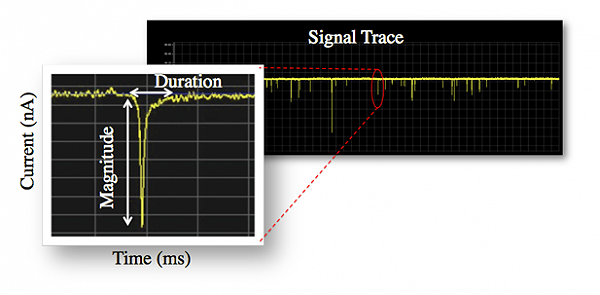
TRPS
Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing (TRPS) is a single-particle technique used to measure the size, concentration and zeta potential of particles as they pass through a size-tunable nanopore. The technique adapts the principle of resistive pulse sensing, which monitors current flow through an aperture, combined with the use of tunable nanopore technology, allowing the passage of ionic current and particles to be regulated by adjusting the pore size. Technique Particles crossing a pore are detected one at a time as a transient change in the ionic current flow, which is denoted as a blockade event with its amplitude denoted as the blockade magnitude. As blockade magnitude is proportional to particle size, accurate particle sizing can be achieved after calibration with a known standard. Nanopore-based detection allows particle-by-particle assessment of complex mixtures. Optimization of pore size to particle size, by adjusting the stretch of the pore, can improve measurement accur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Ion Occlusion Sensing
Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing (TRPS) is a single-particle technique used to measure the size, concentration and zeta potential of particles as they pass through a size-tunable nanopore. The technique adapts the principle of resistive pulse sensing, which monitors current flow through an aperture, combined with the use of tunable nanopore technology, allowing the passage of ionic current and particles to be regulated by adjusting the pore size. Technique Particles crossing a pore are detected one at a time as a transient change in the ionic current flow, which is denoted as a blockade event with its amplitude denoted as the blockade magnitude. As blockade magnitude is proportional to particle size, accurate particle sizing can be achieved after calibration with a known standard. Nanopore-based detection allows particle-by-particle assessment of complex mixtures. Optimization of pore size to particle size, by adjusting the stretch of the pore, can improve measurement accur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izon Science
Izon Science Ltd. provides solutions for the isolation and measurement of biological and synthetic nano-sized particles such as extracellular vesicles, lipid nano particles, viruses and virus-like particles, and various synthetic particles being developed for drug delivery. Their main instruments are based on principles of size exclusion chromatography and tunable resistive pulse sensing, together which are used in thousands of research institutes and universities around the world. Izon’s size-exclusion chromatography columns and related solutions are also used by diagnostics companies focused on developing extracellular vesicle biomarkers. Izon Science’s headquarters are located in Addington (Christchurch, New Zealand), and the company has a wide global distribution network, facilitated by collaborations with distributors, and by sales and technical support offices in Medford, Massachusetts (United States), Portland, Oregon (United States), Lyon (France) and Brisbane (Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanopore
A nanopore is a pore of nanometer size. It may, for example, be created by a pore-forming protein or as a hole in synthetic materials such as silicon or graphene. When a nanopore is present in an electrically insulating membrane, it can be used as a single-molecule detector. It can be a biological protein channel in a high electrical resistance lipid bilayer, a pore in a solid-state membrane or a hybrid of these – a protein channel set in a synthetic membrane. The detection principle is based on monitoring the ionic current passing through the nanopore as a voltage is applied across the membrane. When the nanopore is of molecular dimensions, passage of molecules (e.g., DNA) cause interruptions of the "open" current level, leading to a "translocation event" signal. The passage of RNA or single-stranded DNA molecules through the membrane-embedded alpha-hemolysin channel (1.5 nm diameter), for example, causes a ~90% blockage of the current (measured at 1 M KCl solution). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
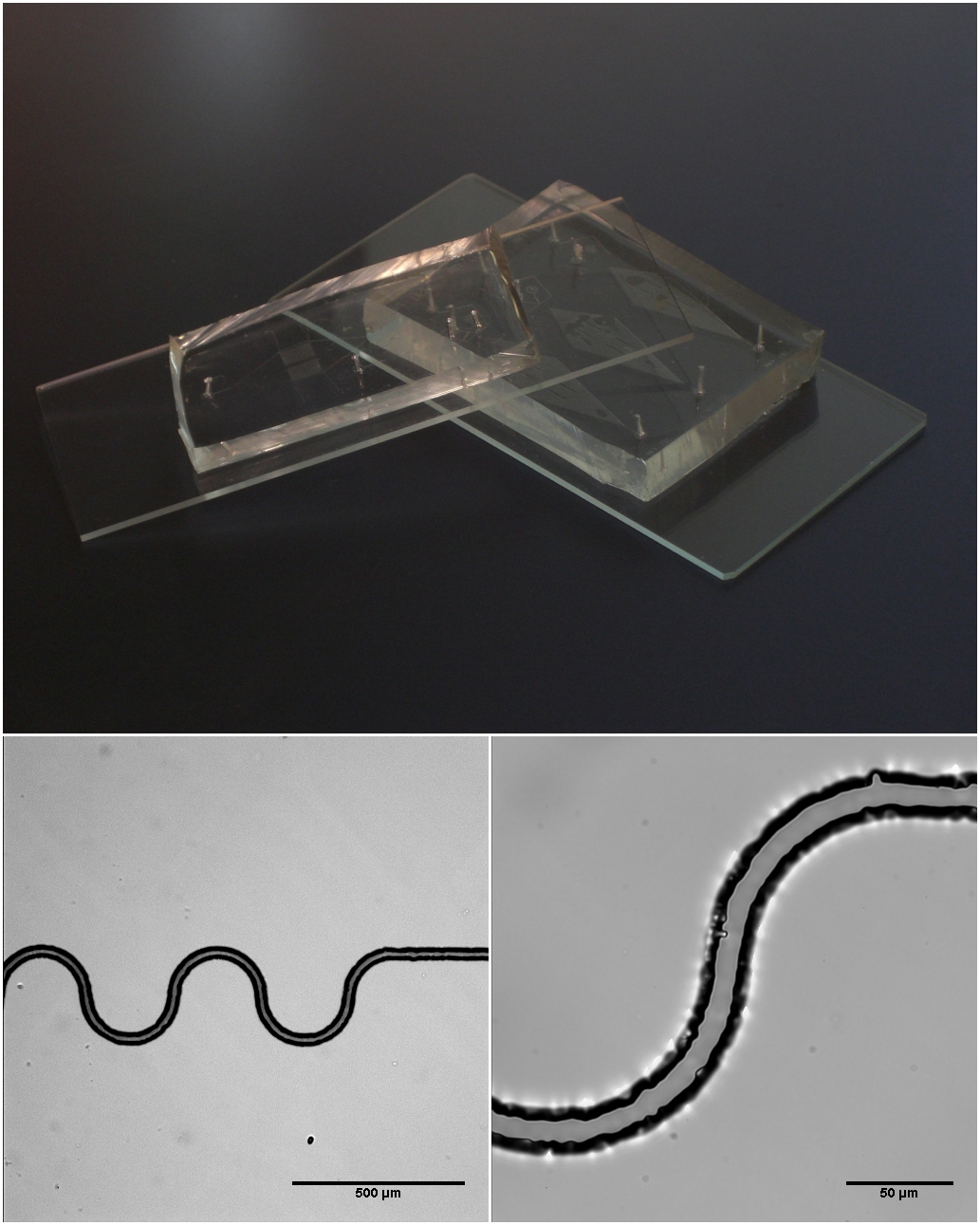
Resistive Pulse Sensing
Resistive pulse sensing (RPS) is the generic, non-commercial term given for the well-developed technology used to detect, and measure the size of, individual particles in fluid. First invented by Wallace H. Coulter in 1953, the RPS technique is the basic principle behind the Coulter Principle, which is a trademark term. Resistive pulse sensing is also known as the electrical zone sensing technique, reflecting its fundamentally electrical nature, which distinguishes it from other particle sizing technologies such as the optically-based dynamic light scattering (DLS) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). An international standard has been developed for the use of the resistive pulse sensing technique by the International Organization for Standardization. Construction and operation. The basic design principle underlying resistive pulse sensing is shown in Fig. 1. Individual particles, suspended in a conductive fluid, flow one-at-a-time through a constriction. The fluids most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Delivery
Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury. Drug deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microvesicles
Microvesicles (ectosomes, or microparticles) are a type of extracellular vesicle (EV) that are released from the cell membrane. In multicellular organisms, microvesicles and other EVs are found both in tissues (in the interstitial space between cells) and in many types of body fluids. Delimited by a phospholipid bilayer, microvesicles can be as small as the smallest EVs (30 nm in diameter) or as large as 1000 nm. They are considered to be larger, on average, than intracellularly-generated EVs known as exosomes. Microvesicles play a role in intercellular communication and can transport molecules such as mRNA, miRNA, and proteins between cells. Though initially dismissed as cellular debris, microvesicles may reflect the antigenic content of the cell of origin and have a role in cell signaling. Like other EVs, they have been implicated in numerous physiologic processes, including anti-tumor effects, tumor immune suppression, metastasis, tumor-stroma interactions, angiogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosome (vesicle)
Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. The multivesicular body (MVB) is an endosome with intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud inward into the endosomal lumen. If the MVB fuses with the cell surface (the plasma membrane), these ILVs are released as exosomes. In multicellular organisms, exosomes and other EVs were discovered in biological fluids including blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. Importantly, exosomes were also identified within the tissue matrix, coined Matrix-Bound Nanovesicles (MBV). They are also released ''in vitro'' by cultured cells into their growth medium. Since the size of exosomes is limited by that of the parent MVB, exosomes are generally thought to be smaller than most other EVs, from about 30 to 150 nanometres (nm) in diameter: around the same size as many lipoproteins but much smaller than cells. Compared with EVs in general, it is unclear whether exosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virology
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his ' contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the full structure of the tobacco mosaic virus in 1955. Virology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylactic (to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)