|
Triphragmium
''Triphragmium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Phragmidiaceae. The genus was first described by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1825. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America. Species: * '' Triphragmium filipendulae'' (Lasch) Pass. * ''Triphragmium ulmariae ''Triphragmium ulmariae'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Sphaerophragmiaceae. It causes meadowsweet rust gall, which develops as a chemically induced swelling, arising from the lower surface of the meadowsweet (''Filipendula ulmaria' ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10704454 Pucciniales Basidiomycota genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
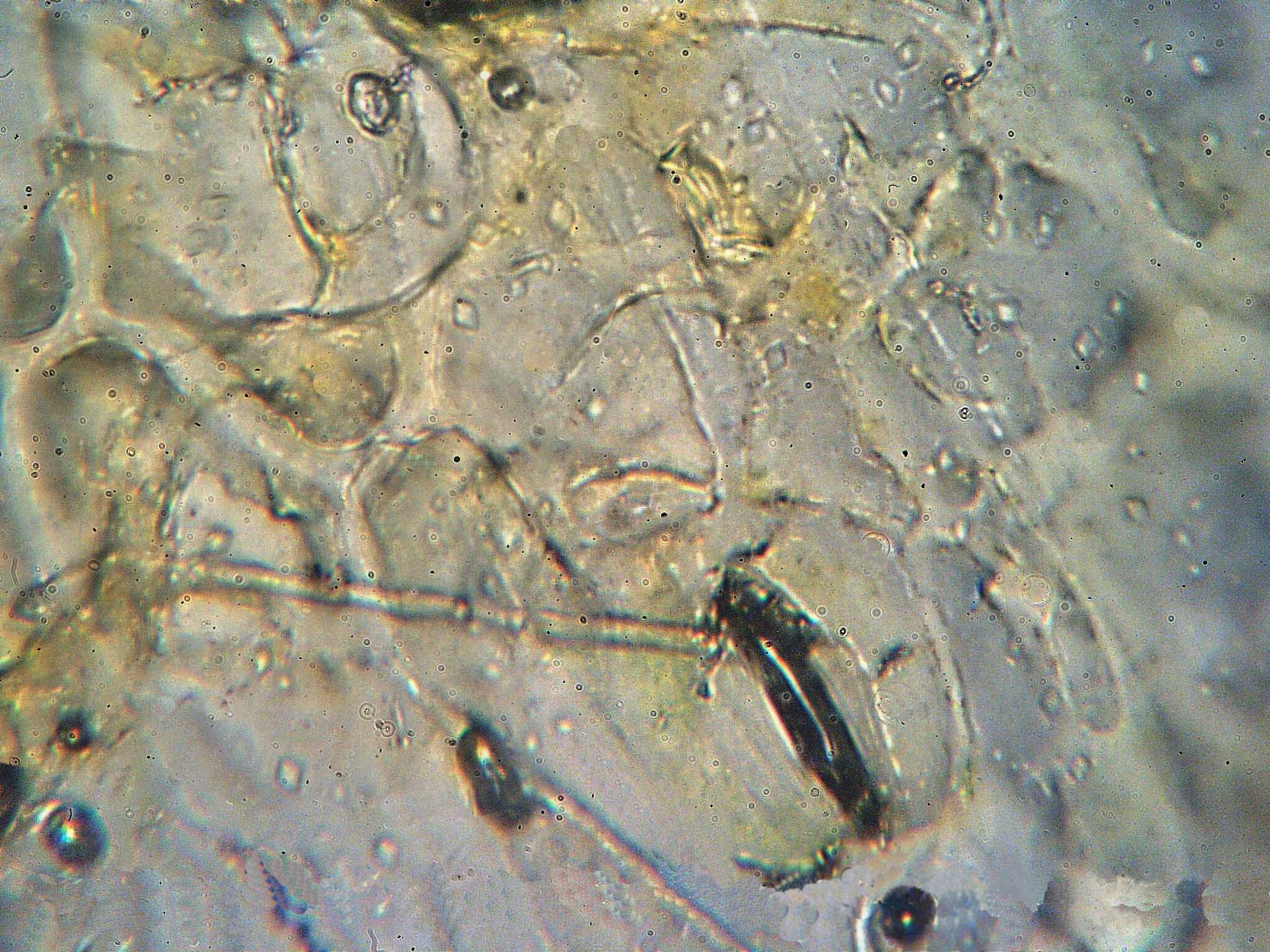
Triphragmium Ulmariae
''Triphragmium ulmariae'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Sphaerophragmiaceae. It causes meadowsweet rust gall, which develops as a chemically induced swelling, arising from the lower surface of the meadowsweet (''Filipendula ulmaria'') leaves. Life cycle The fungus grows in the petioles and/or midribs of the perennial plant meadowsweet (''Filipendula ulmaria''), a member of the rose family Rosaceae (), the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera. The name is derived from the type genus ''Rosa''. Among the most species-rich genera are '' Alchemilla'' (270), '' Sorbu ..., causing swelling and distortion. Sori develop with bright orange spores. The rust's spores reach the new meadowsweet plants via air movements. The rust has a severe effect on the survival of meadowsweet seedlings. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6803444 Pucciniales Galls Fungi described in 1808 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniomycetes
The Pucciniomycetes (formerly known as the Urediniomycetes) are a class of fungi in the Pucciniomycotina subdivision of the Basidiomycota. The class contains 5 orders, 21 families, 190 genera, and 8016 species. It includes several important plant pathogens causing forms of fungal rust. Characteristics Pucciniomycetes develop no basidiocarp, karyogamy occurs in a thick-walled resting spore ( teliospore), and meiosis occurs upon germination of teliospore. They have simple septal pores without membrane caps and disc-like spindle pole bodies. Except for a few species, the basidia, when present, are transversally septate. Mannose is the major cell wall carbohydrate, glucose, fucose and rhamnose Rhamnose (Rha, Rham) is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl-pentose or a 6-deoxy-hexose. Rhamnose predominantly occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L-mannose). This is unusual, since most o ... are the less prevalent ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniales
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidiaceae
The Phragmidiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 14 genera and 164 species. Genera *'' Arthuriomyces'' *'' Frommeella'' *''Gerwasia'' *'' Gymnoconia'' *'' Hamaspora'' *'' Joerstadia'' *'' Kuehneola'' *'' Mainsia'' *'' Morispora'' *''Phragmidium ''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is ...'' *'' Physonema'' *'' Scutelliformis'' *'' Trachyspora'' *'' Xenodochus'' References External links * Pucciniales Basidiomycota families Taxa named by August Carl Joseph Corda Taxa described in 1837 {{Basidiomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link (2 February 1767 – 1 January 1851) was a German natural history, naturalist and botanist. Biography Link was born at Hildesheim as a son of the minister August Heinrich Link (1738–1783), who taught him love of nature through collection of 'natural objects'. He studied medicine and natural sciences at the Hannoverschen Landesuniversität of Göttingen, and graduated as MD in 1789, promoting on his thesis ''"Flora der Felsgesteine rund um Göttingen"'' (Flora of the rocky beds around Göttingen). One of his teachers was the famous natural scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840). He became a private tutor (''Privatdozent'') in Göttingen. In 1792 he became the first professor of the new department of chemistry, zoology and botany at the University of Rostock. During his stay at Rostock, he became an early follower of the antiphlogistic theory of Lavoisier, teaching about the existence of oxygen instead of phlogiston. He was also a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America (including the Caribbean and Central America).Gonzalez, Joseph. 2004"Northern America: Land of Opportunity"(ch. 6). ''The Complete Idiot's Guide to Geography.'' () New York: Alpha Books; pp. 57–8 Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States (the contiguous United States and Alaska only, excluding Hawaii, Navassa Island, Puerto Rico, the United States Virgin Islands, and other minor U.S. Pacific territories). From a geographical perspective, Mexico would also be part of Northern America as it is on the same land as the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |