|
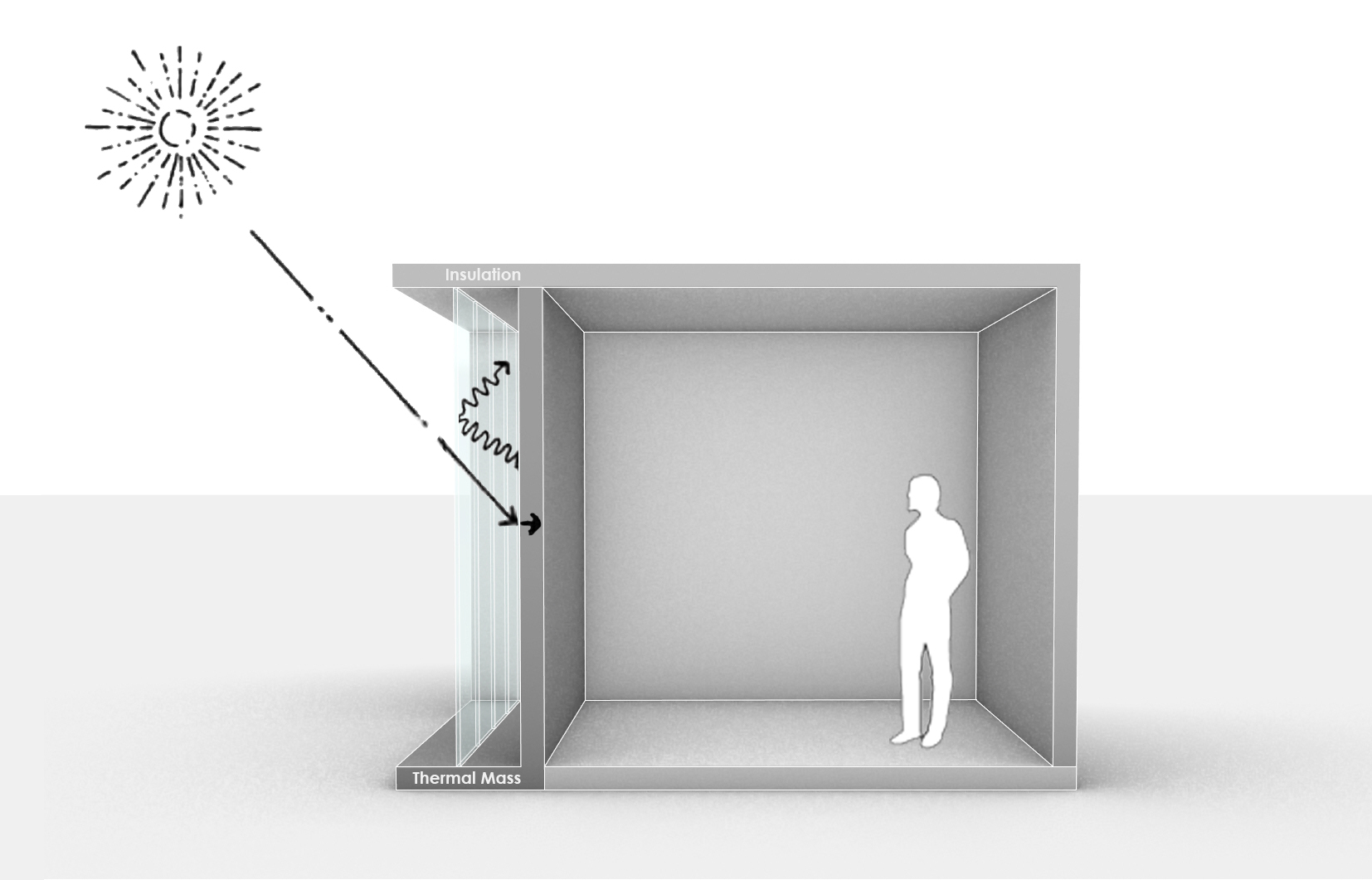
Trombe Wall
A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface in contact with a thermal mass of air. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space. Trombe walls may also be referred to as a mass wall, solar wall, or thermal storage wall. However, due to the extensive work of professor and architect Félix Trombe in the design of passively heated and cooled solar structure, they are often called Trombe Walls. This system is similar to the air heater (as a simple glazed box on the south wall with a dark absorber, air space, and two sets of vents at top and bottom) created by professor Edwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Solar Building
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices. The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate performing an accurate site analysis. Elements to be considered include window placement and size, and Glazing (window), glazing type, thermal insulation, thermal mass, and shading. Passive solar design techniques can be applied most easily to new buildings, but existing buildings can be adapted or "retrofitted". Passive energy gain ''Passive solar'' technologies use solar energy, sunlight without active mechanical systems (as contrasted to ''active solar'', which uses solar thermal collector, thermal collectors). Such technologies convert sunlight i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Trombe Wall
One half is the multiplicative inverse of 2. It is an irreducible fraction with a numerator of 1 and a denominator of 2. It often appears in mathematical equations, recipes and measurements. As a word One half is one of the few fractions which are commonly expressed in natural languages by suppletion rather than regular derivation. In English, for example, compare the compound "one half" with other regular formations like "one-sixth". A ''half'' can also be said to be one part of something divided into two equal parts. It is acceptable to write one half as a hyphenated word, ''one-half''. Mathematics One half is the rational number that lies midway between 0 and 1 on the number line. Multiplication by one half is equivalent to division by two, or "halving"; conversely, division by one half is equivalent to multiplication by two, or "doubling". A number raised to the power of one half is equal to its square root. The area of a triangle is one half its base an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Engineering
Architectural engineering or architecture engineering, also known as building engineering, is a Academic discipline, discipline that deals with the engineering and construction of buildings, such as environmental, structural, mechanical, electrical, computational, embeddable, and other research domains. It is related to Architecture, Mechatronics Engineering, Computer engineering, Computer Engineering, Aerospace engineering, Aerospace Engineering, and civil engineering, Civil Engineering, but distinguished from Interior design, Interior Design and architectural design, Architectural Design as an art and science of designing infrastructure through these various engineering disciplines, from which properly align with many related surrounding engineering advancements. From reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to the construction of resilient buildings, architectural engineers are at the forefront of addressing several major challenges of the 21st century. They apply the latest scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Building
Green building (also known as green construction, sustainable building, or eco-friendly building) refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages.Yan Ji and Stellios Plainiotis (2006): Design for Sustainability. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. Green building also refers to saving resources to the maximum extent, including energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving, etc., during the whole life cycle of the building, protecting the environment and reducing pollution, providing people with healthy, comfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Design
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices. The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate performing an accurate site analysis. Elements to be considered include window placement and size, and Glazing (window), glazing type, thermal insulation, thermal mass, and shading. Passive solar design techniques can be applied most easily to new buildings, but existing buildings can be adapted or "retrofitted". Passive energy gain ''Passive solar'' technologies use solar energy, sunlight without active mechanical systems (as contrasted to ''active solar'', which uses solar thermal collector, thermal collectors). Such technologies convert sunlight i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Architecture
Solar energy is clean and renewable. Solar architecture is designing buildings to use the sun's heat and light to maximum advantage and minimum disadvantage, and especially refers to harnessing solar power. It is related to the fields of optics, thermics, electronics and materials science. Both PlusEnergy, active and Passive house, passive strategies are involved. The use of flexible thin-film photovoltaic modules provides fluid integration with steel Roofing material, roofing profiles, enhancing the building's design. Orienting a building to the sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air also constitute solar architecture. Improvements in solar architecture have been limited by the rigidity and weight of standard solar power panels. The continued development of photovoltaic (PV) thin film solar has provided a lightweight yet robust vehicle to harness solar energy to reduce a building's im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pioneering Solar Buildings
The following buildings are of significance in pioneering the use of solar powered building design: * MIT Solar House #1, Massachusetts, United States ( Hoyt C. Hottel & others, 1939) * Howard Sloan House, Glenview, Illinois, United States ( George Fred Keck, 1940) * " Solar Hemicycle", near Madison, Wisconsin, United States (Frank Lloyd Wright, 1944) * Löf House, Boulder, Colorado, United States ( George Löf, 1945) * Rosenberg House, Tucson, Arizona, United States ( Arthur T. Brown, 1946) * MIT Solar House #2, United States, (Hoyt C. Hottel & others, 1947)''Solar Energy Applications in Houses'', F Jäger, Pergamon Press, * Peabody House (" Dover Sun House", MIT Solar House #6), Dover, Massachusetts, United States ( Eleanor Raymond & Mária Telkes, 1948) * Henry P. Glass House, Northfield, Illinois, United States ( Henry P. Glass, 1948)''Henry P. Glass and World War II'', MIT Design Issues: Volume 22, Number 4 Autumn 2006 * Rose Elementary School, Tucson, Arizona, United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barra System
The Barra system is a passive solar building technology developed by Horazio Barra in Italy. It uses a collector wall to capture solar radiation in the form of heat. It also uses the thermosiphon effect to distribute the warmed air through channels incorporated into the reinforced concrete floors, warming the floors and hence the building. Alternatively, in hot weather, cool nighttime air can be drawn through the floors to chill them in a form of air conditioning. Many successful systems were built in Europe, but Barra seems fairly unknown elsewhere. Passive solar collector To convert the sun's light into heat indirectly, a separate insulated space is constructed on the sunny side of the house walls. Looking at the outside, and moving through a cross section there is an outside clear layer. This was traditionally built using glass, but with the advent of cheap, robust Polycarbonate glazing most designs use twin- or triple-wall polycarbonate greenhouse sheeting. Typically th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Solar Building Design
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices. The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate performing an accurate site analysis. Elements to be considered include window placement and size, and glazing type, thermal insulation, thermal mass, and shading. Passive solar design techniques can be applied most easily to new buildings, but existing buildings can be adapted or "retrofitted". Passive energy gain ''Passive solar'' technologies use sunlight without active mechanical systems (as contrasted to ''active solar'', which uses thermal collectors). Such technologies convert sunlight into usable heat (in water, air, and thermal mass), cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19880412080NR Hopfgarten (Thüringen) Solarhaus Am Weinberg
1988 was a crucial year in the early history of the Internet—it was the year of the first well-known computer virus, the Morris worm, 1988 Internet worm. The first permanent intercontinental Internet link was made between the United States (National Science Foundation Network) and Europe (Nordunet) as well as the first Internet-based chat protocol, Internet Relay Chat. The concept of the World Wide Web was first discussed at CERN in 1988. The Soviet Union began its major deconstructing towards a mixed economy at the beginning of 1988 and began its Dissolution of the Soviet Union, gradual dissolution. The Iron Curtain began to disintegrate in 1988 as People's Republic of Hungary, Hungary began allowing freer travel to the Western world. The first extrasolar planet, Gamma Cephei Ab (confirmed in 2003), was detected this year and the World Health Organization began its mission to Eradication of polio, eradicate polio. Global warming also began to emerge as a more significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effect Of Wall Thickness To Fluctuation
Effect may refer to: * A result or change of something ** List of effects ** Cause and effect, an idiom describing causality Pharmacy and pharmacology * Drug effect, a change resulting from the administration of a drug ** Therapeutic effect, a beneficial change in medical condition, often caused by a drug ** Adverse effect or side effect, an unwanted change in medical condition caused by a drug In media * Special effect, an artificial illusion ** Sound effect, an artificially created or enhanced sound ** Visual effects, artificially created or enhanced images *Audio signal processing ** Effects unit, a device used to manipulate electronic sound *** Effects pedal, a small device attached to an instrument to modify its sound Other uses * Effects, one's personal property or belongings * Effects (G.I. Joe), a fictional character in the G.I. Joe universe * ''Effects'' (film), a 1979 film (give a wide release in 2005) * Effect size, a measure of the strength of a relationship bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |