|
Tuberculin
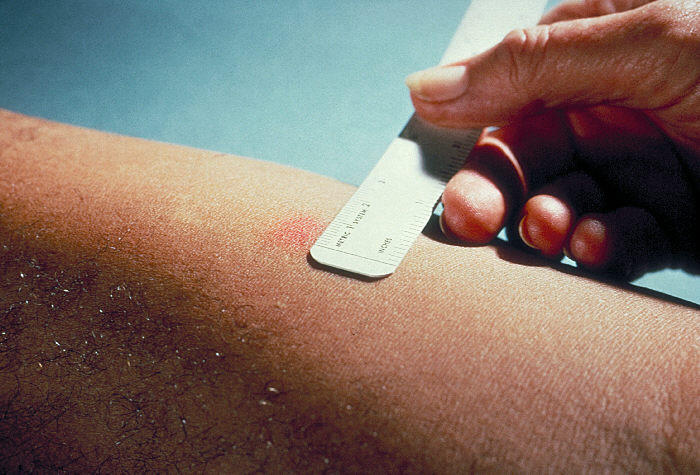
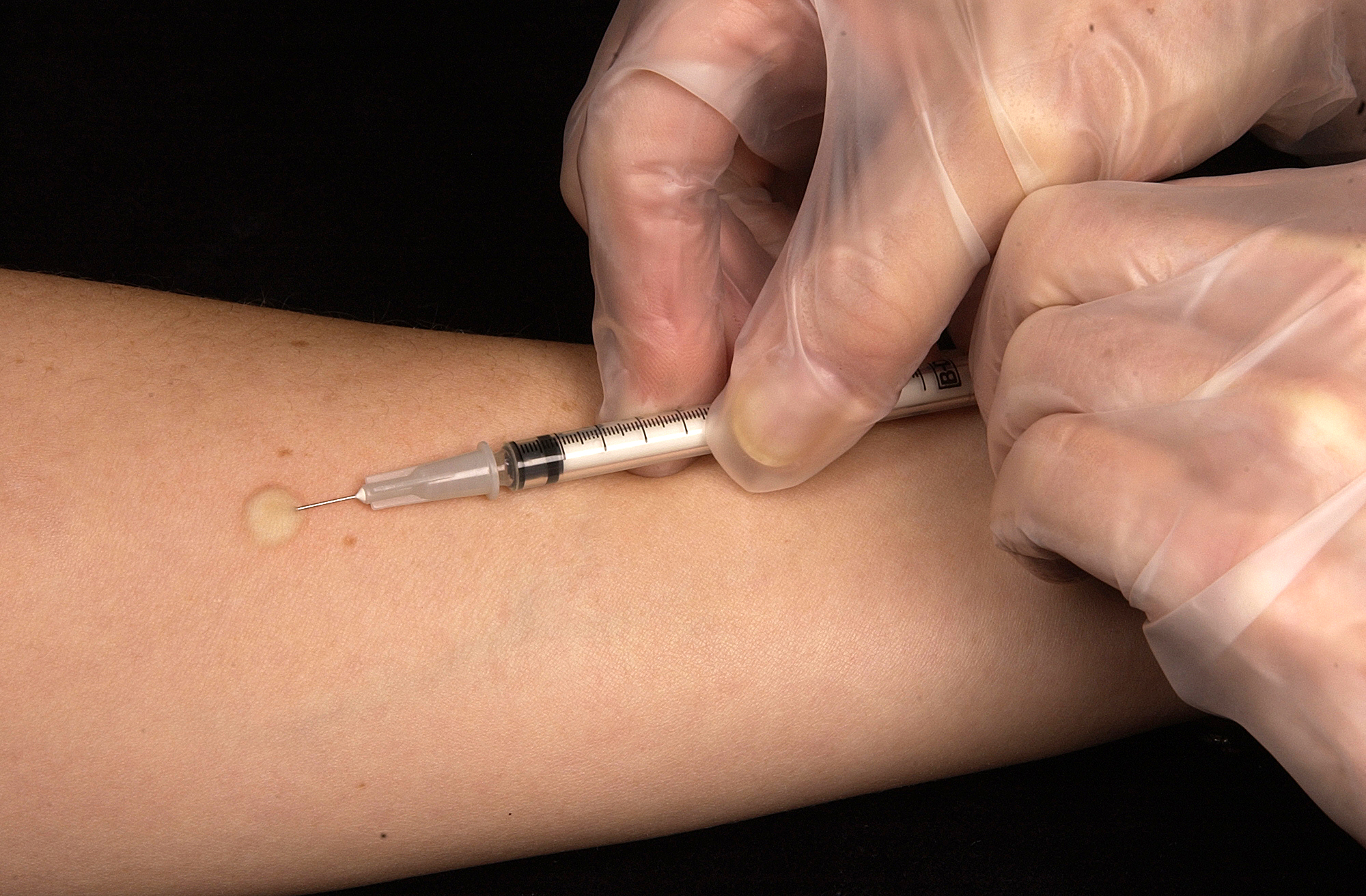
Tuberculin, also known as purified protein derivative, is a combination of proteins that are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. This use is referred to as the tuberculin skin test and is recommended only for those at high risk. Reliable administration of the skin test requires large amounts of training, supervision, and practice. Injection is done into the skin. After 48 to 72 hours, if there is more than a five to ten millimeter area of swelling, the test is considered positive. Common side effects include redness, itchiness (pruritus), and pain at the site of injection. Allergic reactions may occasionally occur. The test may be falsely positive in those who have been previously vaccinated with BCG or have been infected by other types of mycobacteria. The test may be falsely negative within ten weeks of infection, in those less than six months old, and in those who have been infected for many years. Use is safe in pregnancy. Tuberculin was discovered in 1890 by Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantoux Test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening (medicine), screening for tuberculosis, tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the Soviet Union, USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction. History Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculin Skin Test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction. History Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules obtained from filtrates of sterilized, conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he is regarded as one of the main founders of modern bacteriology. As such he is popularly nicknamed the father of microbiology (with Louis Pasteur), and as the father of medical bacteriology. His discovery of the anthrax bacterium ('' Bacillus anthracis'') in 1876 is considered as the birth of modern bacteriology. Koch used his discoveries to establish that germs "could cause a specific disease" and directly provided proofs for the germ theory of diseases, therefore creating the scientific basis of public health, saving millions of lives. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine. While working as a private physician, Koch developed many innovative techniques in microbiology. He was the first to use the oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection (medicine)
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in UK English, or a "jag" in Scottish English and Scots) is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle) and a syringe. An injection is considered a form of parenteral drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injections, as well as less common injections such as epidural, intraperitoneal, intraosseous, intracardiac, intraarticular, and intracavernous injections. Injections are among the most common health care procedures, with at least 16 billion administered in developing and transitional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCG Vaccine
The Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as soon after birth as possible. In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated. Adults who do not have tuberculosis and have not been previously immunized, but are frequently exposed, may be immunized, as well. BCG also has some effectiveness against Buruli ulcer infection and other nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Additionally, it is sometimes used as part of the treatment of bladder cancer. Rates of protection against tuberculosis infection vary widely and protection lasts up to 20 years. Among children, it prevents about 20% from getting infected and among those who do get inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heaf Test
The Heaf test, a diagnostic skin test, was long performed to determine whether or not children had been exposed to tuberculosis infection. The test was named after F. R. G. Heaf. Also known as the Sterneedle test, it was administered by a Heaf gun (trademarked "Sterneedle"), a spring-loaded instrument with six needles arranged in a circular formation which was inserted in the wrist or shoulder. The Heaf test was discontinued in 2005 because the manufacturer deemed its production to be financially unsustainable after manufacturers could not be found for tuberculin or Heaf guns. Until 2005, the test was used in the United Kingdom to determine if the BCG vaccine was needed; the Mantoux test is now used instead. The Heaf test was preferred in the UK, because it was thought to be easier to interpret, with less variability between observers, and less training was required to administer and read the test. Patients who exhibited a negative reaction to the test were considered for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clemens Von Pirquet
Clemens Peter Freiherr von Pirquet (12 May 187428 February 1929) was an Austrian scientist and pediatrician best known for his contributions to the fields of bacteriology and immunology. Career Born in Vienna, he studied theology at the University of Innsbruck and philosophy at the University of Leuven before he enrolled at the University of Graz where he became a doctor of medicine in 1900. He started practicing at the Children's Clinic in Vienna. In 1906 he noticed that patients who had previously received injections of horse serum or smallpox vaccine had quicker, more severe reactions to a second injection. He coined the word allergy (from the Greek ''allos'' meaning "other" and ''ergon'' meaning "work") to describe this hypersensitivity reaction. Soon after, the observation with smallpox led Pirquet to realize that tuberculin, which Robert Koch isolated from the bacteria that cause tuberculosis in 1890, might lead to a similar type of reaction. Charles Mantoux expanded up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dr Hilda Clark
Hilda Clark (12 January 1881 – 24 February 1955) was a British physician and humanitarian aid worker. Early life Clark was born 12 January 1881 at Green Bank, Street, Somerset, Street, Somerset and was the youngest child of the Quaker C. & J. Clark, shoe manufacturer William Stephens Clark and the social reformer Helen Bright Clark, Helen Priestman Bright Clark. As a child, she was involved in athletics and gymnastics. She had a Quaker education at Brighthelmston, at Birkdale in Southport, Lancashire, about 1896–7, and The Mount, in York, from about 1897 to 1900, before studying medicine at University of Birmingham, Birmingham University and the Royal Free Hospital, Royal Free Hospital, London where she graduated M.B. and B.S. in 1908. She was the sister of Alice Clark (historian), Alice Clark, the feminist and historian and the niece of Annie Clark (physician), Annie Clark, one the first women to formally train in medicine in Britain. Her mother and great-aunts helped to fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intradermal
Intradermal injection (also intracutaneous or intradermic, abbreviated as ID) is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. For certain substances, administration via an ID route can result in a faster systemic uptake compared with subcutaneous injections, leading to a stronger immune response to vaccinations, immunology and novel cancer treatments, and faster drug uptake. Additionally, since administration is closer to the surface of the skin, the body's reaction to substances is more easily visible. However, due to complexity of the procedure compared to subcutaneous injection and intramuscular injection, administration via ID is relatively rare, and is only used for tuberculosis and allergy tests, monkeypox vaccination, and certain therapies. Vaccine dose sparing For vaccination many clinical studies have proven efficacy of ID administration over subcutaneous (SC), intramuscular (IM) or other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, ''M. tuberculosis'' can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fastness, Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen stain, Ziehl–Neelsen, or Fluorescence, fluorescent stains such as Auramine O, auramine are used instead to identify ''M. tuberculosis'' with a microscope. The physiology of ''M. tuberculosis'' is highly aerobic organism, aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the Mantoux test, tuberculin skin test, Acid-Fast Stain, aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox Vaccine
The smallpox vaccine is used to prevent smallpox infection caused by the variola virus. It is the first vaccine to have been developed against a contagious disease. In 1796, British physician Edward Jenner demonstrated that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus conferred immunity against the deadly smallpox virus. Cowpox served as a natural vaccine until the modern smallpox vaccine emerged in the 20th century. From 1958 to 1977, the World Health Organization (WHO) conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. Although routine smallpox vaccination is no longer performed on the general public, the vaccine is still being produced for research, and to guard against bioterrorism, biological warfare, and mpox.Anderson MG, Frenkel LD, Homann S, and Guffey J. (2003), "A case of severe monkeypox virus disease in an American child: emerging infections and changing professional values"; ''Pediatr Infect Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |