|
Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus ''Trypanosoma''. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other diseases occur in other animals. Human African trypanosomiasis, which is caused by either '' Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' or ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'', is presently estimated to threaten over 40 million people in sub-Saharan Africa, especially in rural areas and populations affected by war or poverty. However, only 1.5 million people are estimated to live in areas at moderate or high risk, and for over 20 years the number of cases has been going down due to systematic surveillance and control efforts: in 1998 almost 40,000 cases were reported but almost 300,000 cases were suspected to have occurred; in 2009, the number dropped below 10,000; and in 2018 it dropped below 1000, and it has remained under that number ever since. Chagas d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two types, ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' (TbG) and ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' (TbR). TbG causes over 92% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas. Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis involves detecting the parasite in a blood smear or lymph node fluid. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease. Prevention of severe disease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsetse Fly
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies) are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glossinidae. The tsetse is an obligate parasite, which lives by feeding on the blood of vertebrate animals. Tsetse has been extensively studied because of their role in transmitting disease. They have pronounced economic and public health impacts in sub-Saharan Africa as the Vector (epidemiology), biological vectors of trypanosomes, causing African trypanosomiasis, human and animal trypanosomiasis. Tsetse can be distinguished from other large flies by two easily-observed features: primarily, tsetse fold their wings over their abdomens completely when they are resting (so that one wing rests directly on top of the other); Secondly, tsetse also have a long proboscis, extending directly forward, which is attached by a distinct bulb to the bottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
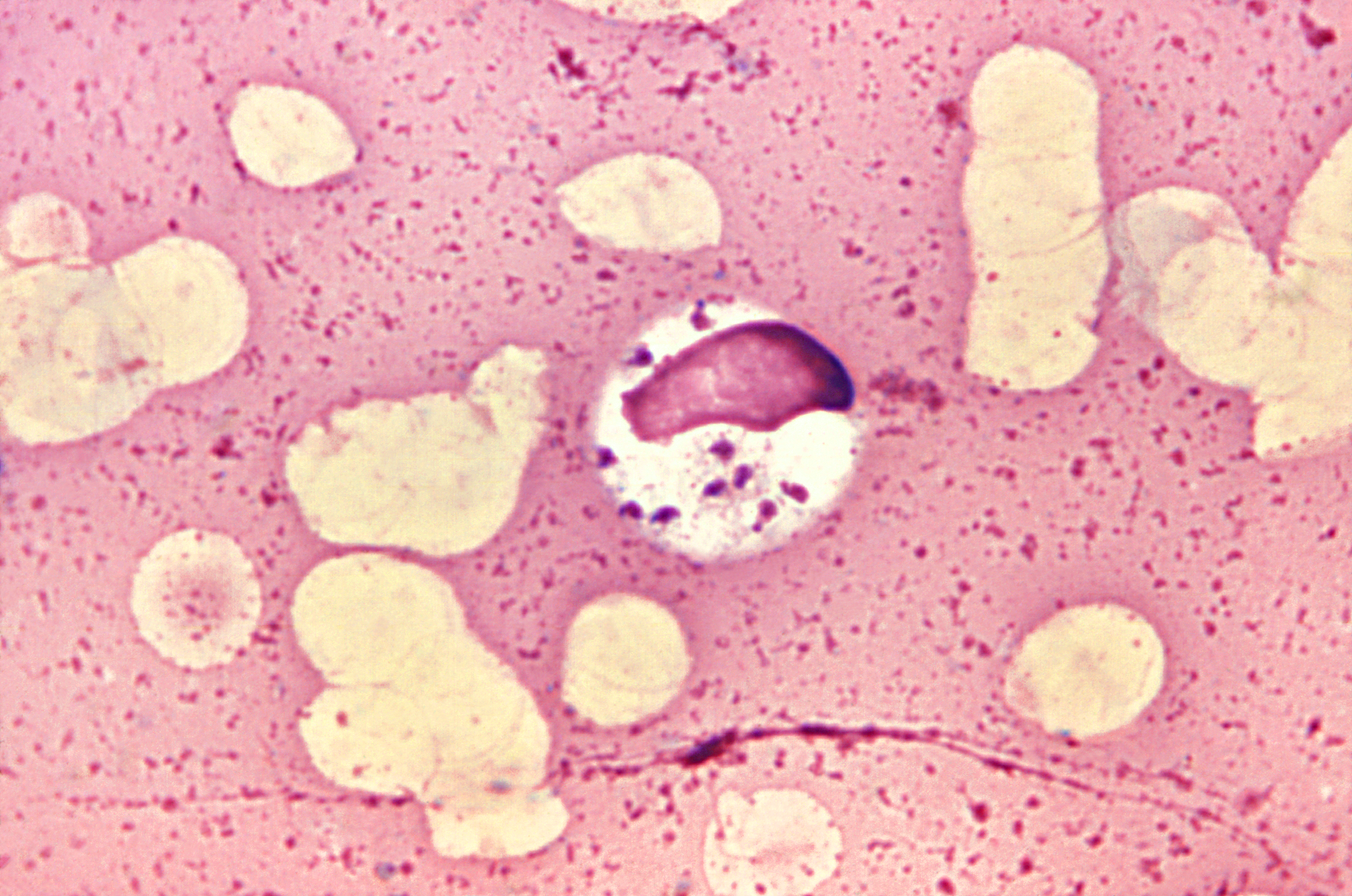
Trypanosoma Brucei Gambiense
''Trypanosoma brucei'' is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus ''Trypanosoma'' that is present in sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike other protozoan parasites that normally infect blood and tissue cells, it is exclusively extracellular and inhabits the blood plasma and body fluids. It causes deadly vector-borne diseases: African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness in humans, and animal trypanosomiasis or ''nagana'' in cattle and horses. It is a species complex grouped into three subspecies: ''T. b. brucei'', ''T. b. gambiense'' and ''T. b. rhodesiense''. The first is a parasite of non-human mammals and causes ''nagana'', while the latter two are zoonotic infecting both humans and animals and cause African trypanosomiasis. ''T. brucei'' is transmitted between mammal hosts by an insect vector belonging to different species of tsetse fly (''Glossina''). Transmission occurs by biting during the insect's blood meal. The parasites undergo complex morphological changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eflornithine
Eflornithine, sold under the brand name Vaniqa among others, is a medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) and excessive hair growth on the face in women. Specifically it is used for the second stage of sleeping sickness caused by '' T. b. gambiense'' and may be used with nifurtimox. It is taken intravenously (injection into a vein) or topically. It is an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor. Common side effects when applied as a cream include rash, redness, and burning. Side effects of the injectable form include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, and seizures. It is unclear if it is safe to use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is recommended typically for children over the age of 12. Eflornithine was developed in the 1970s and came into medical use in 1990. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States the injectable form can be obtained from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagas Disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily Triatominae, known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change throughout the infection. In the early stage, symptoms are typically either not present or mild and may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches, or swelling at the site of the bite. After four to eight weeks, untreated individuals enter the chronic phase of disease, which in most cases does not result in further symptoms. Up to 45% of people with chronic infections develop heart disease 10–30 years after the initial illness, which can lead to heart failure. Digestive complications, including an enlarged esophagus or an enlarged colon, may also occur in up to 21% of people, and up to 10% of people may experience nerve damage. is commonly spread to humans and other mammals by the kissing bug's bite wound and the bug's infected feces. The disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melarsoprol
Melarsoprol is an arsenic-containing medication used for the treatment of sleeping sickness (African trypanosomiasis). It is specifically used for second-stage disease caused by '' Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' when the central nervous system is involved. For '' Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'', eflornithine or fexinidazole is usually preferred. It is effective in about 95% of people. It is given by injection and is known by patients as "fire in the veins" . Melarsoprol has a high number of side effects. Common side effects include brain dysfunction, numbness, rashes, and kidney and liver problems. About 1–5% of people die during treatment, although this is tolerated due to sleeping sickness itself having a practically 100% mortality rate when untreated. In those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, red blood cell breakdown may occur. It has not been studied in pregnancy. It works by blocking pyruvate kinase, an enzyme required for aerobic metabolism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosoma
''Trypanosoma'' is a genus of kinetoplastids (class Trypanosomatidae), a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. Trypanosoma is part of the phylum Euglenozoa. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ''trypano-'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of their corkscrew-like motion. Most trypanosomes are heteroxenous (requiring more than one obligatory host to complete life cycle) and most are transmitted via a vector. The majority of species are transmitted by blood-feeding invertebrates, but there are different mechanisms among the varying species. '' Trypanosoma equiperdum'' is spread between horses and other equine species by sexual contact. They are generally found in the intestine of their invertebrate host, but normally occupy the bloodstream or an intracellular environment in the vertebrate host. Trypanosomes infect a variety of hosts and cause various diseases, including the fatal human diseases sleeping sickness, caused by '' Trypanosoma br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentamidine
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, '' Balamuthia'' infections, babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function. In African trypanosomiasis it is used for early disease before central nervous system involvement, as a second line option to suramin. It is an option for both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Pentamidine can be given by injection into a vein or muscle or by inhalation. Common side effects of the injectable form include low blood sugar, pain at the site of injection, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and kidney problems. Common side effects of the inhaled form include wheezing, cough, and nausea. It is unclear if doses should be changed in those with kidney or liver problems. Pentamidine is not recommended in early pregnancy but may be used in later pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is unclear. Pentamidine is in the arom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomatida
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (African trypanosomiasis, sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by Tsetse fly, tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi, T. cruzi'' and transmitted by Triatominae, triatomine bugs), and leishmanias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suramin
Suramin is a medication used to treat African sleeping sickness and river blindness. It is the treatment of choice for sleeping sickness without central nervous system involvement. It is given by injection into a vein. Suramin causes a fair number of side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, skin tingling, and weakness. Sore palms of the hands and soles of the feet, trouble seeing, fever, and abdominal pain may also occur. Severe side effects may include low blood pressure, decreased level of consciousness, kidney problems, and low blood cell levels. It is unclear if it is safe when breastfeeding. Suramin was made at least as early as 1916. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States it can be acquired from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In regions of the world where the disease is common suramin is provided for free by the World Health Organization (WHO). Medical uses Suramin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living Host (biology), host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |