|
Trickling Filter
A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of some material, such as rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media, over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward and causes a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to grow, covering the bed of media. Aerobic conditions are maintained by splashing, diffusion, and either by forced-air flowing through the bed or natural convection of air if the filter medium is porous. The treatment of sewage or other wastewater with trickling filters is among the oldest and most well characterized treatment technologies. The fundamental components of a complete trickling filter system are: * a bed of filter medium upon which a layer of microbial slime is promoted and developed; * an enclosure or a container which houses the bed of filter medium; * a system for distributing the flow of wastewater over the filter medium; and * a system for removing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benfleet Sewage Treatment Plant, Filter Bed - Geograph
Benfleet may refer to: Places in England * Benfleet railway station, Essex *Benfleet Urban District, a former urban district in Essex *North Benfleet, a village in the Basildon district of Essex *South Benfleet South Benfleet is a town in the Castle Point district of Essex, England, 30 miles east of London. It is adjacent to the village of North Benfleet. The Benfleet (SS7) post town includes South Benfleet, Thundersley, New Thundersley and Hadleigh, ..., a town in the borough of Castle Point, Essex Other uses * Benfleet F.C., a football club based in Benfleet, Essex {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trickle Filter Cross-section
''Trickle'' is the second studio album by English trip hop band Olive, released on 30 May 2000 by Maverick Records. History Following the band's debut album '' Extra Virgin'' and a subsequent promotional tour, keyboard programmer Robin Taylor-Firth left the band. Also during this time the UK arm of record label RCA lost interest in supporting the band; as a result, Olive was dropped from the RCA roster. By this time, the follow-up album had been completed, including a cover of the 1975 UK number-one single "I'm Not in Love" by 10cc (chosen partially as an attempt to obtain better favour with RCA). However, Olive then signed with Maverick Records, after reportedly being discovered by label founder Madonna when she attended one of their concerts in Germany; initially, the band were recruited for a contribution to the soundtrack to the Madonna film '' The Next Best Thing'', and a recording contract resulted from the contact. "I'm Not in Love" became the band's contribution to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
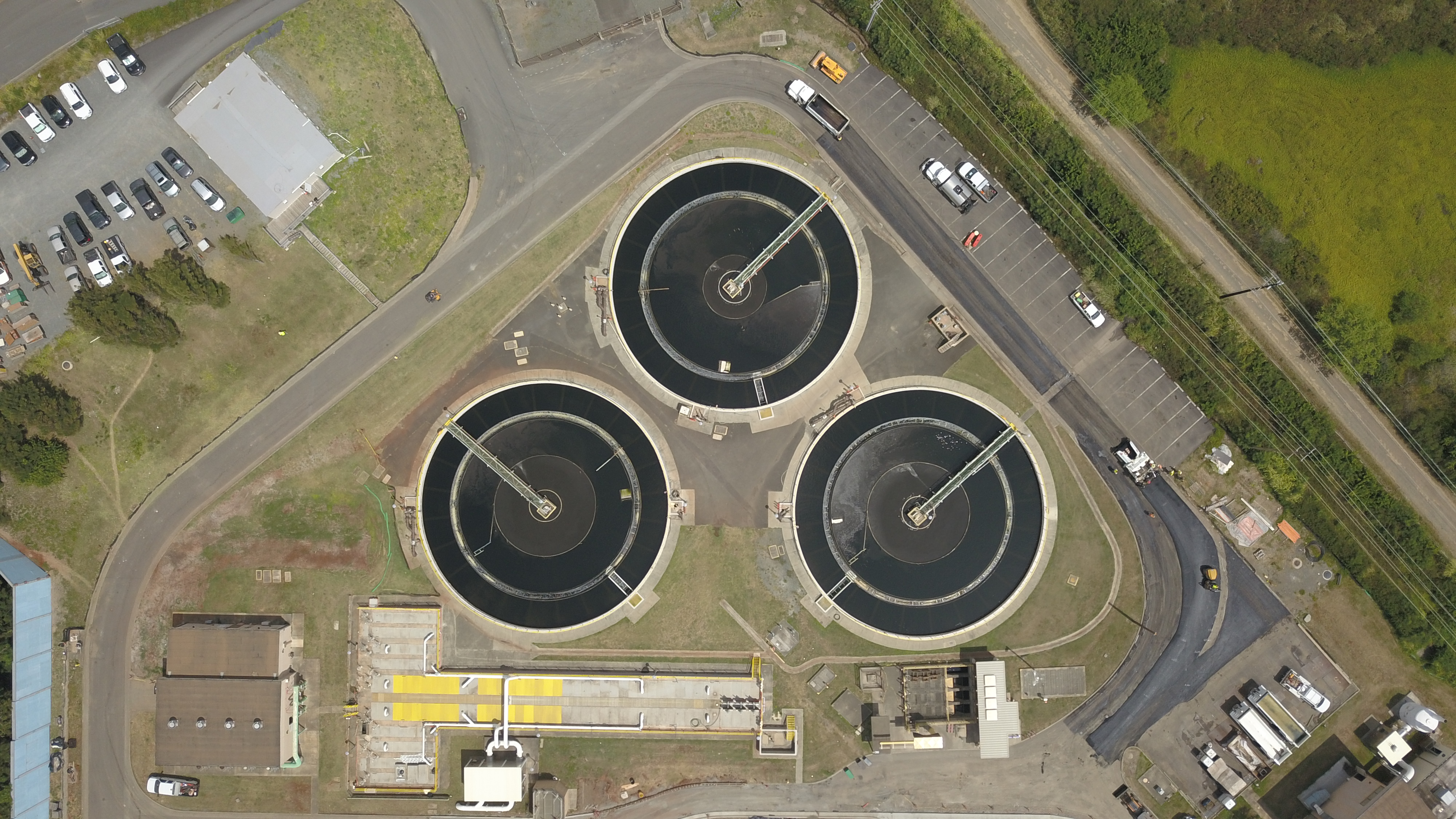
Clarifier
Clarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by Sedimentation (water treatment), sedimentation. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and/or thickening. Inside the clarifier, solid contaminants will settle down to the bottom of the tank where it is collected by a scraper mechanism. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank, are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum. Applications Pretreatment Before the water enters the clarifier, coagulation and flocculation reagents, such as polyelectrolytes and ferric sulfate,Brentwood Industries, Inc. (2013)"Tube Settler Systems For Clarification." Accessed 14 October 2013. can be added. These reagents cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs, that settle more quickly and stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena. Astbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bio Film
Bio or BIO may refer to: Computing * bio(4), a pseudo-device driver in RAID controller management interface in OpenBSD and NetBSD * Block I/O, a concept in computer data storage Politics * Julius Maada Bio (born 1964), Sierra Leonean politician, president since April 4, 2018 Media and entertainment * Bio (Australian TV channel) * The Biography Channel (UK and Ireland) * Bio (graffiti artist) Wilfredo Feliciano (born 1966) * ''Bio'' (album), a Chuck Berry album released in 1973 Organizations * Bedford Institute of Oceanography * Biographers International Organization * Biotechnology Innovation Organization * Belgian Investment Company for Developing Countries Energy * Biofuel, fuel made from biomass **Biodiesel, the biofuel alternative for diesel **Biogas, a blend of gasses formed by the breakdown of organic matter used in renewable energy production **Biogasoline, the biofuel alternative for gasoline Places * Bio, Azerbaijan, village in Astara Rayon * Bio, Lot, commune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Chemical structure The nitrate anion is the conjugate acid, conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of Resonance (chemistry), resonance. Like the isoelectronic carbonate ion, the nitrate ion can be represented by three resonance structures: Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
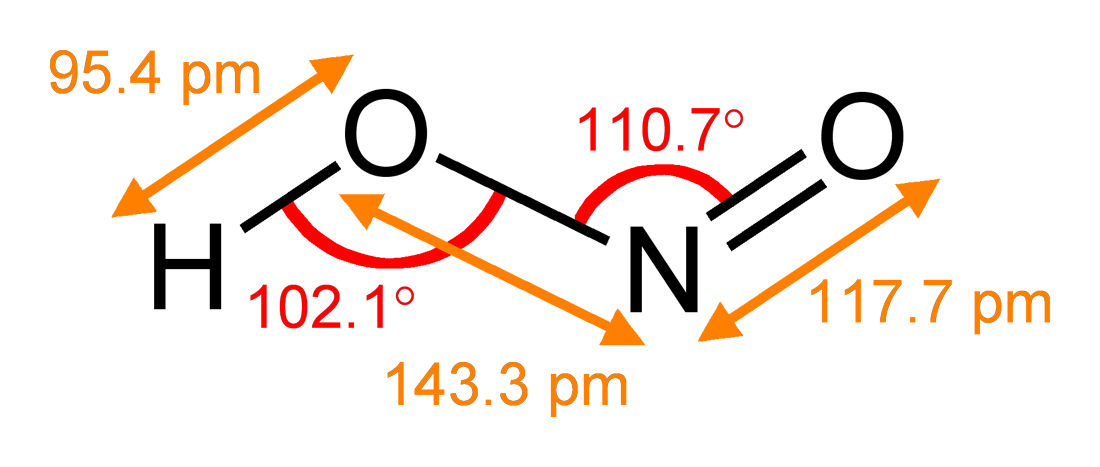
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compounds
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). While adsorption does often precede absorption, which involves the transfer of the absorbate into the volume of the absorbent material, alternatively, adsorption is distinctly a surface phenomenon, wherein the adsorbate does not penetrate through the material surface and into the bulk of the adsorbent. The term '' sorption'' encompasses both adsorption and absorption, and ''desorption'' is the reverse of sorption. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |